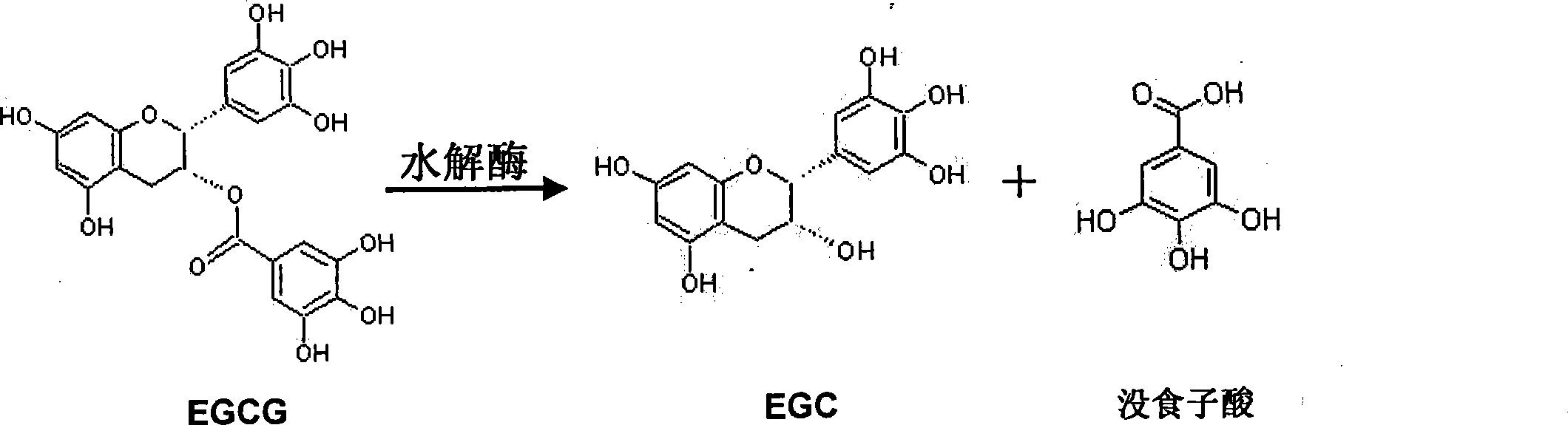
Method for preparing EGCG hydrolytic enzyme and producing EGC and gallic acid by aspergillus oryzae
A technology of gallic acid and Aspergillus oryzae, which is applied in the field of production of EGC and gallic acid, and the induction and preparation of EGCG hydrolase, can solve the problems of low hydrolysis rate, low enzyme yield, easy to be oxidized, etc., and achieves high conversion rate, simple operation, Controllable effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] 1. Seed culture of Aspergillus oryzae ATCC20719
[0034] Aspergillus oryzae seed medium: 1% glucose, 0.1% peptone, 0.05% citric acid, 0.015% Tween80, 2% Vogel's medium N; use Aspergillus oryzae ATCC20719 as the production strain, at pH 5.0, 30°C, 200r / Min conditions for 36 hours.
[0035] 2. Fermentation of Aspergillus oryzae to produce enzymes
[0036] Aspergillus oryzae enzyme production medium: 1% glucose, 0.1% peptone, 0.05% citric acid, 0.015% Tween80, 2% Vogel's medium N, add EGCG to a final concentration of 2.5g / L, pH5.0; with 4% inoculum size, Cultivate at 30°C and 160r / min for 72h to induce enzyme production. The fermented supernatant liquid collected by filtration or centrifugation is the EGCG hydrolase liquid. In the experiment, the fermentation culture without adding EGCG was used as the control.
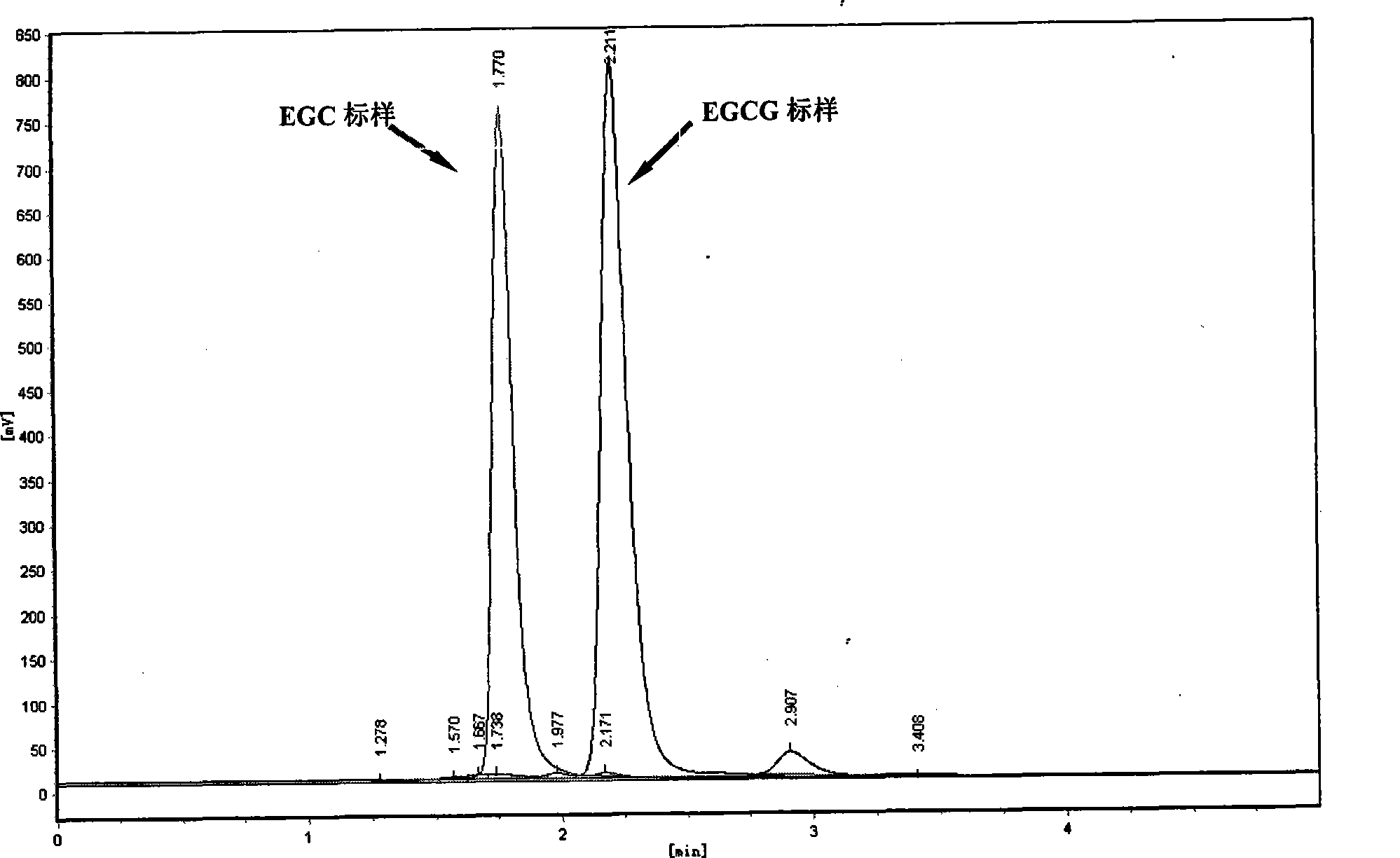
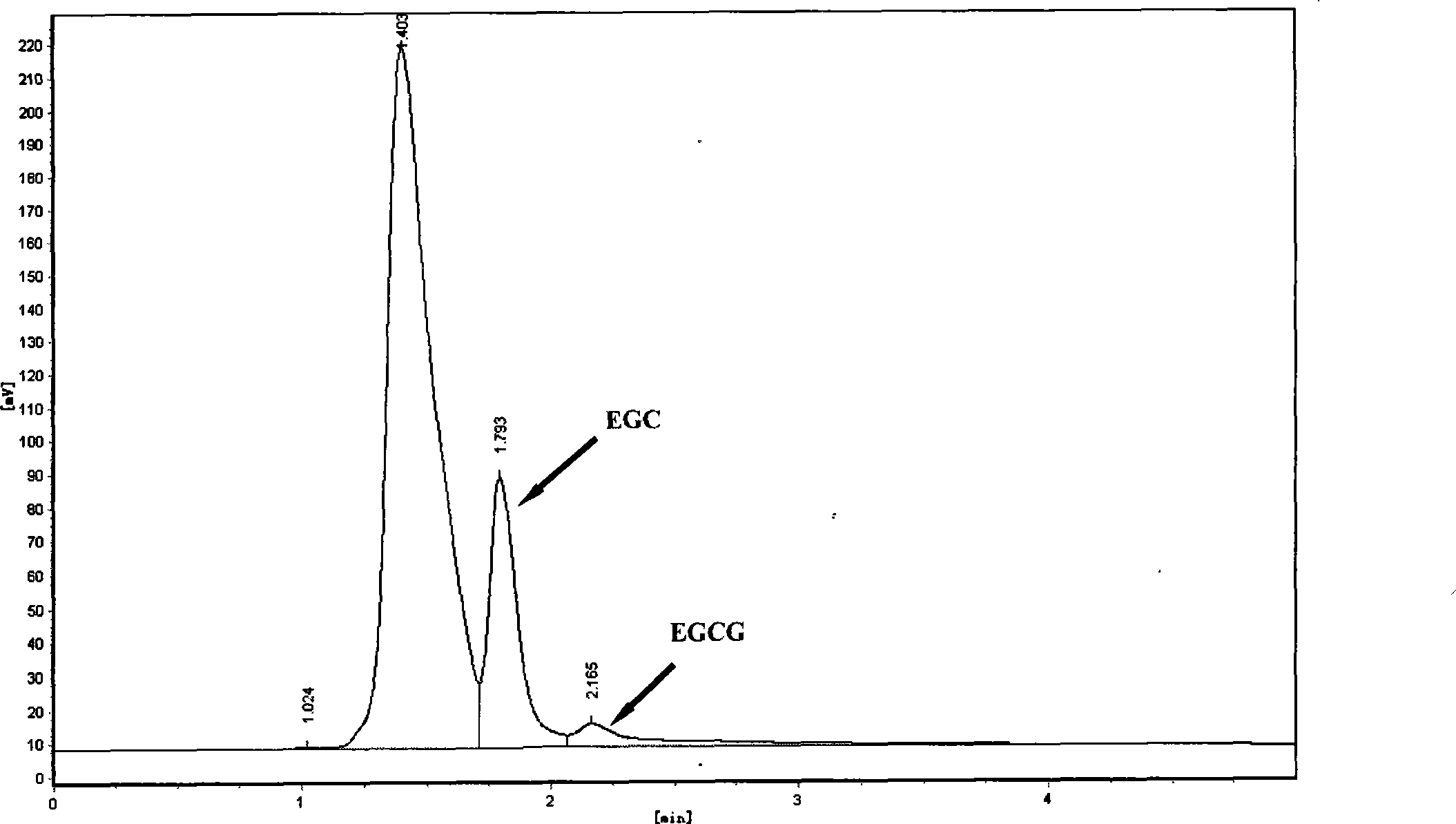
[0037] 3. Enzymatic hydrolysis of EGCG
[0038] Reaction system: 10g / L EGCG substrate 2mL, EGCG hydrolase solution 2mL, pH5.2 acetate buffer 2mL; EGCG hydro...
Embodiment 2
[0043] 1. Seed Culture of Aspergillus oryzae NRRL692
[0044]Aspergillus oryzae seed medium: 1% glucose, 0.1% peptone, 0.05% citric acid, 0.015% Tween80, 2% Vogel's mediumN; use Aspergillus oryzae NRRL692 as the production strain, pH 5.0, 25—30°C, 200rpm culture 36 hours.
[0045] 2. Fermentation of Aspergillus oryzae to produce enzymes
[0046] Aspergillus oryzae enzyme production medium: 1% glucose, 0.1% peptone, 0.05% citric acid, 0.015% Tween80, 2% Vogel's medium N, add EGCG to the final concentration of 5.0g / L, pH5.0; with 8% inoculum size, Cultivate at 30°C and 160r / min for 72h to induce enzyme production. The fermented supernatant liquid collected by filtration or centrifugation is the EGCG hydrolase liquid. In the experiment, the fermentation culture without adding EGCG was used as the control.
[0047] 3. Enzymatic hydrolysis of EGCG
[0048] Reaction system: 15g / L EGCG substrate 2mL, EGCG hydrolase solution 2mL, pH5.2 acetate buffer 2mL; EGCG hydrolase solution ...
Embodiment 3
[0051] 1. Seed culture of Aspergillus oryzae ATCC201873
[0052] Aspergillus oryzae seed medium: 1% glucose, 0.1% peptone, 0.05% citric acid, 0.015% Tween80, 2% Voge1's medium N; use Aspergillus oryzae ATCC201873 as the production strain, at pH5.0, 30°C, 200r / Min conditions for 36 hours.
[0053] 2. Fermentation of Aspergillus oryzae to produce enzymes
[0054] Aspergillus oryzae enzyme production medium: 1% glucose, 0.1% peptone, 0.05% citric acid, 0.015% Tween80, 2% Vogel's medium N, add EGCG to a final concentration of 10.0g / L, pH5.0; with 8% inoculum size, Cultivate at 30°C and 130r / min for 72h to induce enzyme production. The fermented supernatant liquid collected by filtration or centrifugation is the EGCG hydrolase liquid. In the experiment, the fermentation culture without adding EGCG was used as the control.
[0055] 3. Enzymatic hydrolysis of EGCG
[0056] Reaction system: 30g / L EGCG substrate 2mL, EGCG hydrolase solution 2mL, pH5.2 acetate buffer 2mL; EGCG hyd...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com