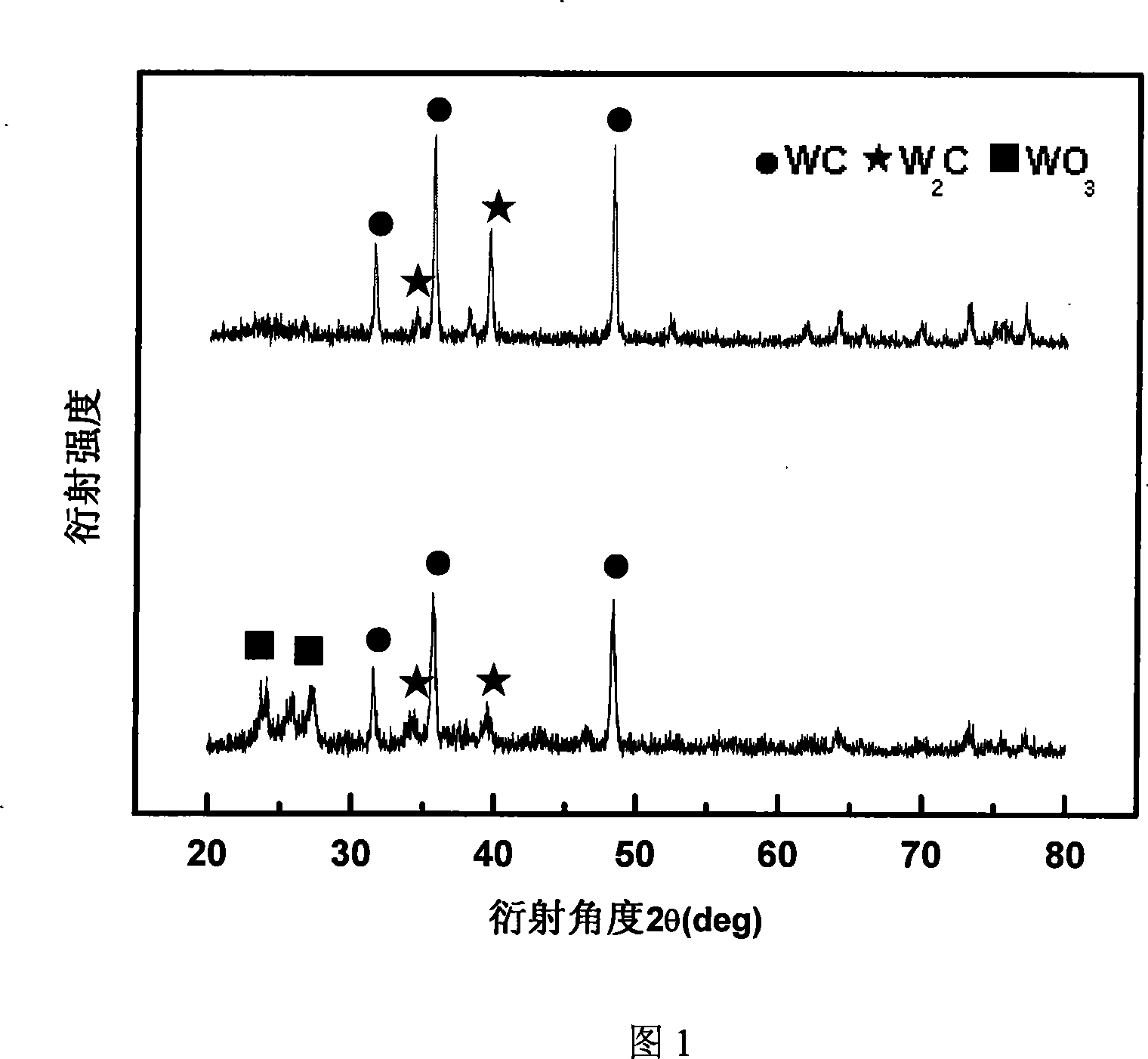
Microwave induction catalytic preparation method of nano tungsten carbide
A technology of nano-tungsten carbide and induced catalysis, which is applied in the field of nano-materials and can solve the problems of low specific surface area and purity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0018] Dissolve 1.0 g of W in 100 ml of hydrogen peroxide, then add 1 g of activated carbon powder and 100 ml of ethanol, put it into an ultrasonic cleaner for 30 minutes to disperse evenly, take it out and stir until it becomes a viscous slurry. Then the viscous slurry is put into a microwave oven, and the slurry is heated in a manner of alternately operating the microwave for 5 seconds and stopping for 5 seconds to obtain a dry powder. Next, mechanically mix the dry powder with 1 gram of iron powder, put it into a ceramic crucible, and wrap microwave-resistant insulation material around the ceramic crucible. Finally, put the crucible into a microwave oven and continue heating for 20 minutes to obtain nanoscale tungsten carbide particles.
Embodiment 2
[0020] Dissolve ammonium metatungstate containing 1.0g of tungsten in a 300ml beaker filled with 40ml of deionized water, add 30ml of isopropanol, add 1g of carbon nanotubes, and put them into an ultrasonic cleaning machine for ultrasonic dispersion. , take out and stir until viscous slurry. Then put the viscous slurry into a microwave oven with a frequency of 2.54 GHz, and heat the slurry in a manner of alternating microwave operation for 10 seconds and stopping for 20 seconds to obtain a dry powder. Next, mechanically mix the dry powder with 0.5 g of cobalt powder, put it into a ceramic crucible, and wrap a microwave-resistant thermal insulation material with a thickness of 5 cm around the ceramic crucible. Finally, put the crucible into a microwave oven and heat it for 2 minutes to obtain nanoscale tungsten carbide particles.
Embodiment 3
[0022] WO with a tungsten content of 1.0g 3 Dissolve in a 300ml beaker with 40ml of deionized water, add 50ml of acetone, add 3g of carbon microsphere powder, put it into an ultrasonic cleaner for ultrasonic dispersion, take it out and stir until it becomes a viscous slurry. Then the viscous slurry is put into a microwave oven, and the slurry is heated in a manner of alternately operating the microwave for 5 seconds and stopping for 5 seconds to obtain a dry powder. Next, mechanically mix the dry powder with 0.1 g of nickel powder, put it into a crucible, and wrap the microwave-resistant thermal insulation material around the crucible. Finally, put the crucible into a microwave oven and continue heating for 15 minutes to obtain nanoscale tungsten carbide particles.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com