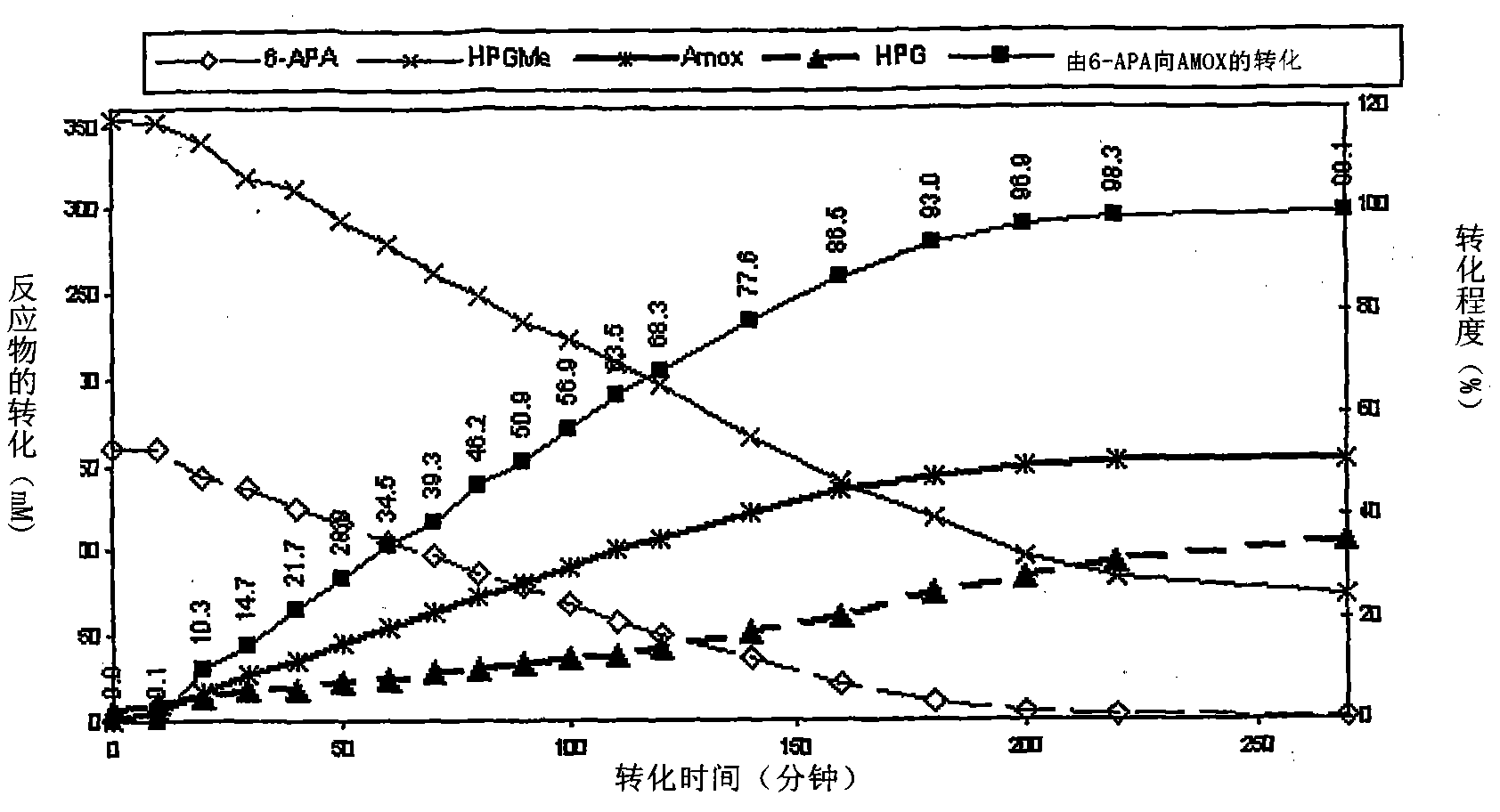
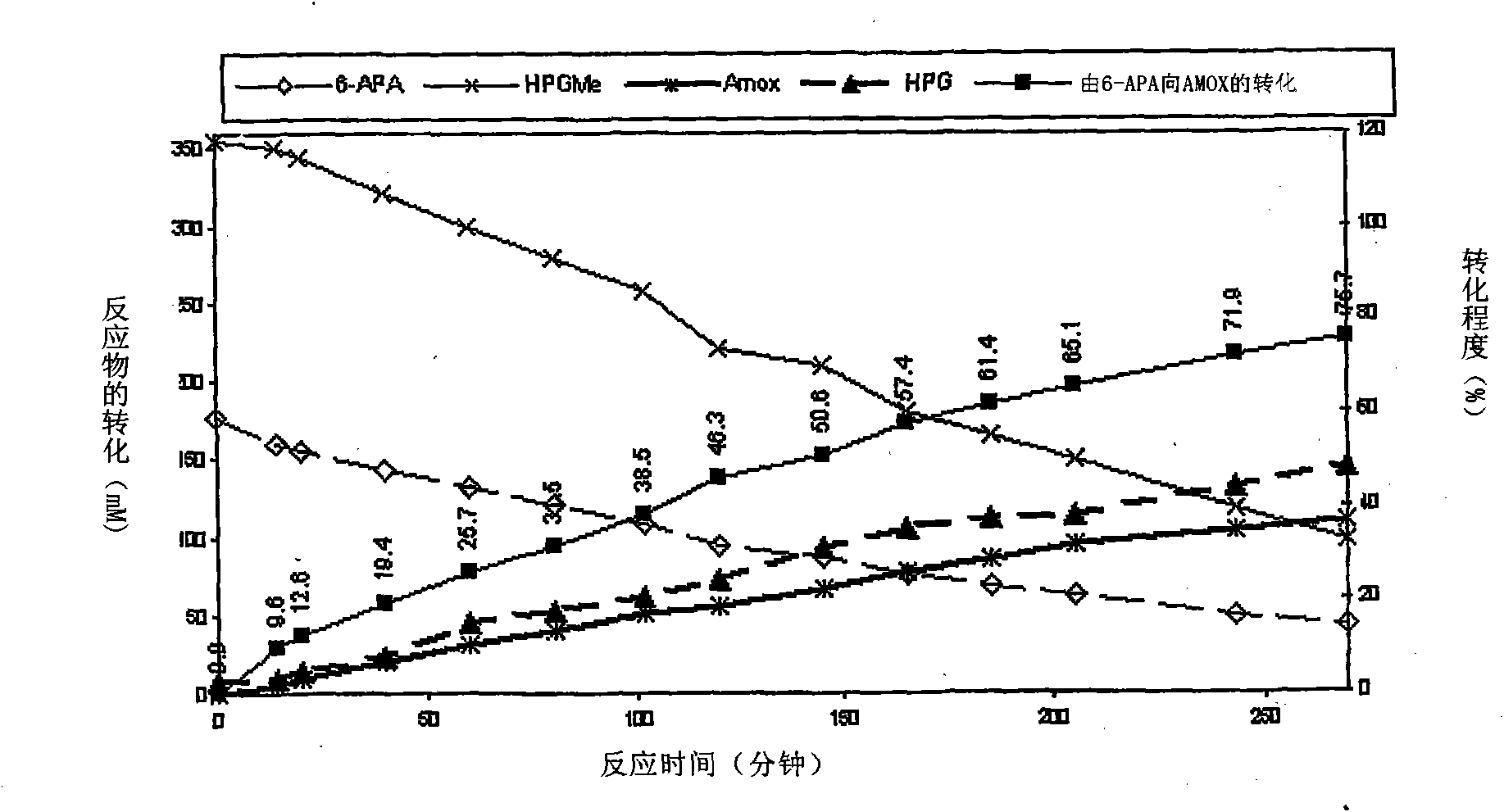
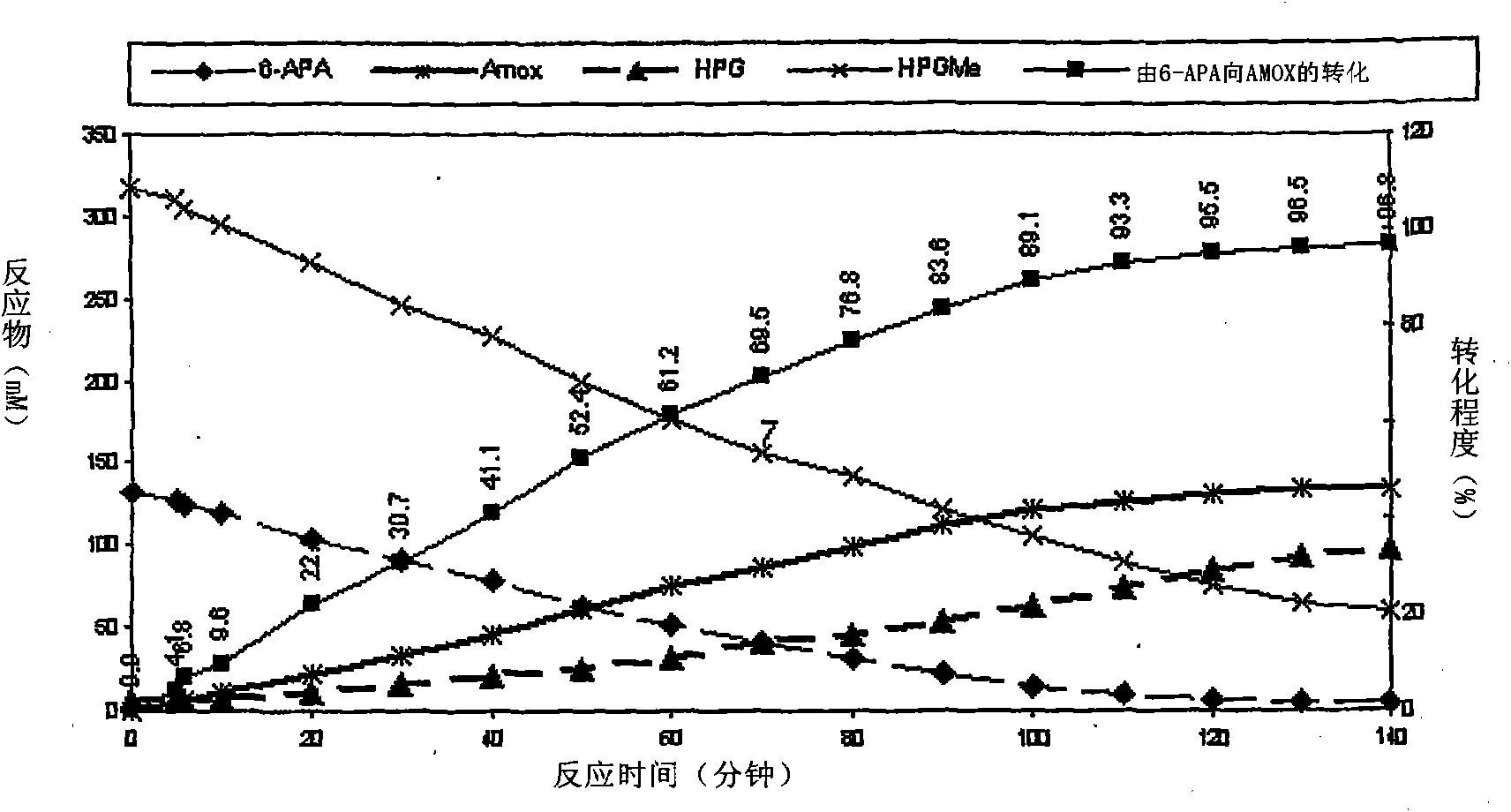
Process for the preparation of immobilized recombinant penicillin acylase catalyst from Achromobacter sp. CCM 4824 expressed in E. coli BL 21 CCM 7394 and its use for the synthesis of beta-lactam antibiotics
A BL21CCM7394, penicillin acylase biological technology, applied in the field of penicillin acylase, can solve the problems of increasing time and cost, hindering the use, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0122] Disintegration of cells under high pressure homogenization
[0123] Escherichia coli BL21CCM7394 was obtained from the culture medium by centrifugation as a cytoplasm (volume centrifuge) or as a cell suspension (alpha centrifuge) with the activity of the penicillin acylase obtained from Achromobacter sp. CCM4824. The microorganisms obtained were suspended in 0.02M sodium phosphate to give 5% (cdw / v), the pH of the suspension was adjusted to 7 and kept constant with 20% w / v sodium hydroxide. The cell suspension (2350ml, 4.9% cdw / v, AHPenGof 86.5U / ml) cooled to 8-13°C started to rupture. (uniform, pressure 40-50MPA, three consecutive cycles). After each cycle, the temperature of the homogeneous cell solution was lowered to 8-13 °C and the pH was adjusted to 7.0. Cellular debris and a small fraction of protein debris were removed by thermal coagulation, which involved adjusting the pH to 5.0 with 50% acetic acid, adding Sedipur CL 930 flocculant (2-4 g / L) and maintaining...
Embodiment 2
[0125] A. Extraction of Enzymes by Mild Chemical Extraction
[0126] In another specific embodiment of the invention, the cell suspension (1050ml, 5% cdw / v, AHpenG 10.2U / ml) was diluted with 0.1M sodium phosphate buffer (pH7.5) at 20°C. Gentle chemical lysis is performed in a three-necked glass reactor with pH electrodes, temperature probes and variable stirring devices. After adjusting the pH to 7.0 with dilute ammonia solution, the temperature reached 28°C. To dilute the biomass, 1% solvents such as toluene, ethyl acetate, chloroform, and butyl acetate were added to the initial cell lysis reaction, and the pH of the reaction was monitored at constant temperature. Samples were taken periodically to assess the extent of cell lysis. The reaction was continued for 2 hours at pH 7.0 and 28°C. The degree of lysis due to solubility was determined by analyzing the sample surface for AHpenG and compared to the initial activity of the cell suspension (% cell lysis, Table 1).
[01...
Embodiment 3
[0140] Preparation of concentrated enzymes
[0141] Prepare 350 gm of cell slurry as in Example 1 and dilute with distilled water to a final concentration of 5% (cdw / v) at 20-25°C. The pH of the cell suspension was adjusted to 7.0 with 2% (v / v) glacial chloroform, and 0.2% (w / v) sodium lauryl sulfate was added to the initial lysis. Samples were drawn periodically during the total time period of 5 hours. The lysed material was stored at 5°C for 12 hours prior to the protein isolation process from the lysed cells. The temperature of the suspension was raised to 28-30°C and diluted 2-fold with distilled water. The pH was adjusted to 5.0 with 2M acetic acid. Acidic protein coagulum was separated from the suspension by adding 1% polyethyleneimine for one hour at 40°C. The flocs were separated from the solution in a centrifuge at 7000 rpm. The pH of the supernatant was adjusted to 7.5 with sodium tetrahydroxide solution, and the resulting solution was called soluble enzyme (SE)...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com