Method for detecting fumonisin toxigenic strain in asparagus using composite PCR technique
A detection method and technical detection technology, applied in the direction of biochemical equipment and methods, microbial measurement/inspection, etc., can solve the problems of not directly revealing the toxicity of the strains to be tested, and cannot fully guarantee the reliability of the results, so as to meet the requirements of plant quarantine And food safety testing, strong practicability and simple process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0042] Example 1 Isolation of strains in asparagus in Zhejiang area to detect fumonin-producing strains
[0043] The asparagus materials used in this experiment are edible stems, collected from various planting bases in Zhejiang Province, a total of 16 parts, including 5 parts in Ningbo, 5 parts in Fuyang, and 6 parts in Xinchang.
[0044] Step 1: Isolation and purification of strains
[0045] Wash the asparagus samples and cut them into 2cm long sections, disinfect them with 70% alcohol for 3 minutes, 10% sodium hypochlorite for 7 minutes, and then rinse them with sterile water for 3 times. Under sterile conditions, spread the samples on PDA (potato-dextrose-agar) medium and seal with parafilm. Placed in an incubator at 25°C in the dark.
[0046] Count the colonies of each sample on the PDA medium, observe the growth of the fungi, observe the characteristics of the fungi under a microscope after 4-5 days, separate out different fungi, pick them out from the colonies, and in...
Embodiment 2
[0081] Example 2: Sensitivity and minimum detection limit of primers designed in the present invention to detect fumonisin-producing strains
[0082] Step 1: Primer Synthesis
[0083] The operation steps are the same as the third step of Example 1.
[0084] Step 2: Template DNA Dilution
[0085] Dilute Fusarium moniliforme wild-type chromosomal DNA concentration with sterile water to 10ng, 1ng, 100pg, 10pg, 1pg,
[0086] Step 3: Multiplex PCR amplification
[0087] The template DNA diluted in the second step was directly added to the PCR reaction system in the fourth step of Example 1 for multiplex PCR amplification.
[0088] Step 4: Judgment of test results
[0089] Same as the fifth step in Example 1.
[0090] Implementation results:
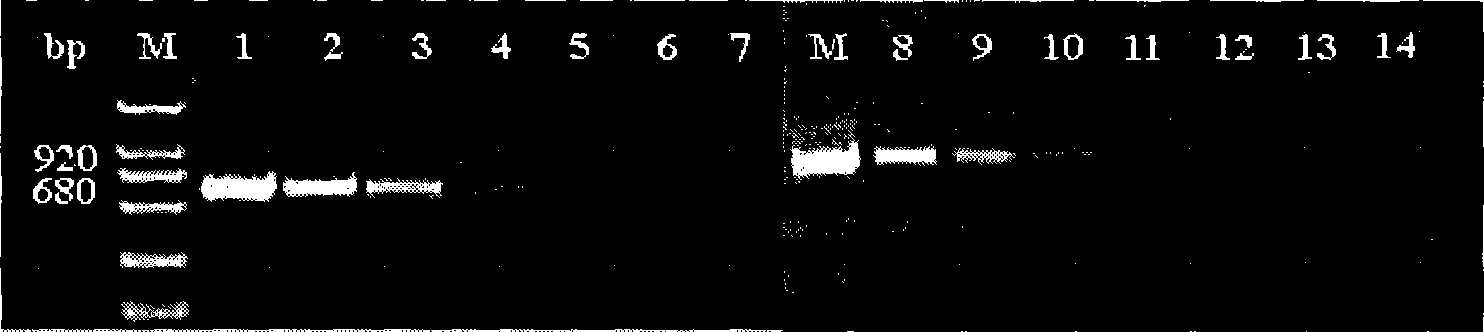
[0091] Measured primer pair rp32 / rp33, the detection limit of rp679 / rp680 is 10pg ( figure 2 ), the water control result without adding DNA was negative, and the detection limit of composite PCR was 100pg ( image 3 ).
Embodiment 3
[0092] Example 3: Detection of virulence of isolated bacterial strains under in vitro conditions
[0093] The strain materials used in this experiment were all the strains isolated from asparagus samples collected from various places in previous experiments.
[0094] Step 1: Preparation of strain spore suspension
[0095] Take 15ml of GYP liquid medium (glucose-peptone-yeast extract), add it to a 50ml Erlenmeyer flask, and use an inoculation loop to pick out a small amount from the preserved wild-type Fusarium moniliforme (F.verticillioides) or the test tube of the test strain The bacteria were put into a conical flask, placed in a constant temperature shaking incubator at 200rpm / min, 27°C, and cultivated for 40-48h. Take 2ml of culture solution and add it to a 2ml centrifuge tube, centrifuge at 12000rpm / min for 10min, discard the upper layer carefully, add 1ml of sterile water, centrifuge at 12000rpm / min for 10min, discard the supernatant, then add 1ml of sterile water, 1200...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com