Method for refining carbonization crude benzole
A technology for coking crude benzene and a refining method, which is applied in the directions of organic chemistry, distillation purification/separation, etc., can solve the problems of high processing cost, low benzene recovery rate, large equipment investment, etc., and achieves reduction in processing cost, process environmental protection, and equipment investment. reduced effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
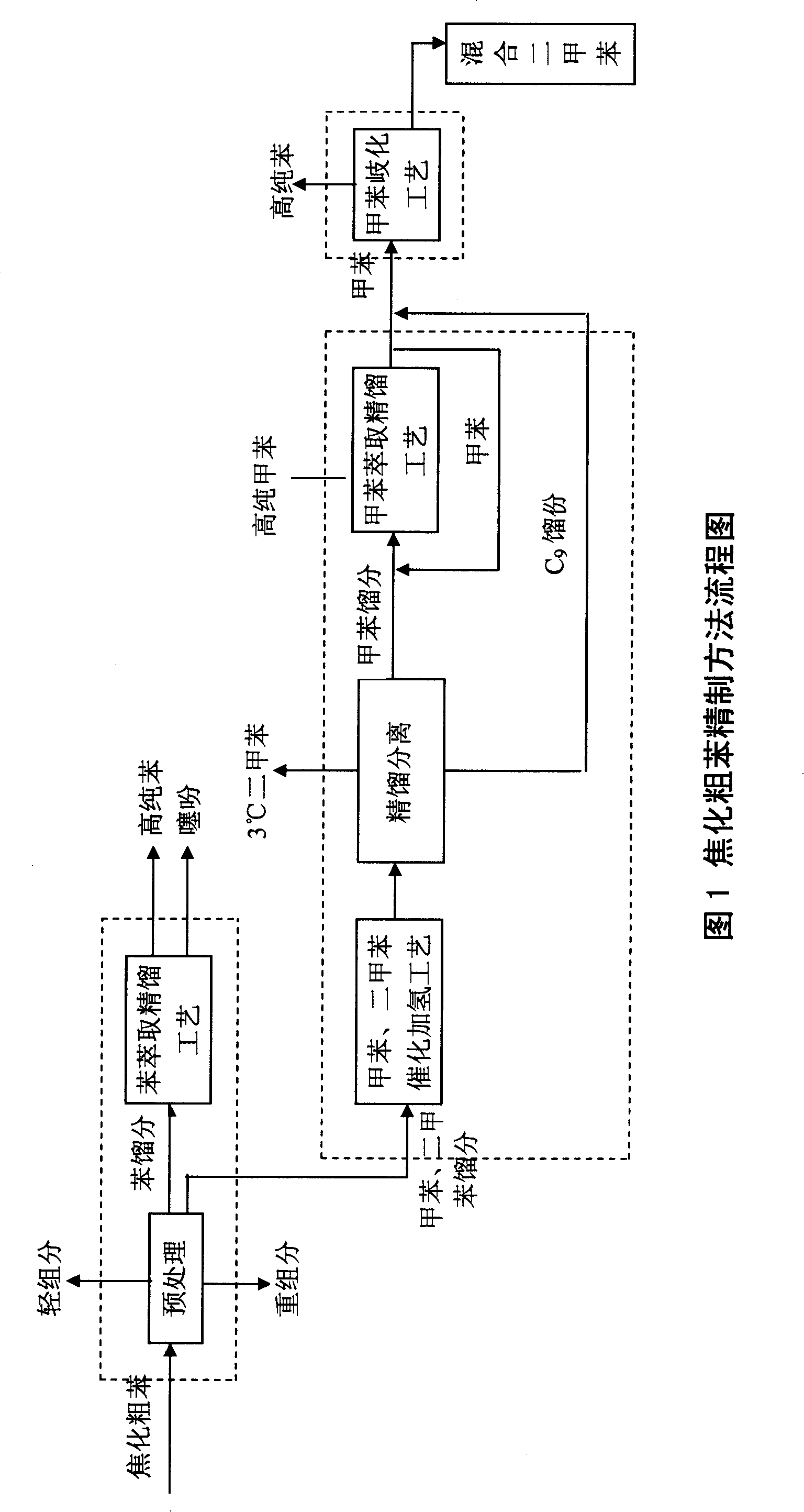
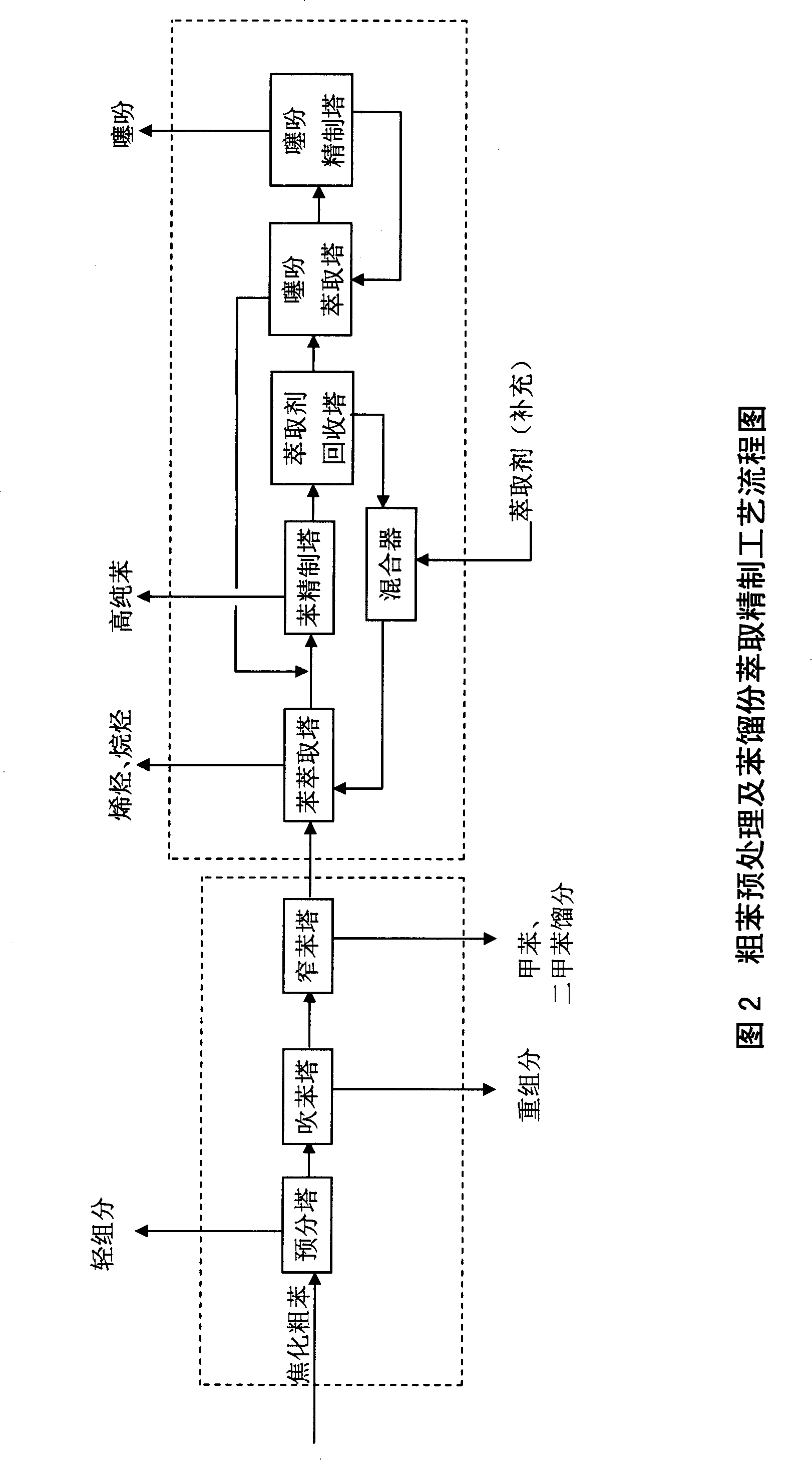
[0032] Using crude benzene, a by-product of coal coke factory, as raw material (which contains 69.1% benzene, 14.6% toluene, 3.6% xylene, 0.577% thiophene, etc.) to remove light components (hydrogen sulfide, carbon disulfide, cyclopentadiene, etc.) ), then enter the benzene blowing tower; remove heavy components (naphthalene, coumarone, indene, etc.) The narrow benzene fraction containing thiophene (98% of which is benzene content) is distilled from the top of the tower, and enters the benzene extraction tower of the benzene fraction extraction and refining unit, while the toluene and xylene fractions discharged from the tower bottom are used as raw materials for the hydrorefining process and enter the pre-hydrogenation process reactor. The above-mentioned pretreatment unit operations are general distillation operations.
[0033] The narrow benzene fraction from the narrow benzene tower enters the benzene extraction tower. At the top of the benzene extraction tower, alkanes a...
Embodiment 2
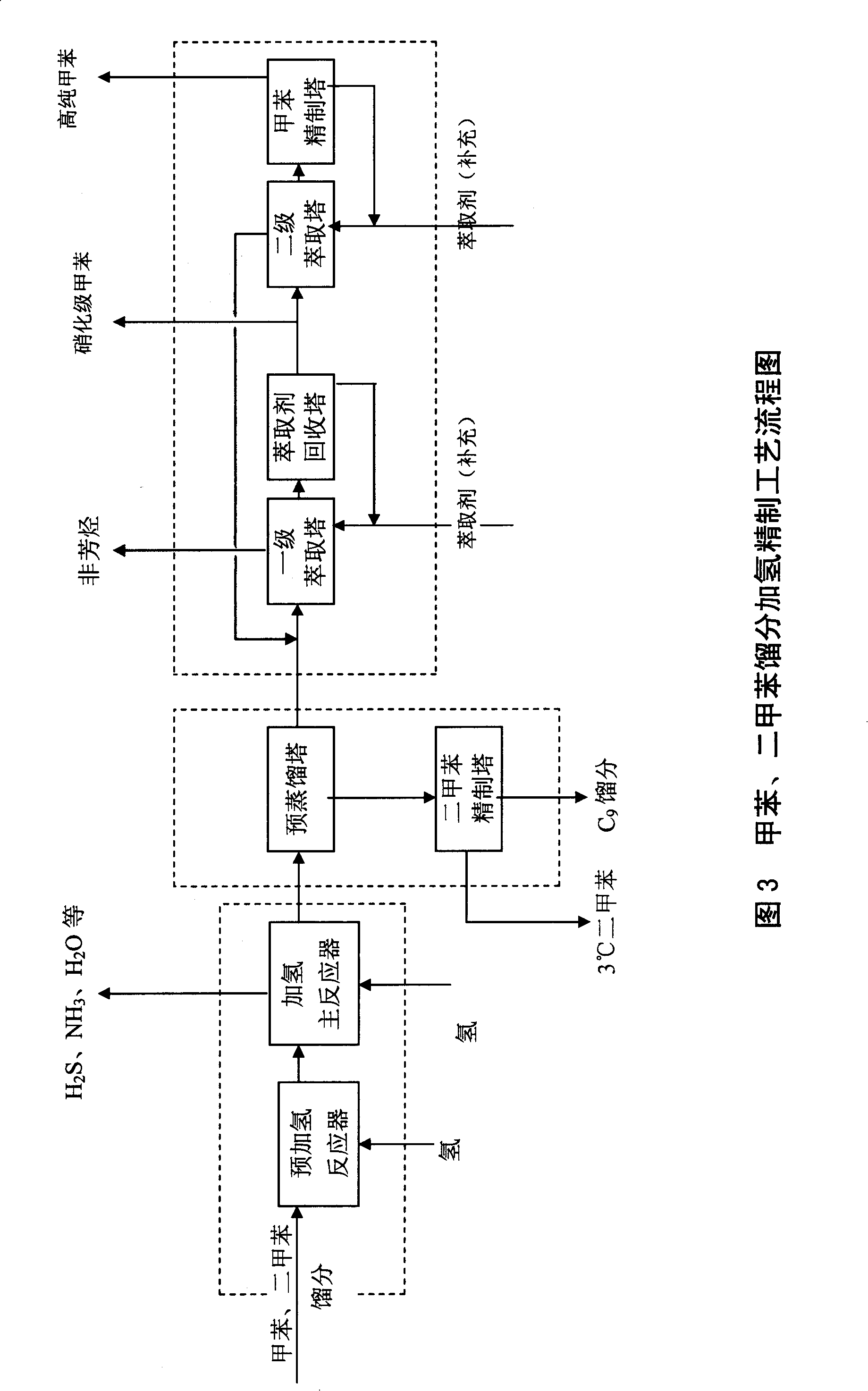
[0035] Toluene and xylene fractions obtained in Example 1 are used as raw materials (71.5% of toluene, 15% of xylene, 2% of trimethylbenzene, 5% of unsaturated substances such as styrene, 0.7% of sulfides such as methylthiophene, and pyridines containing Nitrogen compounds 1.5%, coumarone and other oxygen-containing compounds 1.1%), carry out hydrogenation refining, the process conditions are: pre-hydrogenation reactor filled with commercially available Ni-Mo catalyst, reactor inlet temperature 190 ° C, pressure 3.2MPa The catalytic hydrogenation main reactor is filled with commercially available Co-Mo catalyst, the reactor inlet temperature is 320°C, and the pressure is 3.0MPa; 9 After the fractionation, the toluene fraction obtained enters the toluene primary extraction tower, the extractant is commercially available N-formyl morpholine, the tower top temperature is 98 ° C, the pressure is normal pressure, and the solvent ratio is 6. The obtained product is nitration grade to...
Embodiment 3
[0037] Using the nitration-grade toluene obtained in Example 2 as a raw material, the high-purity toluene product is obtained through the secondary extraction tower and the toluene refining tower. The process parameters are as follows: the extraction agent is N-formyl morpholine, and the temperature at the top of the secondary extraction tower is 98°C , the pressure is normal pressure, the solvent ratio is 5, the total sulfur content in high-purity toluene is less than 1ppm, the non-aromatic content is less than 1.0%, and there is no benzene and C 9 , Distillation scope<0.6 ℃ (comprising 110.6 ℃), others are the same as embodiment 2.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com