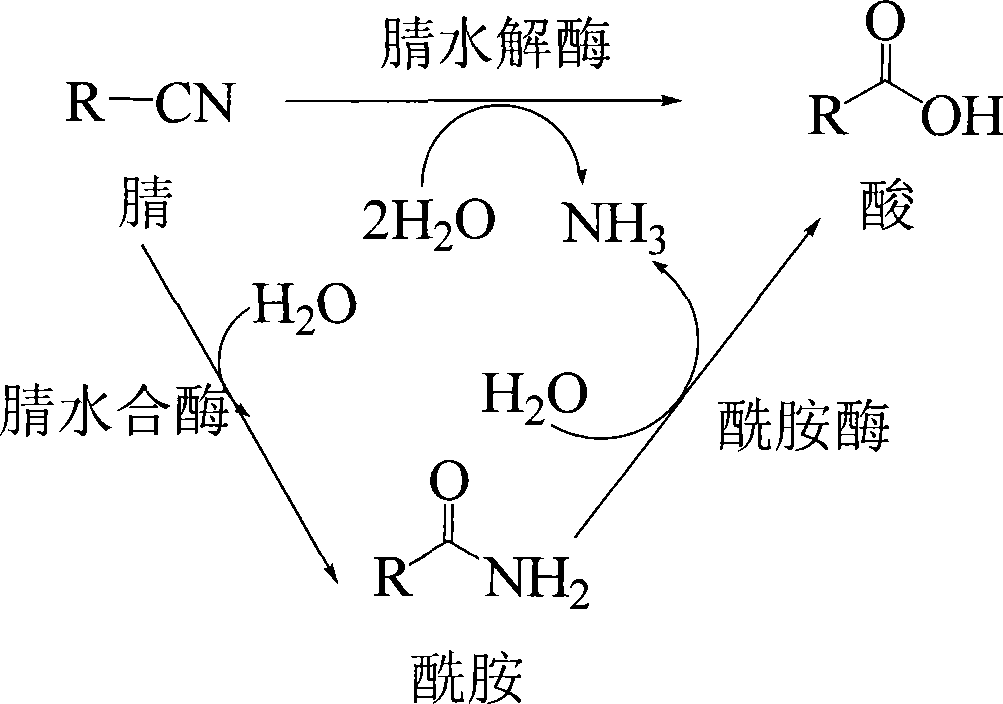
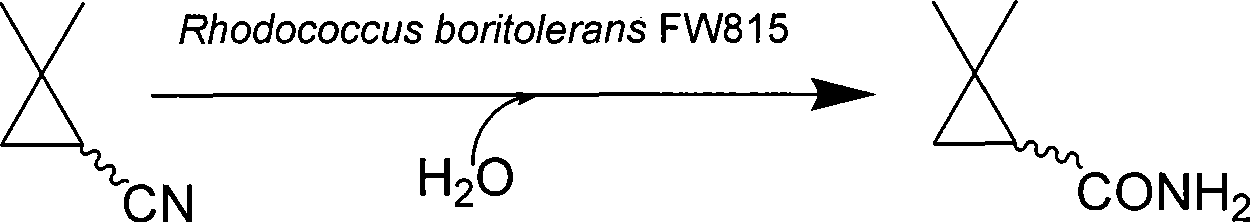
Method for preparing 2,2-dimethyl cyclopropanecarboxamide and bacterial strain thereof by biological catalysis
A technology for dimethylcyclopropanecarboxamide and dimethylcyclopropanecarbonitrile is applied in the field of biocatalytic preparation of 2,2-dimethylcyclopropanecarboxamide and strains thereof, and can solve the problem of lengthy reaction steps and unobtainable products. Problems such as low rate and excessive waste water
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0041] Example 1: Screening microbial strains with catalytic 2,2-dimethylcyclopropanenitrile hydration activity
[0042] Collect soil samples around chemical plants in Zhejiang Province, take 1.0g of soil samples and disperse them into 10.0ml of 0.95% normal saline solution, mix thoroughly; take 2.0ml of bacterial suspension and inoculate to 50.0ml containing 1.0‰ (v / v) 2,2-Dimethylcyclopropanecarbonitrile rich medium (preparation: 10.0g glucose, 1.0g K 2 HPO 4 , 0.2gMgSO 4 , 1.0gKH 2 PO 4 , 0.002gFeSO 4 ·7H 2 O, 0.002g CoCl 2 ·6H 2 O, 0.015g CaCl 2 , the pH is natural, and the water is added to 1.0L; the culture medium is sterilized at 121°C for 20 minutes, and after cooling to room temperature, 1.0mL of 2,2-dimethylcyclopropanenitrile is added, here, racemic 2,2-dimethyl cyclopropanecarbonitrile as the only carbon source and nitrogen source of the enrichment medium), shake culture under the conditions of 30°C and 150rpm until the culture medium is turbid; ) was tra...
Embodiment 2
[0045] Example 2: Preparation of biocatalyst R.boritolerans CCTCC M 208108 cells
[0046] The new nitrile hydratase that obtains from the present invention's breeding produces bacterial classification R.boritolerans CCTCC M208108 on the test tube inclined surface and picks a ring thalline, inoculates to 20.0ml aseptic seed culture medium (preparation: glucose 10.0g, yeast extract 3.0g , NaCl 1.0g, K 2 HPO 4 0.3g, KH 2 PO 4 0.3g, MgSO 4 0.2g, pH natural, make up to 1.0L with water. The medium was sterilized at 121° C. for 20 minutes), and cultured with shaking at 30° C. and 150 rpm for 24 hours.
[0047] Investigate the induction effect of different inducers, design the fermentation medium of the control group, the composition is: 10.0g / l glucose, 8.0g / l yeast powder, 1.0g / l KH 2 PO 4 , 1.0g / l K 2 HPO 4 , 1.0g / l NaCl, 0.2g / l MgSO4, 0.01g / l FeSO4, 0.05g / l CaCl 2 , the solvent is water; the fermentation medium of the experimental group was added 1.0g / l sodium glutama...
Embodiment 3
[0050] Embodiment 3: 2,2-dimethylcyclopropanamide biotransformation in the phosphate buffer system
[0051] The biosynthesis of 2,2-dimethylcyclopropanamide uses the biocatalyst R.boritolerans CCTCC M208108 bacterium cells prepared by the present invention. Select 10.0ml pH7.0 phosphate buffer (50.0mM) for the transformation system, the final concentration of R.boritolerans CCTCC M 208108 cells is 0.1gDCW / L, the substrate is fed in 3 batches, and 5.0μL 2,2-dimethylcyclopropane is added to each batch For cyanonitrile, the conversion temperature is 30°C, each batch is converted for 5 minutes, and the total conversion time is 15 minutes. After the transformation, centrifuge at 10,000rpm for 10min, discard the precipitate, collect the supernatant, and then filter the transformation liquid through a 0.45μm microfiltration membrane. The permeate is analyzed by gas chromatography. The conversion rates of the three batches are 100%, 99.1% and 100% respectively. , the cumulative conce...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com