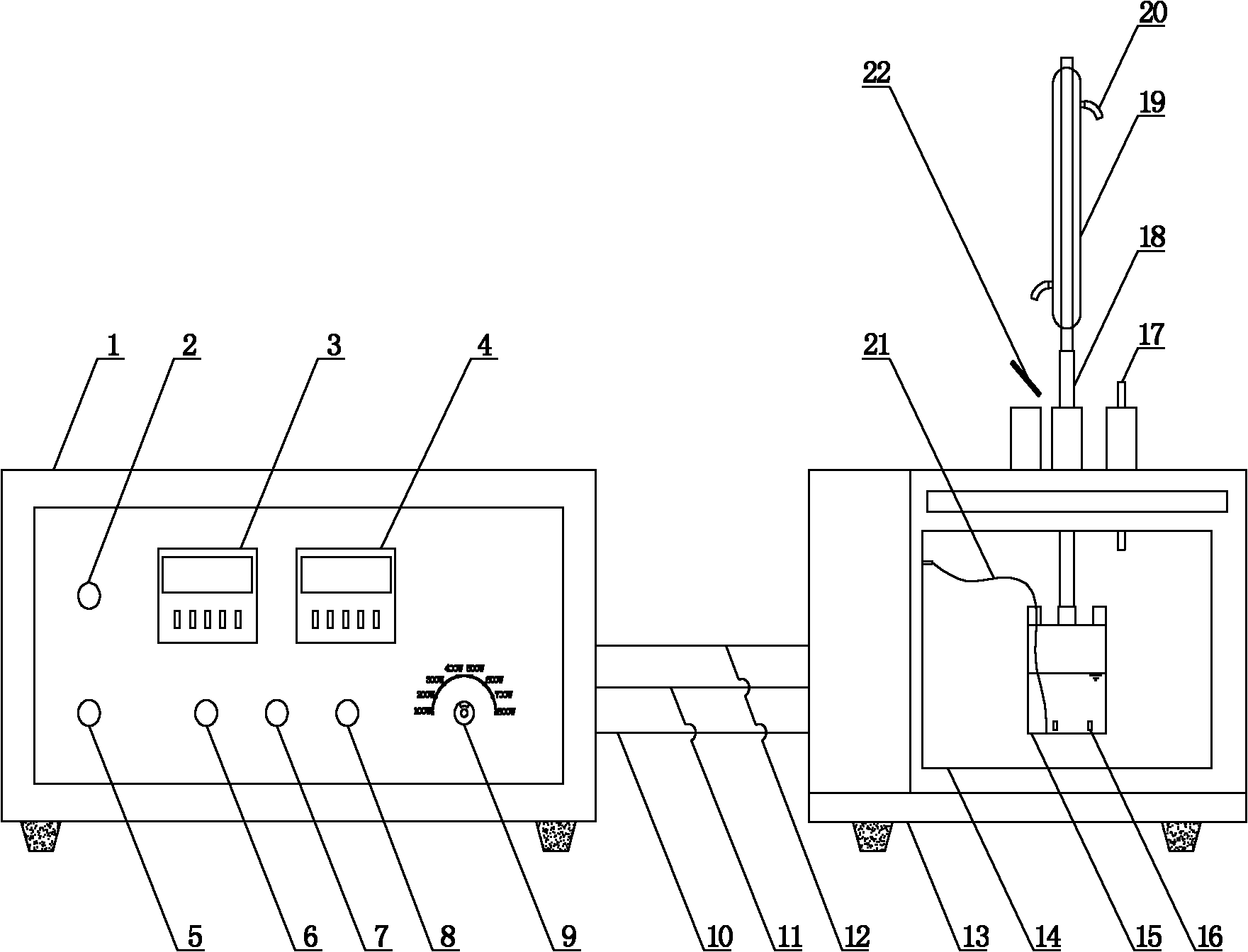
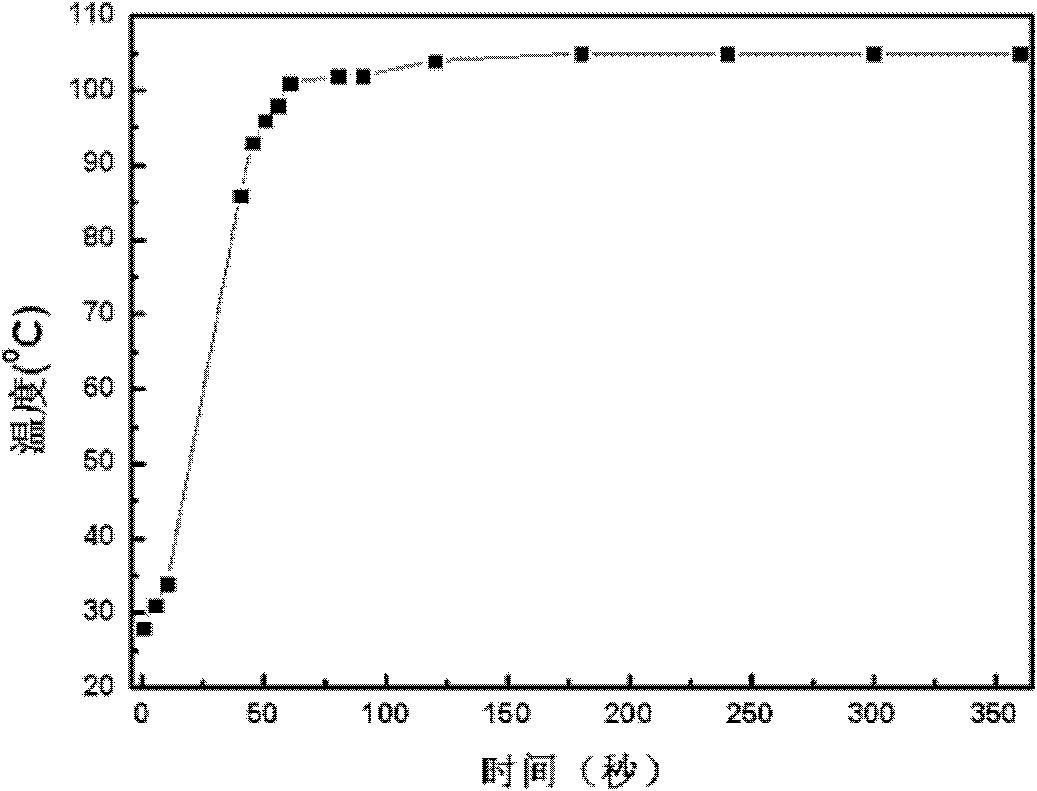
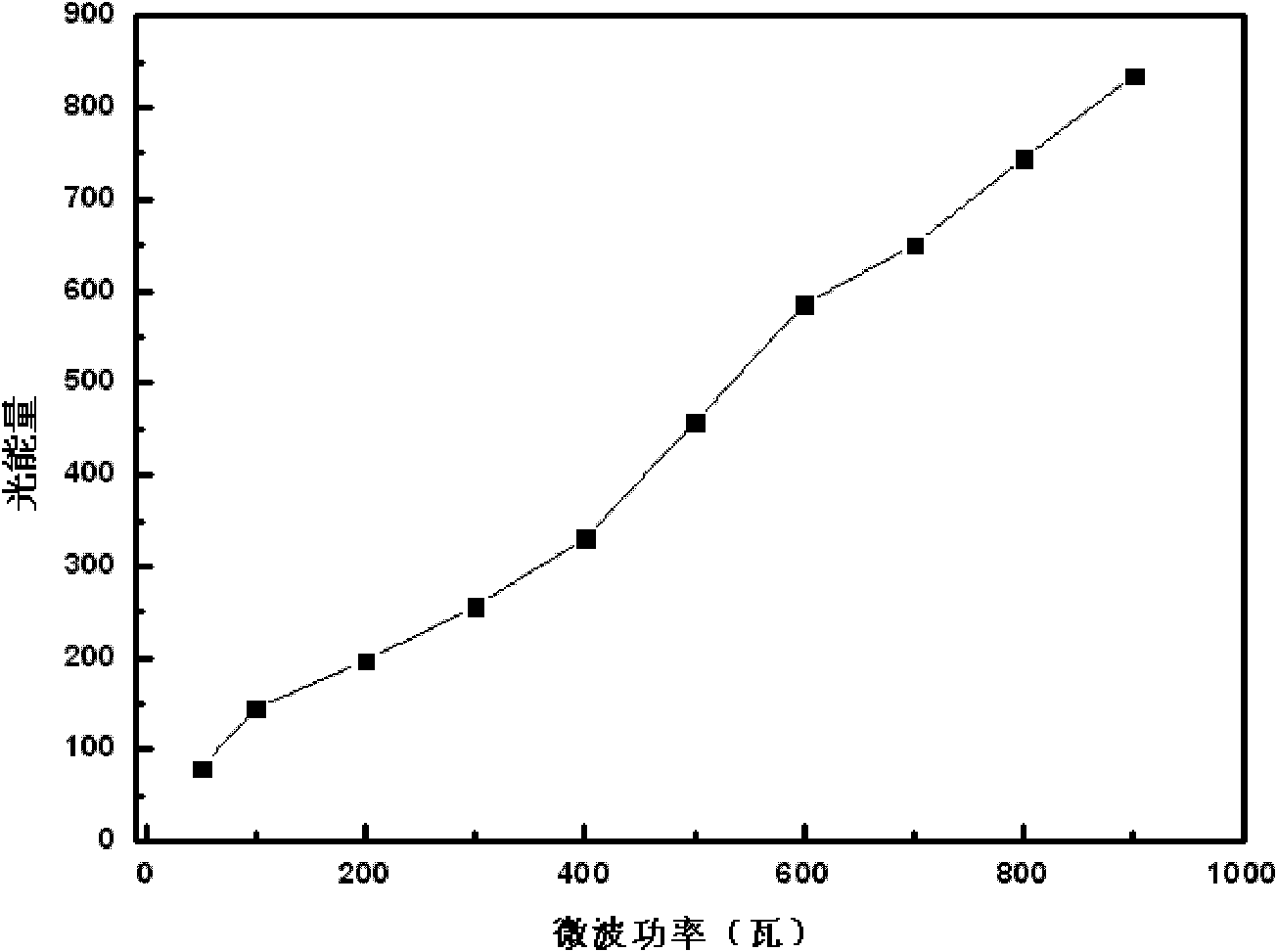
Method for efficiently removing typical triphenylmethane dye from water
A technology for triphenylmethane and water removal, which is applied in the field of triphenylmethane dye treatment in water, and can solve environmental problems, such as that a microwave reaction device cannot work for a long time and accurately measure the temperature of the reaction system and the emission spectrum of an electrodeless lamp.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0041] Example 1: Exploring the initial organic concentration for microwave radiation to excite electrodeless lamps to emit ultraviolet-visible light to initiate P25-TiO 2 The influence of photodegradation reaction is as follows: use microwave radiation to excite the electrodeless lamp to emit ultraviolet-visible light to initiate P25-TiO 2 (produced by degussa company) photodegradation method to process malachite green solution (its concentration is 20, 100, 150ppm respectively), the maximum volume is 250mL Pyrex glass reactor is placed inside the microwave oven reactor, microwave input power 800W, use 2 EDL -2 ), water sample volume V=50mL, P25-TiO 2 When the catalyst dosage is C=1g / L and the reaction time t=5min, the decolorization rate of malachite green solution has obvious difference.
[0042] Figure 5 It shows that as the concentration of the reaction solution increases, the microwave-excited electrodeless lamp emits ultraviolet-visible light to initiate the P25-TiO 2...
Embodiment 2
[0043] Example 2: Exploring the solution volume for microwave radiation to excite electrodeless lamps to emit ultraviolet-visible light to initiate P25-TiO 2 The effect of photodegradation is as follows: use microwave radiation to excite the electrodeless lamp to emit ultraviolet-visible light to initiate P25-TiO 2 Photochemical degradation method is used to process malachite green solution (concentration is 150ppm), the maximum volume is 250mL. -2 ), P25-TiO 2 The catalyst dosage is 1g / L, the solution volumes are V=50, 75, 100ml respectively, and the reaction time t=5min, the decolorization rate of malachite green solution has obvious difference.
[0044] Image 6 It shows that as the volume of the reaction solution increases, the decolorization rate of MG decreases significantly after 5 minutes of degradation. The MG solution of 150ppm of 50ml, the decolorization rate of 5min is 81.4% (the same as above); The MG solution of 150ppm of 75ml, the decolorization rate of 5min ...
Embodiment 3
[0045] Example 3: Exploring the number of electrodeless lamps for microwave radiation to excite electrodeless lamps to emit ultraviolet-visible light to induce P25-TiO 2 The influence of photocatalytic reaction is as follows: use microwave radiation to excite electrodeless lamp to emit ultraviolet-visible light to initiate P25-TiO 2 Photochemical degradation method is used to process malachite green solution (concentration is 150ppm), the maximum volume is 250mL. 2 The catalyst dosage is C=1g / L, the solution volume V=50ml, and 1 to 4 electrodeless lamps (denoted as: EDL -1 , EDL -2 , EDL -3 , EDL -4 ), under the situation of reaction time 5min, the decolorization rate of malachite green solution has obvious difference.
[0046] Figure 7 It shows that: increasing the number of electrodeless lamps, the decolorization rate of MG is obviously increased. After 5min decolorization reaction, EDL -4 The decolorization rate basically reaches 98%; EDL -3 The decolorization rate...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com