Carbon-silicon composite material, preparation method and application thereof
A technology of composite materials and silicon-based materials, applied in the direction of electrode manufacturing, structural parts, electrical components, etc., can solve the problems of current collector fracture, difficulty in realizing cycle characteristics, and inability to obtain cycle characteristics, etc., to achieve high electronic conductivity and excellent charging Effects of /discharge cycle characteristics, excellent charge/discharge characteristics
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0042] The preparation method of the above-mentioned carbon-silicon composite material specifically includes the following steps:
[0043] 1) Preparation of catalyst solution
[0044] Acetate of at least one of Fe, Co, Ni, Cu, Mg, Mn, Ti, Sn, Si, Zr, Zn, Ge, Pb and In is formulated into a catalyst solution of 0.0001M to 0.1M, and the solvent is selected from One or more of distilled water, ethanol, methanol, isopropanol, ethylene glycol or glycerin.
[0045] The choice of acetate was based on extensive testing by the inventors, other salts did not result in composites containing both large and small fibers. The concentration of the catalyst solution is 0.0001M to 0.1M. The composite material produced with a high concentration has a high content of carbon nanofibers and the working hours are short. When the concentration is small, the working hours required to prepare fibers with the same content will be extended.
[0046] The choice of solvent is based on selecting the solve...
Embodiment 1
[0066] Embodiment 1 Preparation of carbon-silicon composite material of the present invention
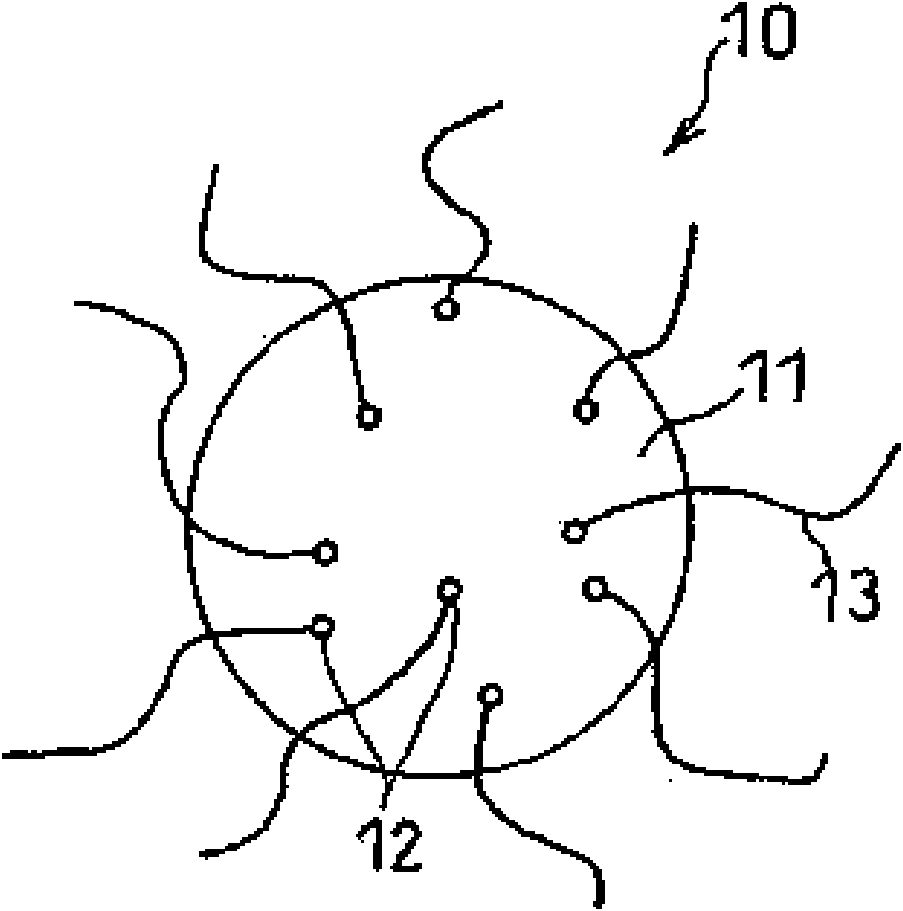
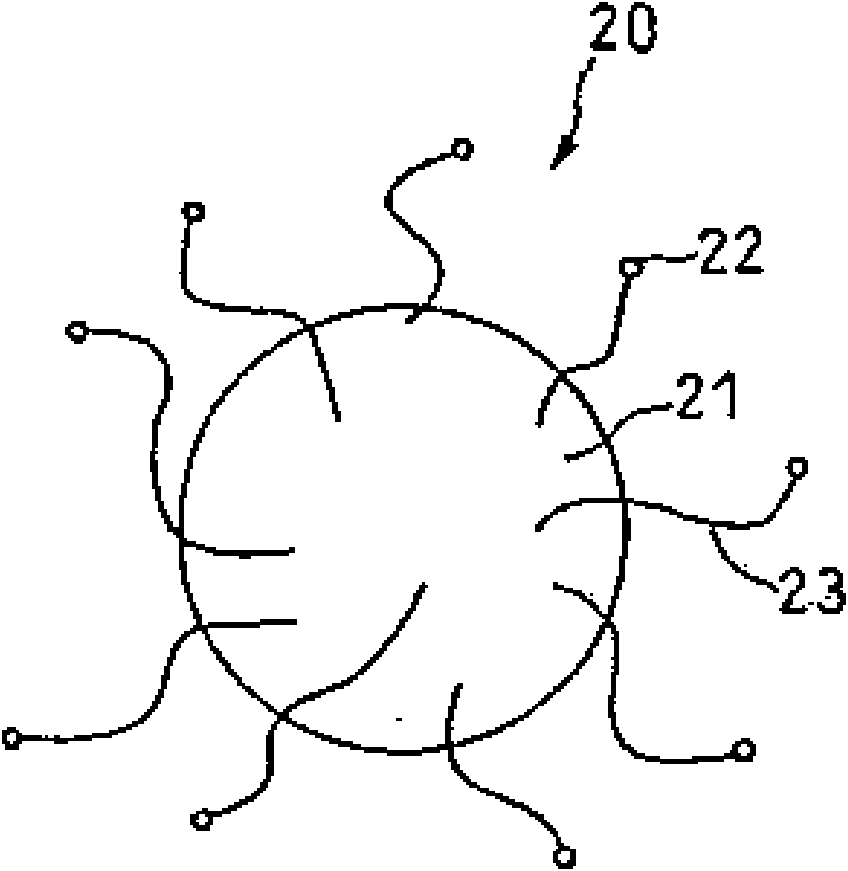
[0067] Dissolve 5 g of nickel acetate tetrahydrate in 100 g of methanol. The solution thus obtained was mixed with 35 g of silicon oxide (SiO) pulverized to a particle size of 3 μm or less, and the mixture of the silicon oxide particles and the solution was stirred for 1 hour, and then water was removed by an evaporator to allow the silicon oxide particles to be supported on the surface thereof. Nickel acetate.
[0068] The silica particles loaded with nickel acetate were placed in a quartz reaction vessel, and the temperature was raised to 550 °C in the presence of helium. Then, the helium gas was replaced with a mixed gas consisting of 50% by volume of hydrogen and 50% by volume of methane gas, and the inside of the reaction vessel was maintained at 550° C. for 90 minutes to grow fine particles including fibers with a diameter of about 20 nm on the surface of the silicon oxide pa...
Embodiment 2
[0070] Embodiment 2 Preparation of carbon-silicon composite material of the present invention
[0071] Except that 3.5 g of nickel acetate tetrahydrate was dissolved in 100 g of methanol solution instead of 5 g of nickel acetate tetrahydrate, the same operation as in Example 1 was carried out, and this was set as electrode material B for a non-aqueous electrolyte secondary battery. The particle size of the nickel particles carried on the silicon oxide particles was substantially the same as that of the nickel particles in Example 1. The fiber diameter and fiber length of the grown carbon nanofibers were almost the same as in Example 1, and the weight ratio to the active material particles was 20%. Here, in SEM observation, in addition to fibers having a fiber diameter of about 80 nm, the existence of fine fibers having a fiber diameter of 30 nm or less was also confirmed.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com