Preparation method of sulfated polysaccharide
A technology of sulfation and polysaccharides, applied in the field of functional polymers, can solve the problems of not being able to obtain products with high substitution degrees, and achieve the effects of wide range of sulfation degrees, mild reaction, and high yield
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0013] Example 1: Suspend 5 grams of chitin powder (degree of deacetylation 12%) in 100ml of dry DMF, stir at 80°C for 24h, then add 50ml of trimethylchlorosilane, stir at 80°C for 24h. After the reactant was cooled to room temperature, anhydrous acetone was added and stirred, precipitated, filtered with suction, washed with acetone and dried to obtain silylated chitin. Suspend the obtained silylated chitin in 120ml of dry DMSO, swell at 80°C for half an hour, add 26g of SO 3 ·Py, react at 80°C for 12h. Cool the reaction mixture to room temperature, add 60ml of ice water, neutralize with 1M NaOH aqueous solution to pH 7, purify by ultrafiltration, concentrate by distillation under reduced pressure, precipitate with ethanol, and dry in vacuo to obtain sulfated chitin, the product is slightly light yellow , the degree of substitution is 1.96.
Embodiment 2
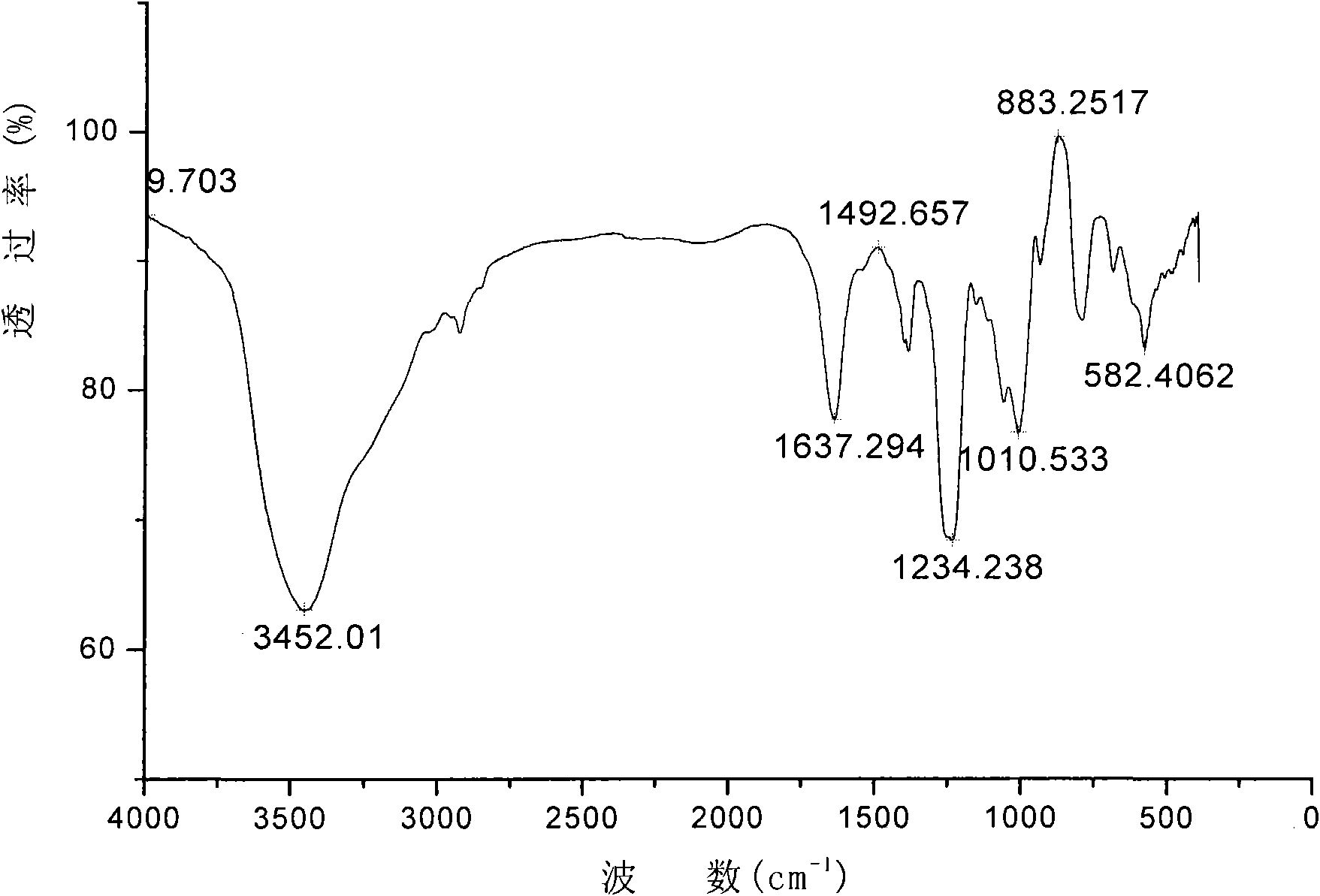
[0014] Embodiment 2: 10 grams of chitosan (deacetylation degree 95%) are in 400ml dry DMF, stirred at 75 ℃ for 12h, then added the mixed reagent of 105ml trimethylchlorosilane and hexamethyldisilazane (The molar ratio of substances is 1:1), stirred and reacted at 70°C for 36h. After the reactant was cooled to room temperature, anhydrous acetone was added and stirred, precipitated, filtered with suction, washed with acetone and dried to obtain silylated chitosan. Suspend the silylated chitosan in 400ml of DMF, and swell at 30°C for half an hour. Add 92 g SO 3 · DMF, react at 30°C for 24h. The reaction mixture was cooled to room temperature, added 120ml of ice water, neutralized to pH 7 with 1M NaOH aqueous solution, after ultrafiltration and purification, concentrated by distillation under reduced pressure, ethanol precipitation, and vacuum drying to obtain sulfated chitosan (infrared spectrum is shown in Figure 1), the product is slightly light yellow, and the degree of sub...
Embodiment 3
[0015] Example 3: Suspend 1 g of cellulose in 80 ml of dry DMSO, stir at 90° C. for 12 h, then add 19 ml of triethylchlorosilane, and react with stirring at 80° C. for 48 h. After the reactant was cooled to room temperature, anhydrous acetone was added to stir, the precipitate was filtered with suction, the precipitate was washed with acetone and dried to obtain silylated cellulose. Suspend silylated cellulose in 80ml of dry pyridine, swell at 80°C for half an hour, add 7g of ClSO 3 H, reacted at 80°C for 24h. Cool the reaction mixture to room temperature, add 30ml of ice water, neutralize with 1M NaOH aqueous solution to pH 7, dialyze against distilled water for 72 hours, concentrate the liquid in the dialysis bag by distillation under reduced pressure, precipitate with ethanol, and dry in vacuo to obtain sulfated cellulose. The product is pale yellow, and the degree of substitution is 2.95.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com