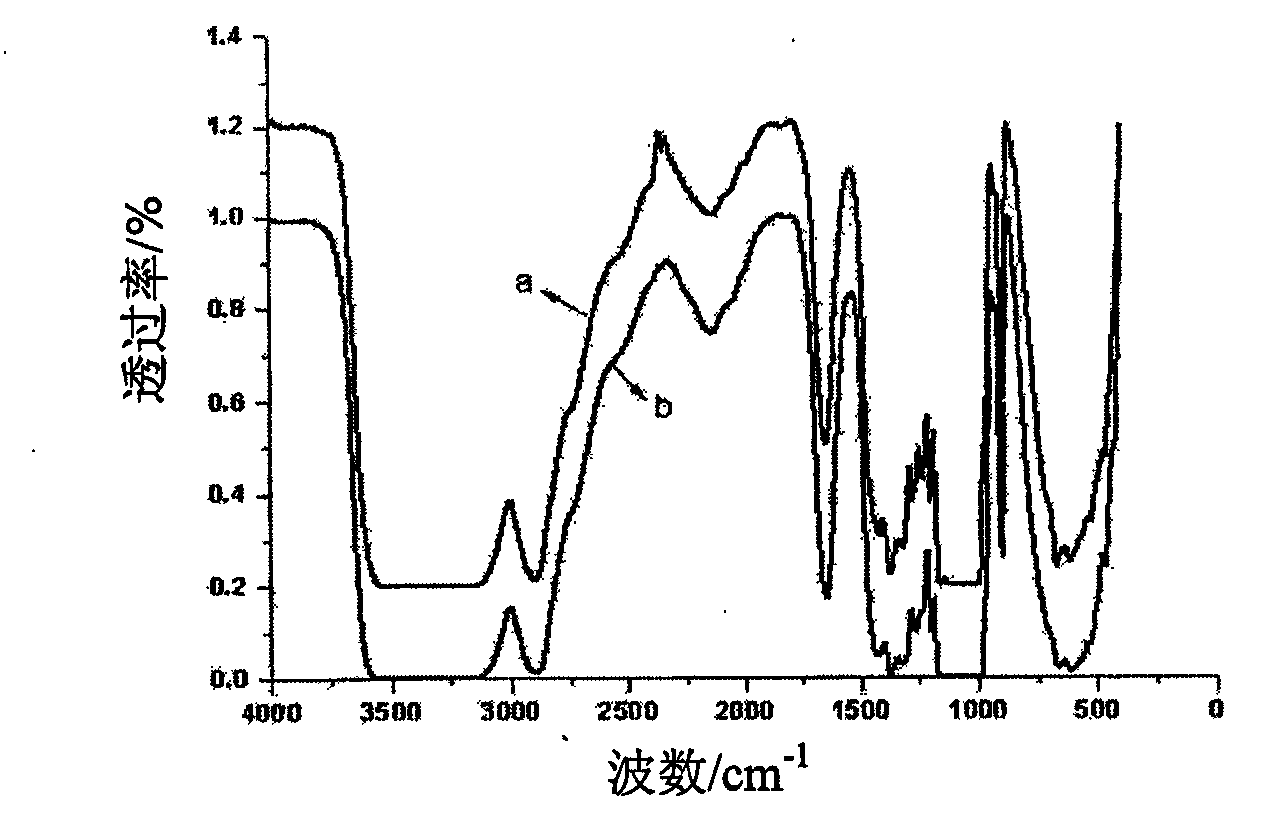
Method for recycling waste glassine
A technology of waste glass and cellophane, applied to artificial filaments made of viscose, synthetic cellulose fibers, etc., can solve problems such as environmental pollution, many reaction by-products, complicated procedures, etc. It is easier to control the process conditions and reduce production cost and shorten the process flow
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] After drying the cleaned and broken waste cellophane and solvent LiCl until its moisture content is ≤5%, first weigh 7% of waste cellophane and 0.02% of the weight of cellophane and add potassium permanganate to DMAc solvent, and completely immerse the waste cellophane In it, activate it in an oil bath at 160°C for 35 minutes, squeeze out excess solvent DMAc; fully dissolve 9% LiCl in 84% DMAc solvent, and then add the activated cellophane after extrusion to the DMAc / LiCl solvent system Mix it with it, heat and stir it in a constant temperature water bath at 90°C for 3 hours, and let it stand at room temperature for 17 hours to obtain a uniform and stable cellophane / DMAc / LiCl solution.
Embodiment 2
[0029] After drying the cleaned and broken waste cellophane and solvent LiCl until its moisture content is ≤5%, first weigh 5% of waste cellophane and 0.02% of the weight of cellophane and add potassium permanganate to DMAc solvent, and completely immerse the waste cellophane In it, activate it in an oil bath at 161°C for 30 minutes, squeeze out the excess solvent DMAc; fully dissolve 10% LiCl in 85% DMAc solvent, and then add the activated cellophane after extrusion to the DMAc / LiCl solvent system Mix it with it, heat and stir it in a constant temperature water bath at 92°C for 4 hours, and let it stand at room temperature for 15 hours to obtain a uniform and stable cellophane / DMAc / LiCl solution.
Embodiment 3
[0031] After drying the cleaned and broken waste cellophane and solvent LiCl until its moisture content is ≤5%, first weigh 4% of waste cellophane and 0.02% of the weight of cellophane and add potassium permanganate to DMAc solvent, and completely immerse the waste cellophane In it, then activated in an oil bath at 162°C for 34min, extruding to remove excess solvent DMAc; fully dissolving 8% LiCl in 88% DMAc solvent, and then adding the extruded activated cellophane to DMAc / LiCl solvent system Mix it with it, heat and stir it in a constant temperature water bath at 91°C for 7 hours, and let it stand at room temperature for 28 hours to obtain a uniform and stable cellophane / DMAc / LiCl solution.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| elongation | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com