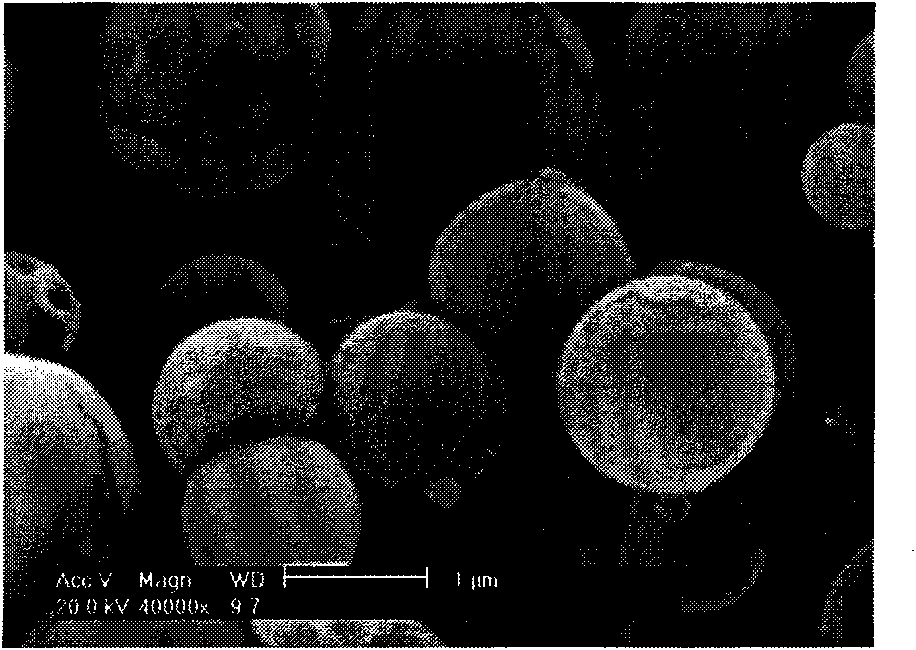Degradable medical hemostatic non-viscous material and preparation method thereof
An anti-adhesion and preparation process technology, applied in the field of medicine, can solve the problems of lack of hemostasis and wound repair, poor hemostasis effect, slow hemostasis, etc., to achieve hemostasis and anti-adhesion wound healing, promotion of wound healing, and less pain.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0040] Example 1 Preparation of microsphere-type hemostatic and anti-adhesion materials
[0041] 1g chitosan was dissolved in 10mL, 10wt% hydrochloric acid aqueous solution, added 40mLNH 4 HCO 3 Aqueous solution (containing NH 4 HCO 3 9.6g), stand at 20°C for 3 days, centrifuge at 12,000 rpm, discard the supernatant, add 200mL water to the precipitate to dilute, stir at high speed for 30s, add 100ml sodium hyaluronate aqueous solution (containing 0.2g sodium hyaluronate), stir To obtain the chitosan-hyaluronic acid complex solution, the complex solution was spray-dried at 150° C. to obtain microsphere-type hemostatic and anti-adhesion materials. The results of the scanning electron microscope (Philips ESEM-30) are shown in figure 1 .
[0042] New Zealand white rabbits underwent epistaxis after partial turbinectomy, and 1 g of the microsphere-type hemostatic and anti-adhesion material prepared in this example was sprayed on the wound surface. The control group used high-exp...
Embodiment 2
[0043] Example 2 Preparation of microsphere-type hemostatic and anti-adhesion materials
[0044] Dissolve 1g of phosphorylated chitosan in 50mL of water, add 100mL of sodium hyaluronate aqueous solution (containing 0.5g of sodium hyaluronate) dropwise, stir to obtain a chitosan-hyaluronic acid complex solution, and spray the complex solution at 150°C Dry to obtain the microsphere-type hemostatic and anti-adhesion material.
[0045]A bleeding wound of about 1cm×0.5cm in size was made on the kidney surface of New Zealand rabbits, and 1g of the microsphere-type hemostatic and anti-adhesion material prepared in this example was used to stop bleeding. The blood loss was 75±12s, the blood loss was 0.8±0.1mL, and no intraoperative adhesion occurred within 30 days.
Embodiment 3
[0046] Example 3 Preparation of microsphere-type hemostatic and anti-adhesion materials
[0047] 1g of chitosan was dissolved in 50mL of acetic acid aqueous solution (containing 0.5g of acetic acid), and the chitosan solution was added dropwise to 100mL of sodium hyaluronate aqueous solution (containing 1g of sodium hyaluronate) using an electrostatic droplet generator, and centrifuged to obtain Chitosan-hyaluronic acid gel microspheres are sequentially immersed in chitosan and sodium hyaluronate aqueous solution to assemble 6 layers of polyelectrolyte membranes on the surface of the microspheres, centrifuged and freeze-dried to obtain microsphere-type hemostatic and anti-adhesion materials.
[0048] Nosebleeds occurred in New Zealand white rabbits after part of the maxillary turbinate was removed. Spray 1 g of the microsphere-type hemostatic and anti-adhesion material prepared in this example on the wound surface. The hemostatic time was 160±10s, and no nosebleed occurred with...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com