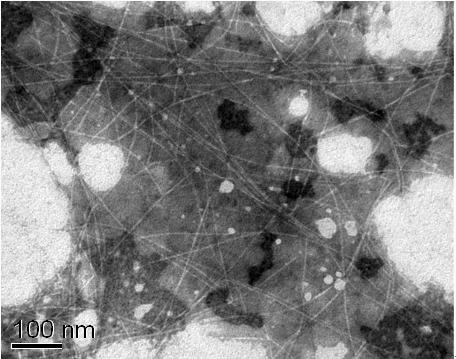
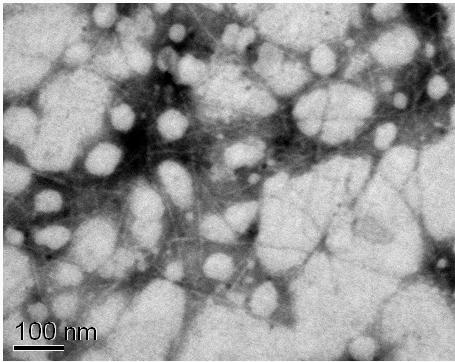
Preparation method of homogenized fine nano-cellulose fiber
A nanocellulose and homogenization technology, applied in the field of nanocellulose fiber preparation, can solve the problems of uneven distribution of biomass nanocellulose diameter, narrow application range of TEMPO catalytic oxidation method, easy aggregation of nanofibers, etc., to achieve The effect of uniform diameter size distribution and uniform dispersion
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
[0016] Specific implementation mode 1: The preparation method of the homogenized fine nano-cellulose fiber in this embodiment is carried out according to the following steps: 1. Weigh the biomass fiber and benzene alcohol solution according to the mass ratio of 1:50 to 100. Alcohol solution, and the biomass fiber was added to the benzyl alcohol solution, and extracted at a temperature of 85°C to 95°C for 5h to 7h; 2. Prepare sodium chlorite with a concentration of 1% to 2% (mass) solution, and adjust its pH value to 4-5 with glacial acetic acid, then add the biomass fiber treated in step 1 into the sodium chlorite solution for 4h-6h, during which the sodium chlorite solution is added every 0.9-1.1h Add sodium chlorite and glacial acetic acid in the middle, be 1%~2% (quality), pH value to be 4~5 to keep the concentration of sodium chlorite in the sodium chlorite solution; Biomass fiber is added to the alkali solution with a concentration of 1% to 3% (mass), mixed evenly, and ke...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0019] Specific embodiment 2: The difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment 1 is that the biomass fiber in step 1 is wood flour with a particle size of 50-70 mesh, bamboo powder with 50-70 mesh, and crop straw fiber with 50-70 mesh. 50-70 mesh hemp fiber, 50-70 mesh cotton fiber, 50-70 mesh pulp fiber or 50-70 mesh microcrystalline cellulose fiber. Other steps and parameters are the same as in the first embodiment.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0020] Specific embodiment three: the difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment one or two is: the drying method described in step seven is freeze drying, supercritical drying or critical point drying; wherein the step of freeze drying is: suspending the nanofiber The turbid liquid is frozen at -5°C~-20°C for 20h~24h, and then placed in a freeze dryer for freeze drying. The temperature of the cold trap of the freeze dryer is -55°C~-60°C. The vacuum degree is 15Pa~1Pa, and the freezing time is 20h~24h; supercritical drying method or critical point drying method is the existing conventional technology. Other steps and parameters are the same as those in Embodiment 1 or 2.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com