Preparation method of phytosterin ester rich in oleic acid
A technology of phytosterol esters and phytosterols, which is applied in the field of food additive preparation, can solve problems such as long reaction time, complex reaction, and harsh operating conditions, and achieve the effects of low reaction condition requirements, high detection accuracy, and reduced side reactions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
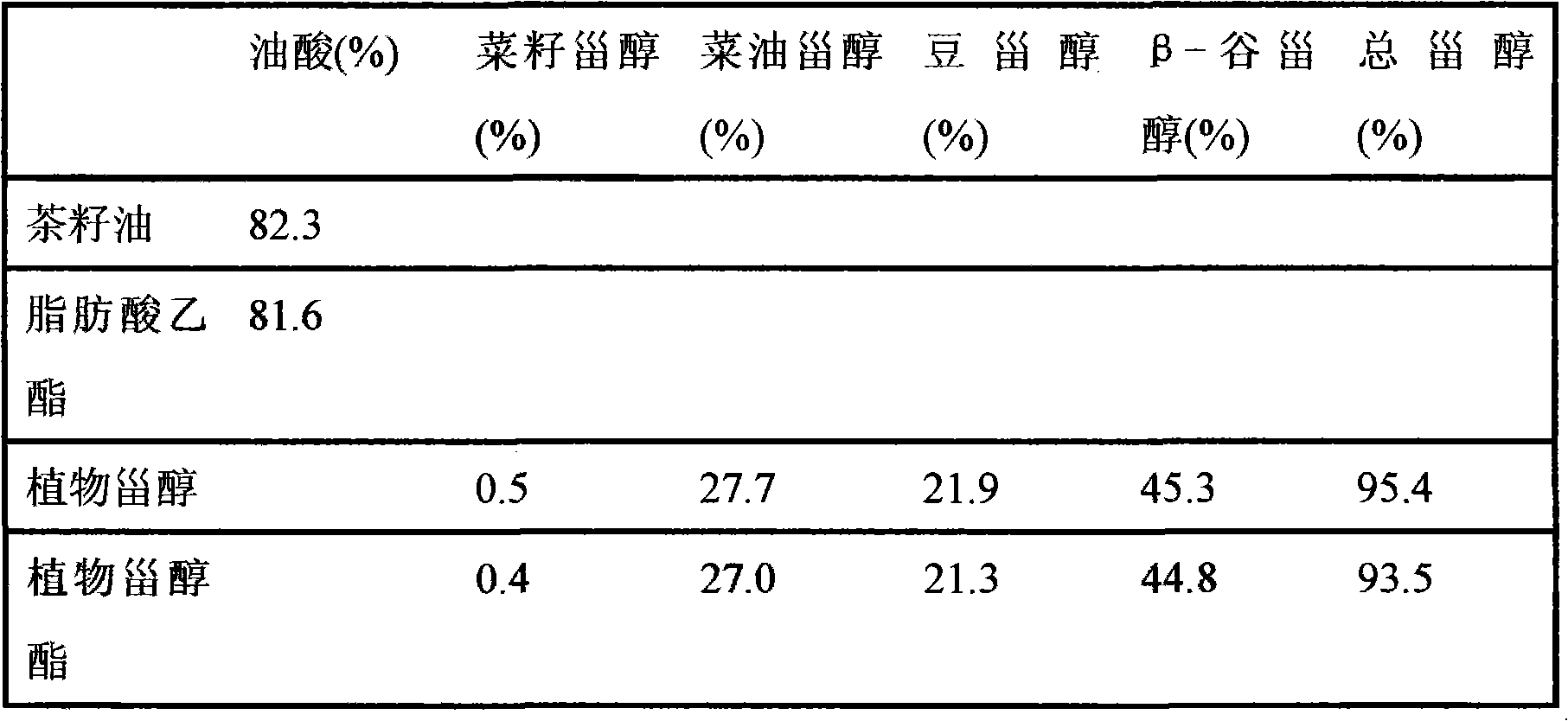
[0023] Take 10kg of tea seed oil and mix with 20kg of ethanol, heat up to reflux at 80°C, add 1.5kg of sodium ethoxide, and keep this temperature for 2.5h. Then add 30kg of deionized water, leave to stand for stratification after slight stirring, remove the lower hydration layer, then wash with 30kg of deionized water to neutrality, dry the oil layer after washing under vacuum to obtain 8.6kg of fatty acid ethyl ester, The conversion was 98% and the yield was 95%.
[0024] Mix 1 kg of phytosterol with 4 kg of fatty acid ethyl ester prepared above and heat up to 120° C. to dissolve the phytosterol. After heating up, vacuum-dry the reactant at a vacuum degree of -0.08 MPa and keep for 2 hours. After the dehydration was completed, 1.5 kg of 35% sodium ethylate solution was added. The mixture was kept at 140°C for 4 hours under a vacuum of 50 Pa until the reaction was complete. After the reaction was completed, the temperature of the reaction solution was lowered to 70°C, the vac...
Embodiment 2
[0026] Take 1kg of tea seed oil and mix it with 1.5kg of ethanol, heat it up to reflux at 80°C, add 100g of sodium ethoxide, and keep it at this temperature for 2 hours. Then add 1 kg of deionized water, stir slightly and leave to stand for stratification, remove the lower hydration layer, then wash with 1 kg of deionized water until neutral, and degas and dry the oil layer after washing to obtain 830 g of fatty acid ethyl ester , the conversion rate is 97%, and the yield is 96%.
[0027] Mix 100g of phytosterol with 500g of the fatty acid ethyl ester prepared above and heat up to 120°C to dissolve the phytosterol. After heating up, vacuum-dry the reactant at a vacuum degree of -0.09MPa and keep for 1h. After the dehydration was completed, 150 g of 35% sodium ethoxide solution was added. The mixture was kept at 140°C for 4 hours under a vacuum of 50 Pa until the reaction was complete. After the reaction was completed, the temperature of the reaction solution was lowered to 70...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com