Metal alloy nano-stick or nano-wire manufactured with Laves phase hydrogenation method and process thereof
A technology of metal alloys and nanorods, which is applied in the field of metal alloy nanorods or nanowires prepared by Laves phase hydrogenation, can solve the problems that the strength potential of metal materials is not fully utilized, and achieve unique magnetic properties, high melting point and hardness Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
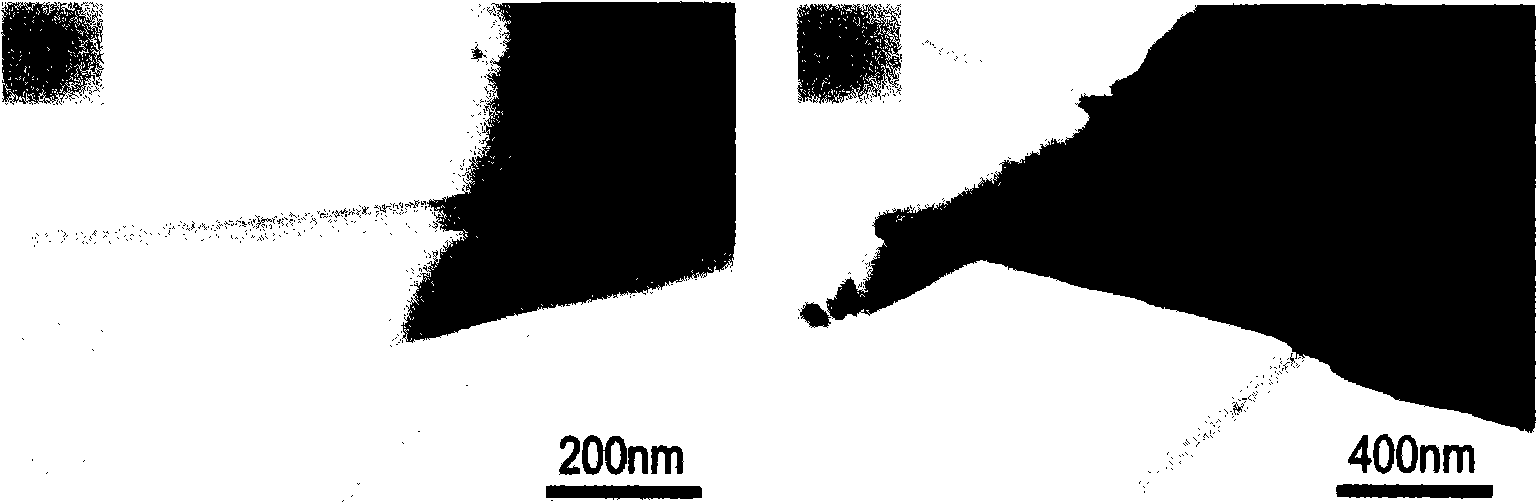
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0031] Ti 0.5 Zr 0.5 (Mn 0.5 Cr 0.5) 2 Alloy (alloy composition is atomic percentage, at.%, the same below).
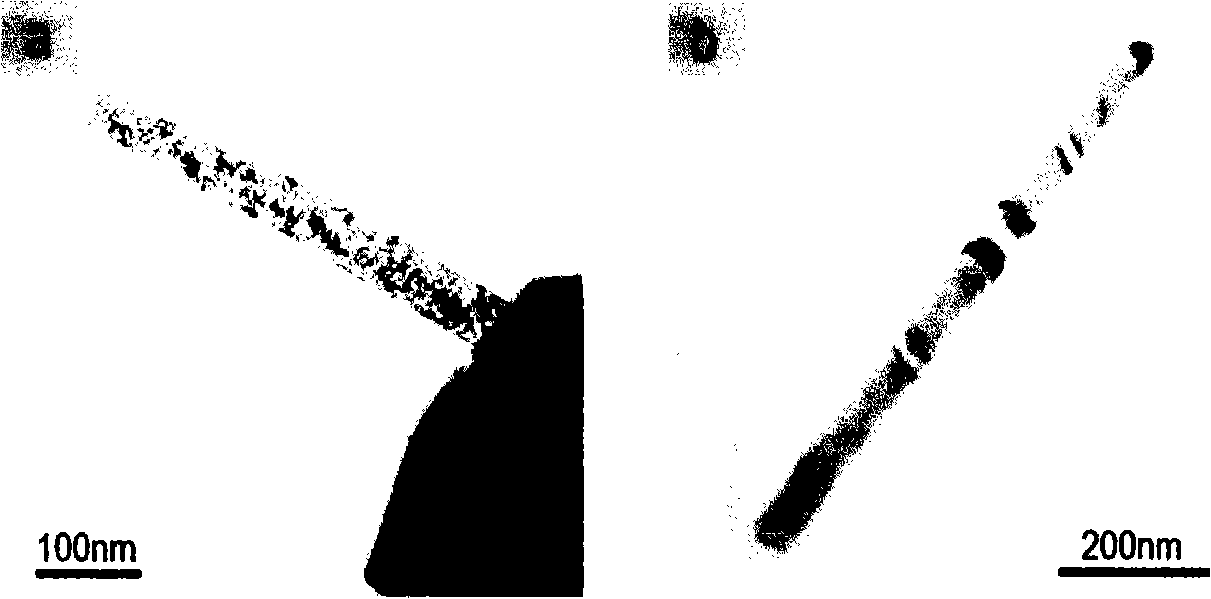
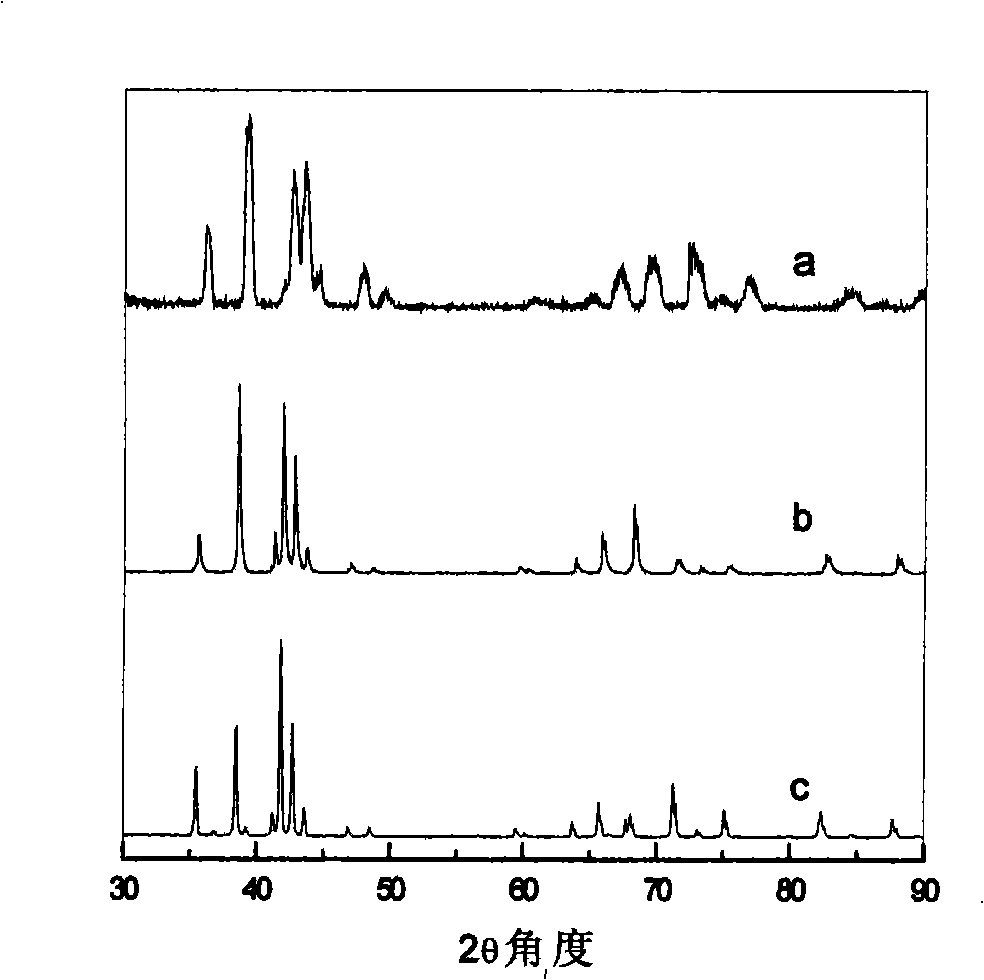
[0032] The commercial metal elements titanium, zirconium block and manganese, chromium flakes are used as starting materials, and the element purity is higher than 99.9%. According to the nominal composition of Ti 0.5 Zr 0.5 (Mn 0.5 Cr 0.5 ) 2 After being formulated into an alloy, it is repeatedly smelted three times in a magnetron electric arc furnace protected by a high-purity Ar (99.999%) atmosphere to produce an alloy ingot with a weight of about 50 grams. The alloy ingot was sealed into an argon-protected quartz tube and annealed at 900°C for 72 hours. Then the quartz tube was air-cooled to room temperature, and the alloy ingot was taken out. Remove the sample of about 0.5 gram from the alloy ingot, mechanically grind it into a finer powder, do X-ray diffraction analysis, show that the alloy is a single hexagonal Laves phase structure (see X-ray diffrac...
Embodiment 2
[0034] Ti 0.1 Zr 0.9 (Mn 0.5 Cr 0.5 ) 2 alloy.
[0035] The commercial metal elements titanium, zirconium block and manganese, chromium flakes are used as starting materials, the purity of the elements is higher than 99.9%, and the nominal composition is formulated as Ti 0.1 Zr 0.9 (Mn 0.5 Cr 0.5 ) 2 alloy, which is then smelted into alloy ingots weighing about 50 grams. Alloy ingot melting method and heat treatment method are the same as embodiment 1. Remove about 0.5 gram of sample from the treated alloy ingot, mechanically grind it into a finer powder, and do X-ray diffraction analysis, showing that the alloy is a single hexagonal Laves phase structure (see X-ray diffraction spectrum). figure 1 (b)). Take about 1 gram of Ti 0.1 Zr 0.9 (Mn 0.5 Cr 0.5 ) 2 The alloy is activated to absorb hydrogen in a self-made hydrogen reactor at room temperature and a hydrogen pressure of 1 atm, and the activation process is the same as in Example 1. After the alloy is full...
Embodiment 3
[0037] Zr(Mn 0.5 Cr 0.5 ) 2 alloy.
[0038] Using commercial metal elements titanium, zirconium block and manganese, chromium flakes as starting materials, the purity of the elements is higher than 99.9%, and the nominal composition is formulated as Zr (Mn 0.5 Cr 0.5 ) 2 alloy, which is then smelted into alloy ingots weighing about 50 grams. Alloy ingot melting method and heat treatment method are the same as embodiment 1. Remove about 0.5 gram of sample from the treated alloy ingot, mechanically grind it into a finer powder, and do X-ray diffraction analysis, showing that the alloy is a single hexagonal Laves phase structure (see X-ray diffraction spectrum). figure 1 (c)). Take about 1 gram of Zr(Mn 0.5 Cr 0.5 ) 2 The alloy sample was activated to absorb hydrogen in a self-made hydrogen reactor at room temperature and a hydrogen pressure of 1 atm, and the activation process was the same as in Example 1. After the alloy is fully activated, the alloy is subjected to ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com