Soyabean protein glycosylation graft modification method
A soybean protein, graft modification technology, applied in the field of glycosylation graft modification of soybean protein, can solve the problems of difficulty in industrial production of glycosylated products, long reaction time, difficult process control, etc., to overcome the reaction Non-uniformity, fast response, antibacterial improvement effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
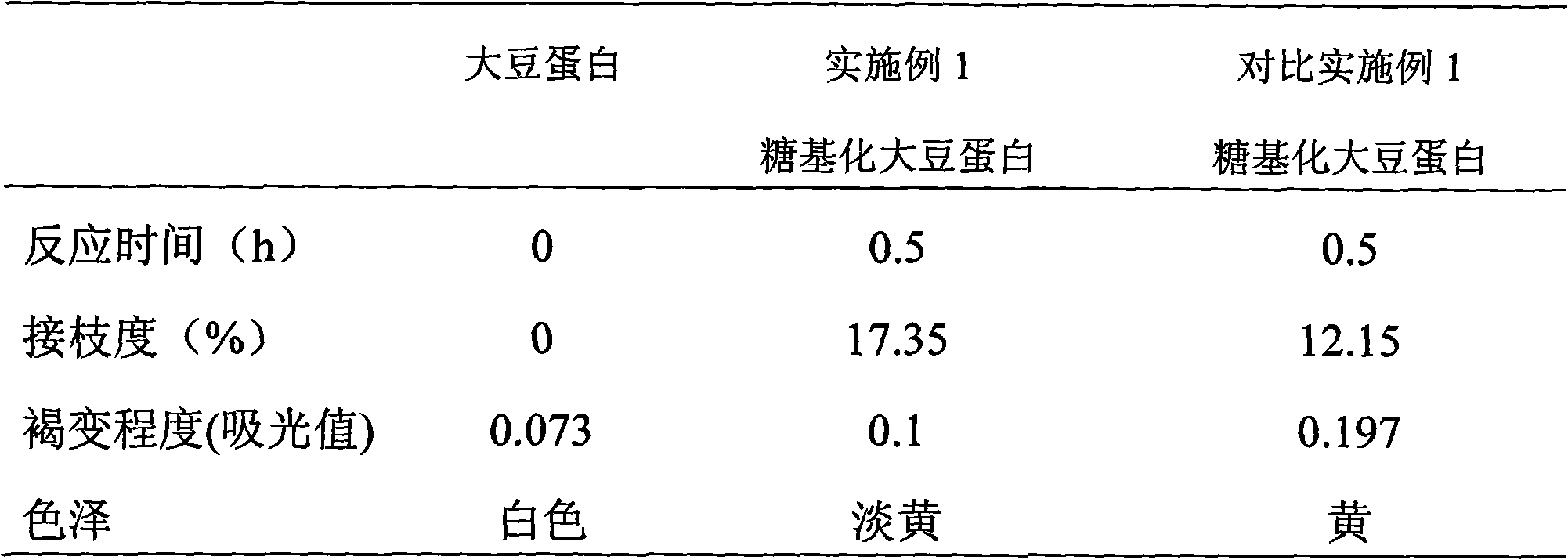
[0022] (1) dissolving soybean protein isolate and glucose with a mass ratio of 1:2 in a phosphate buffer solution of pH 7.0 to obtain a mixed solution; the mass percentage concentration of the soybean protein isolate and glucose is 2%;
[0023] (2) Place 20ml of the mixed solution obtained in step (1) in a closed pressure reactor, pressurize it to 3Mpa with nitrogen, raise the temperature to 95°C, and react for 0.5 hours to obtain the reaction solution;
[0024] (3) Cool the reaction solution obtained in step (2) to 40° C., purify, and freeze-dry to obtain the finished product of glycosylated soybean protein.
[0025] The degree of grafting of the obtained glycosylated soybean protein was measured by the method of o-phthalaldehyde, and the degree of browning was judged according to the degree of absorption of the reaction product at 420 nm in the visible region. The results are shown in Table 1.
Embodiment 2
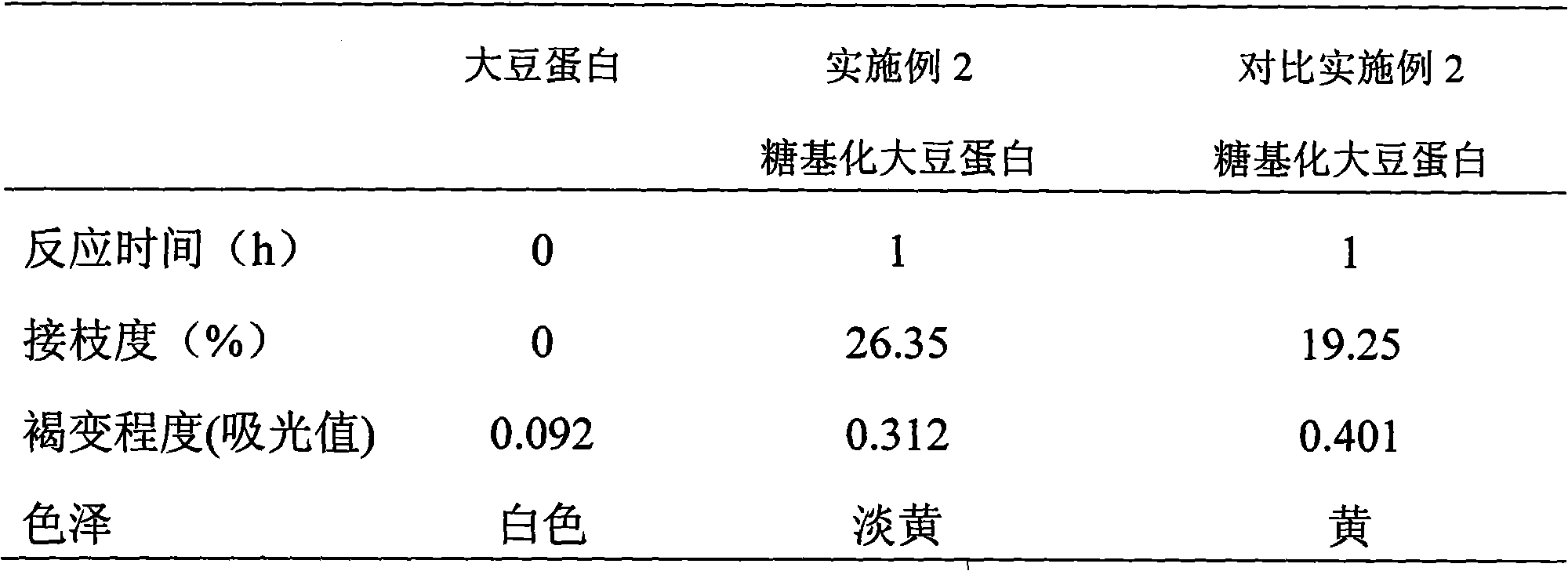
[0035] (1) Soybean protein isolate and dextran (molecular weight 67KD) that mass ratio is 1: 1 are dissolved in the phosphate buffer saline solution of pH7.2, obtain mixed solution; The mass percentage that described soybean protein isolate and glucose occupy The concentration is 2.5%;
[0036] (2) Place 20ml of the mixed solution obtained in step (1) in a closed pressure reactor, pressurize it to 10Mpa with nitrogen, raise the temperature to 120°C, and react for 1 hour to obtain the reaction solution;
[0037] (3) Cool the reaction solution obtained in step (2) to 10° C., purify, and freeze-dry to obtain the finished product of glycosylated soybean protein.
[0038] The degree of grafting of the obtained glycosylated soybean protein was measured by the method of o-phthalaldehyde, and the degree of browning was judged according to the degree of absorption of the reaction product at 420 nm in the visible region. The results are shown in Table 2.
Embodiment 3
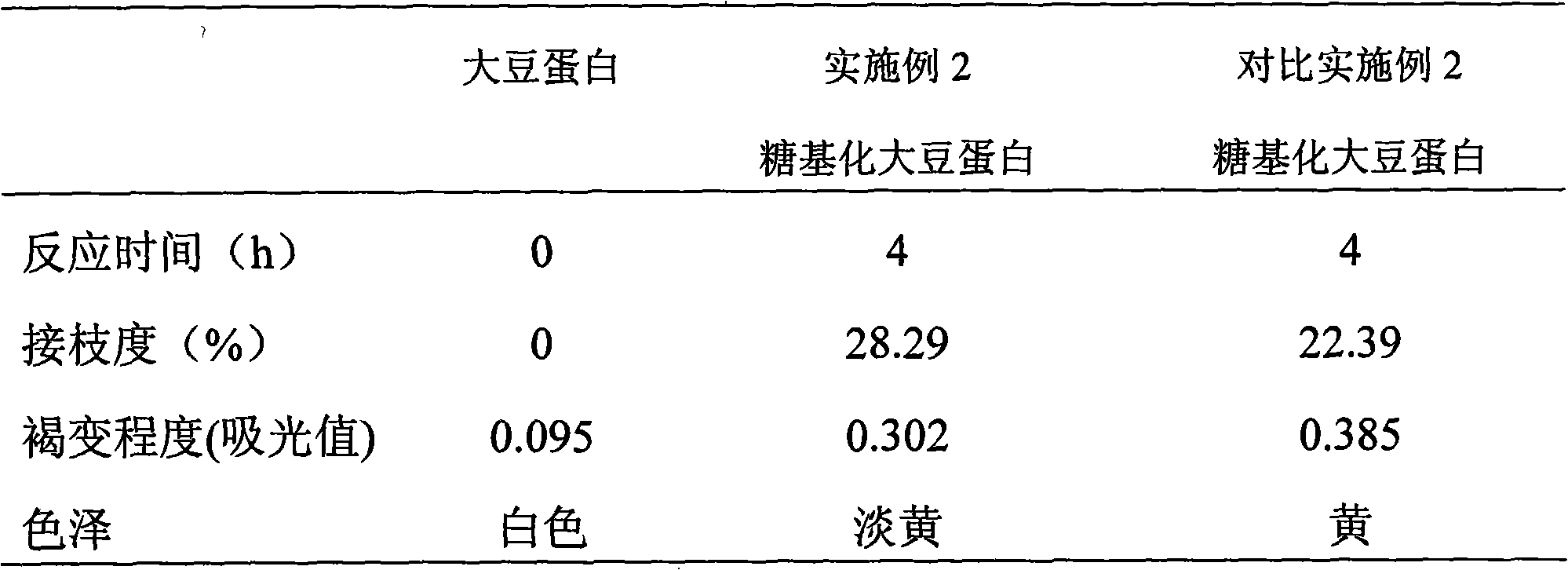
[0048] (1) Soybean 7S globulin (obtained by extraction by Nagano method) and dextran (molecular weight 67KD) with a mass ratio of 1:1 were dissolved in phosphate buffer solution of pH 7.2 to obtain a mixed solution; The mass percent concentration that protein and glucose account for is 0.4%;
[0049] (2) Place 20ml of the mixed solution obtained in step (1) in a closed pressure reactor, pressurize it to 10Mpa with nitrogen, raise the temperature to 100°C, and react for 4 hours to obtain the reaction solution;
[0050] (3) Cool the reaction solution obtained in step (2) to 20° C., purify, and freeze-dry to obtain the finished product of glycosylated soybean protein.
[0051] The degree of grafting of the obtained glycosylated soybean protein was measured by the method of o-phthalaldehyde, and the degree of browning was judged according to the degree of absorption of the reaction product at 420 nm in the visible region. The results are shown in Table 3.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com