Pretreatment method for biomass raw material
A biomass raw material, pretreatment technology, applied in the direction of biofuel, fermentation, etc., can solve the problems of complex by-products, high cost and high requirements, and achieve the effect of being conducive to hydrolysis
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] Embodiment 1: Determination of samples
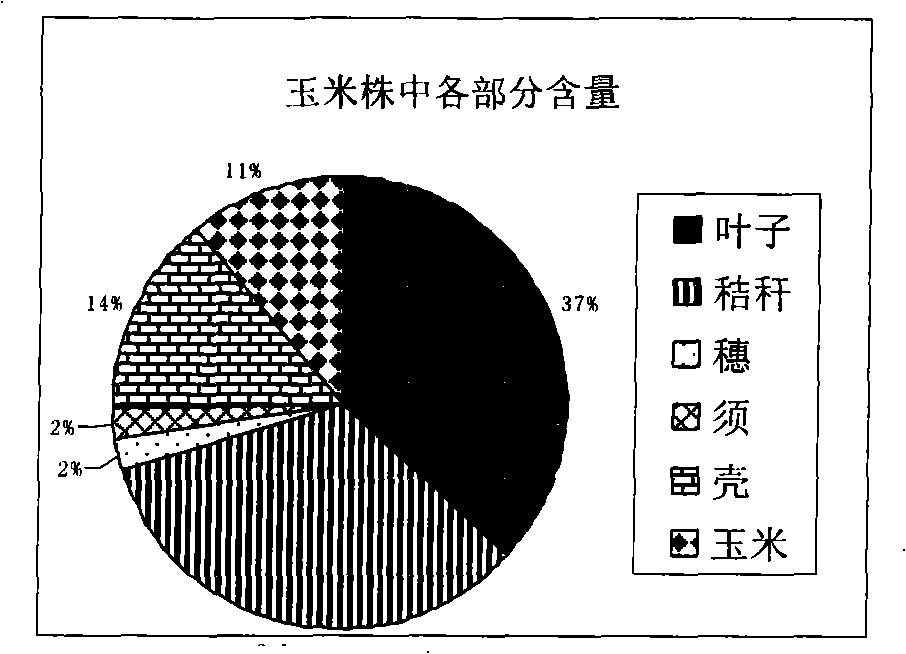
[0031] In this example, corn stalks purchased from the State Key Laboratory of East China University of Science and Technology were used. Divide the whole corn stalk into six parts: stalk, corn, leaf, tassel, husk, and whisker, and the proportion of each part is, for example, figure 1 shown. Among them, straw and leaves account for the largest proportion, so this embodiment uses leaves and straw as materials for processing and comparison.
Embodiment 2
[0032] Embodiment 2: Pulverization of samples
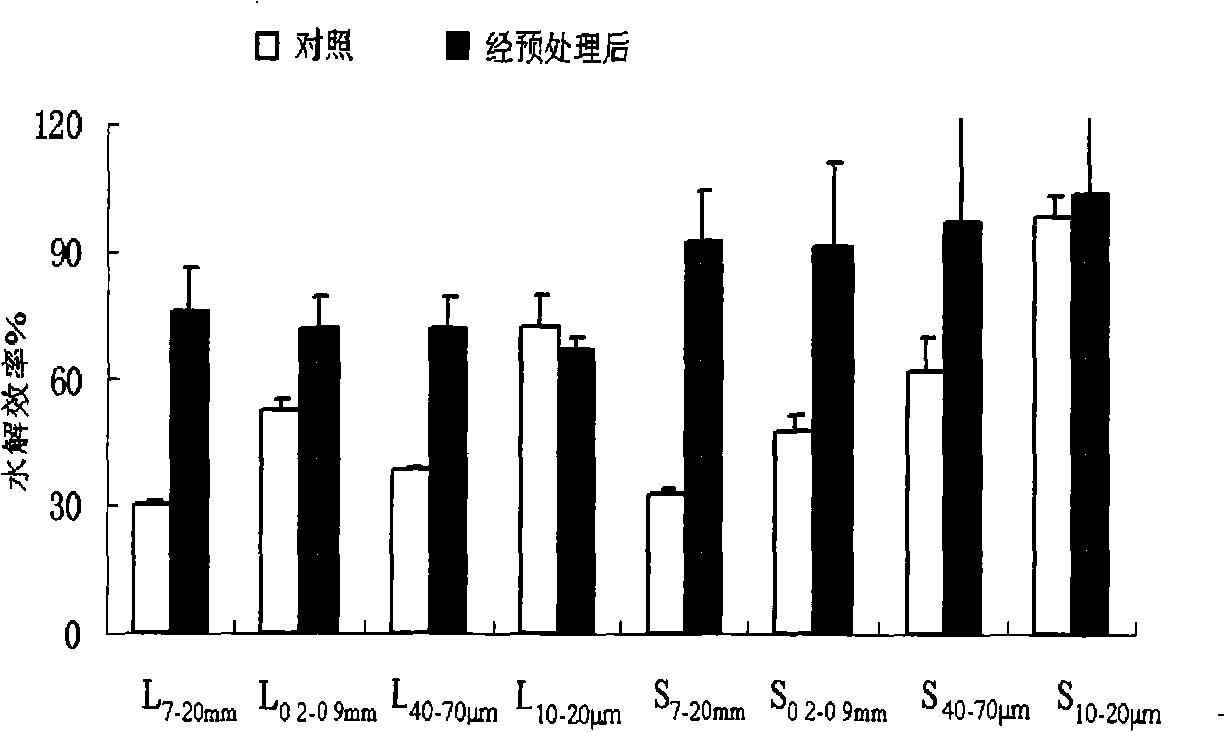
[0033] The leaves and stalks were pulverized with a pulverizer, passed through 20mm, 7mm, 0.9mm, 0.2mm, 0.074mm, 0.04mm sieves, and some samples passed through a 0.9mm sieve were pulverized with an ultrasonic airflow nano pulverizer, and four gradients of 8 A sample: 7-20mm (L 7-20mm , S 7-20mm ), 0.2-0.9mm (L 0.2-0.9 , S 0.2-0.9 ), 40-70μm (L 40-70μm , S 40-70μm ), the sample 10-20μm (L 10-20μm , S 10-20μm ).
Embodiment 3
[0034] Embodiment 3: the analysis of sample particle size distribution
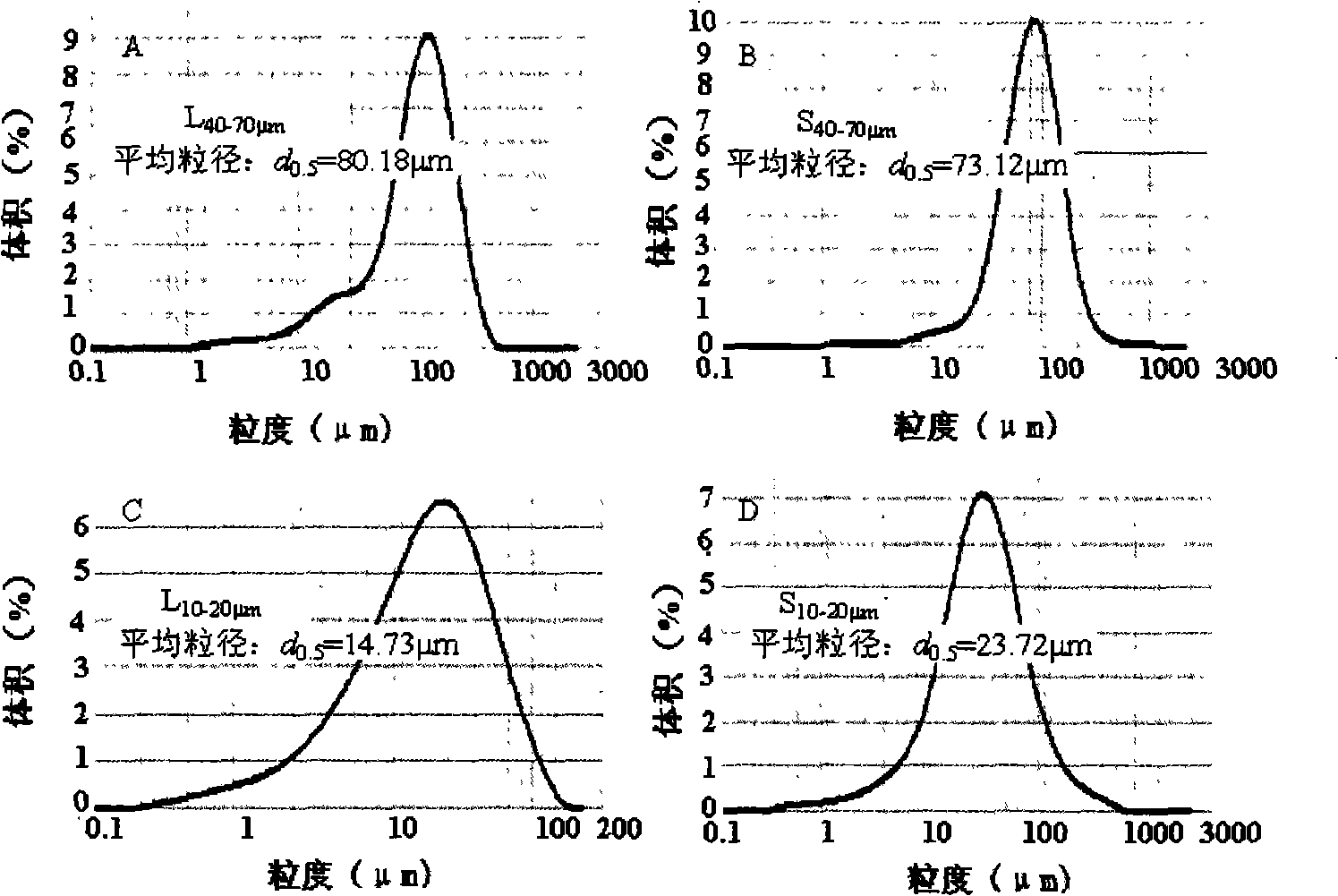
[0035] Wherein the sample range is 40-70 μ m and the sample after the nano pulverizer is pulverized (purchased in Shanghai Huali Sofi Technology Co., Ltd.), the particle size range is 10-20 μ m, and the particle size distribution is measured with a laser particle size analyzer, and the measurement results are as follows: figure 2 shown.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com