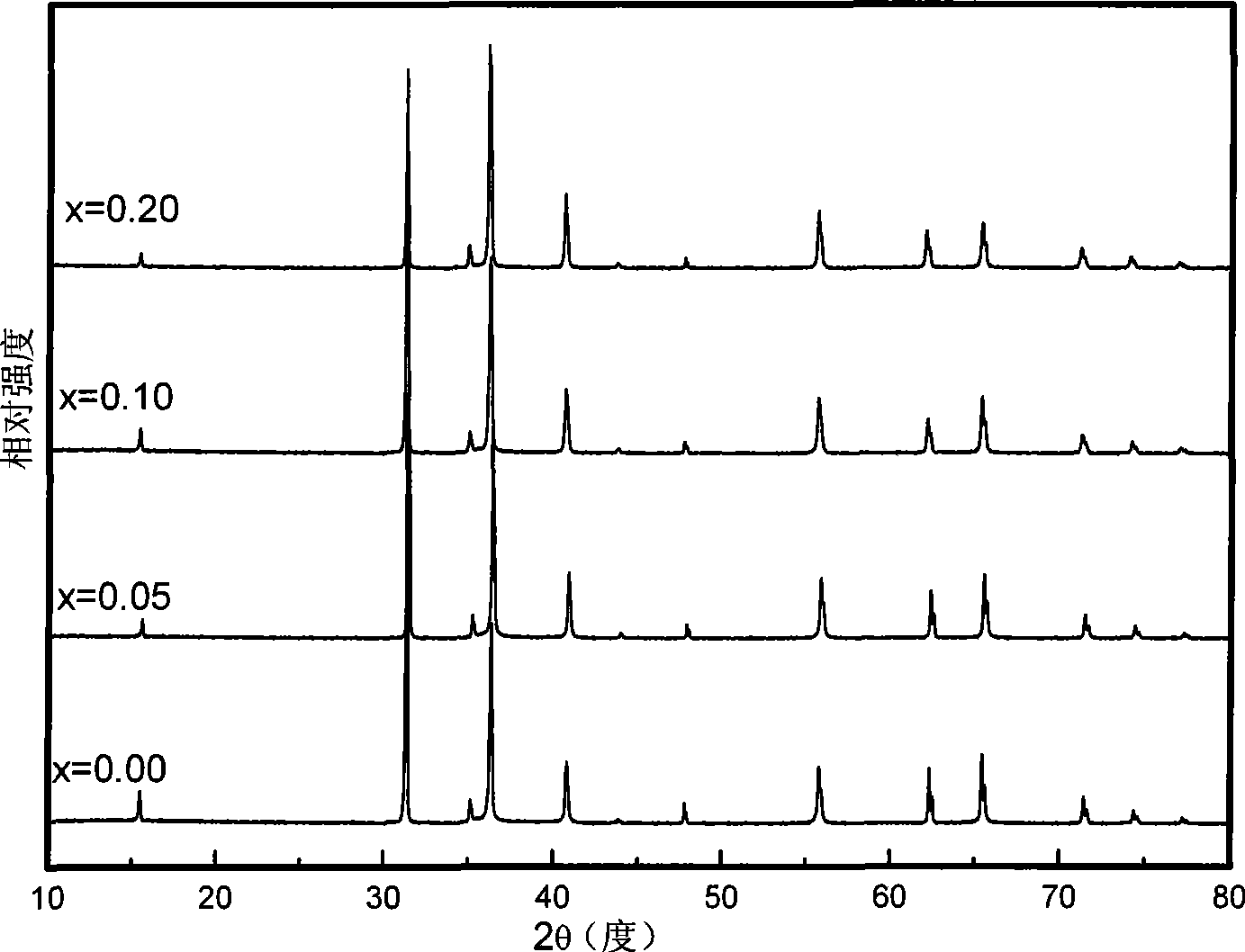
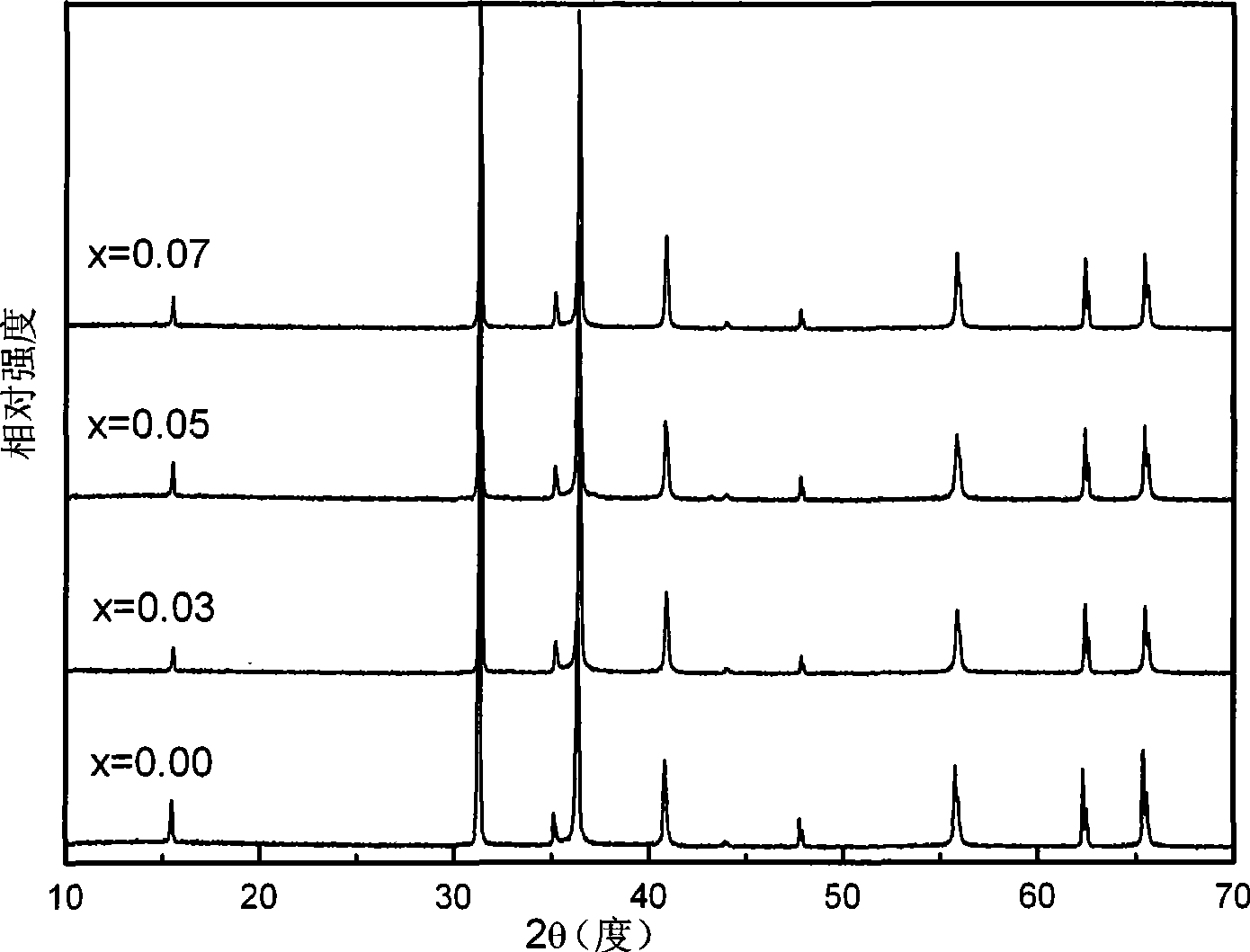
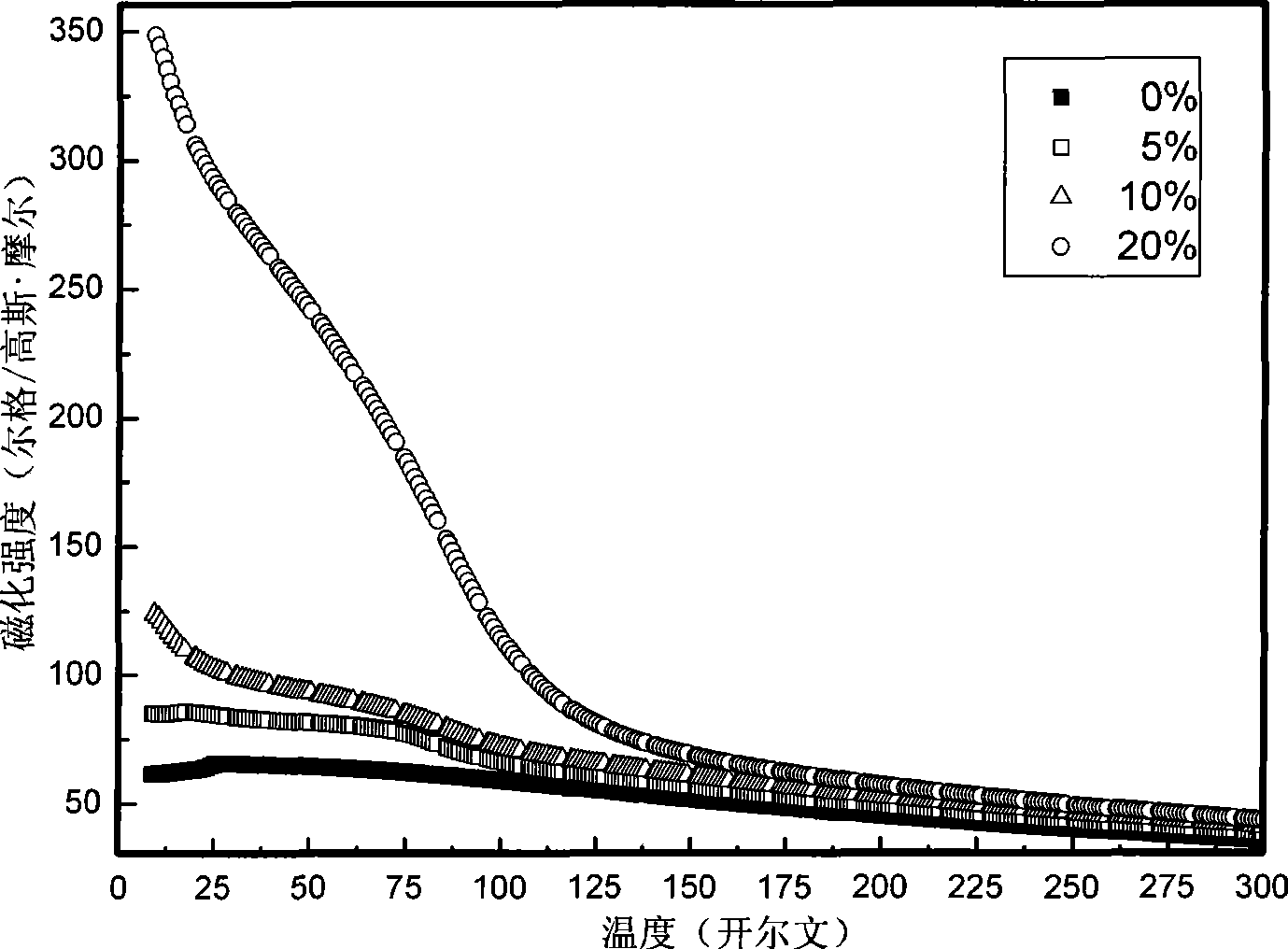
P type doping CuCrO2 based diluted magnetic semiconductor material and preparation thereof
A technology of dilute magnetic semiconductors and bulk materials, applied in the direction of inorganic material magnetism, inductance/transformer/magnet manufacturing, electrical components, etc., to achieve the effect of simple technology and low energy consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0029] Embodiment 1: complete the preparation according to the following steps:
[0030] (a) According to the molar ratio of copper, chromium and manganese as 1:0.90:0.10, weigh copper acetate, chromium nitrate and manganese acetate, add powder into distilled water and add appropriate amount of citric acid, stir at room temperature until completely dissolved , to obtain a uniformly mixed solution;
[0031] (b) drying the stirred solution in an oven at 100° C. to obtain a precursor powder;
[0032] (c) Grinding the precursor powder and putting it into a furnace for pre-sintering at 300-500° C. for 3 hours to remove organic matter in the powder.
[0033] (d) The powder obtained by pre-calcination was sintered at 1100°C for 10 hours to prepare CuCr 0.90 mn 0.10 o 2 powder.
[0034] (e) Press the obtained powder into a circular sheet-like block with a tablet machine, and sinter at 1100°C for 10 hours to obtain CuCr 0.90 mn 0.10 o 2 bulk material.
Embodiment 2
[0035] Embodiment 2: complete the preparation according to the following steps:
[0036] (a) According to the molar ratio of copper, chromium and manganese as 1:0.80:0.20, weigh copper acetate, chromium nitrate and manganese acetate, add powder into distilled water and add appropriate amount of citric acid, stir at room temperature until completely dissolved , to obtain a uniformly mixed solution;
[0037] (b) drying the stirred solution in an oven at 100° C. to obtain a precursor powder;
[0038] (c) Grinding the precursor powder and putting it into a furnace for pre-sintering at 300-500° C. for 3 hours to remove organic matter in the powder.
[0039] (d) The powder obtained by pre-calcination was sintered at 1100°C for 10 hours to prepare CuCr 0.80 mn 0.20 o 2 powder.
[0040] (e) Press the obtained powder into a circular sheet-like block with a tablet machine, and sinter at 1100°C for 10 hours to obtain CuCr 0.80 mn 0.20 o 2 bulk material.
Embodiment 3
[0041] Embodiment 3: complete the preparation according to the following steps:
[0042] (a) According to the molar ratio of copper, chromium and nickel is 1:0.95:0.05, weigh copper acetate, chromium nitrate and nickel acetate, add powder into distilled water and add appropriate amount of citric acid, stir at room temperature until completely dissolved , to obtain a uniformly mixed solution;
[0043] (b) drying the stirred solution in an oven at 100° C. to obtain a precursor powder;
[0044] (c) Grinding the precursor powder and putting it into a furnace for pre-sintering at 300-500° C. for 3 hours to remove organic matter in the powder.
[0045] (d) The powder obtained by pre-calcination was sintered at 1100°C for 10 hours to prepare CuCr 0.95 Ni 0.05 o 2 powder.
[0046] (e) Press the obtained powder into a circular sheet-like block with a tablet machine, and sinter at 1100°C for 10 hours to obtain CuCr 0.95 Ni 0.05 o 2 bulk material.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com