Genome chip for analyzing microbial community structure in acidic environment
A microbial community and genome technology, applied in the field of gene chips, can solve the problems of difficult microbial community structure, large workload of gene cloning and sequence analysis, limitations of fluorescent dye types, etc., and achieve the effect of overcoming the complexity of the process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0010] Embodiment 1: Preparation of genome chip of the present invention
[0011] At least 10 strains of Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans, at least 2 strains of Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans, at least 1 strain of Acidithiobacillus caldus, and at least 1 strain of Acidithiobacillus albertensis , At least 6 strains of Leptospirillum sp., at least 8 strains of Acidiphiliums sp., at least 1 strain of Sulfolobus Metallicus, at least 1 strain of Acidophilus sp. (Acidianus sp.), at least one strain of Metallosphaera sedula and at least two strains of Sulfobacillus were extracted with a DNA extraction kit. Using the extracted whole genome DNA as a probe, it was dissolved in 50% DMSO to a final concentration of 50 pmol / μl, and then the OmniGridAccent Arraying System (Genomic Solutions, USA ) spotting the probe on the siliconized glass slide treated with amination surface. There were 8 probe array replicates on each slide. The spotted chip was dried overnight at room temperature, and f...
Embodiment 2
[0012] Example 2: Chip hybridization specificity assessment
[0013] Acithiobacillus ferrooxidans (Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans), referred to as A.f bacteria, was selected to detect the hybridization specificity of the chip probe. The DNA of the whole genome of A.f bacteria was labeled with cy3 fluorescent dye and then hybridized with the oligonucleotide chip at 50°C. The results showed that strong fluorescent signals were generated at the probe positions corresponding to A.f bacteria on the chip (see Figure 1 shown), and no non-specific cross-hybridization with non-target genes was found on the chip. It shows that there is a strong specificity between the specific oligonucleotide probe and its corresponding target gene.
Embodiment 3
[0014] Example 3: Sensitivity detection of chip hybridization
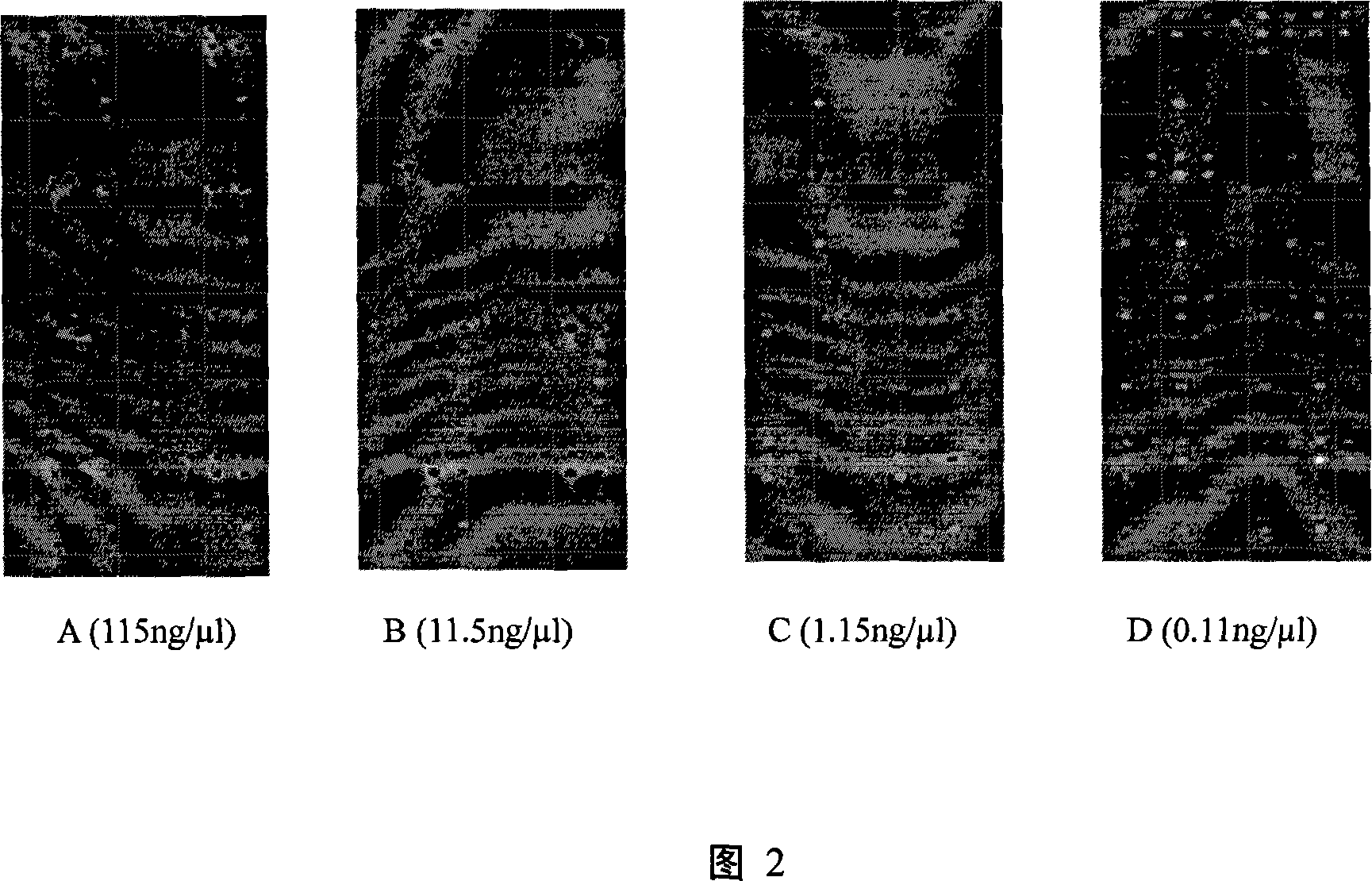
[0015] The pure genomic DNA of Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans 23270 was used to test the sensitivity of the chip of the present invention. The pure genomic DNA was diluted according to a certain concentration gradient (concentrations were 0.11, 1.15, 11.5, 115 ng / ul), labeled with cy3 and then hybridized with the chip. From the chip hybridization analysis results (see accompanying drawing 2), it is found that the detection limit of the chip to the purely cultured microbial genomic DNA is 0.11ng / ul.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com