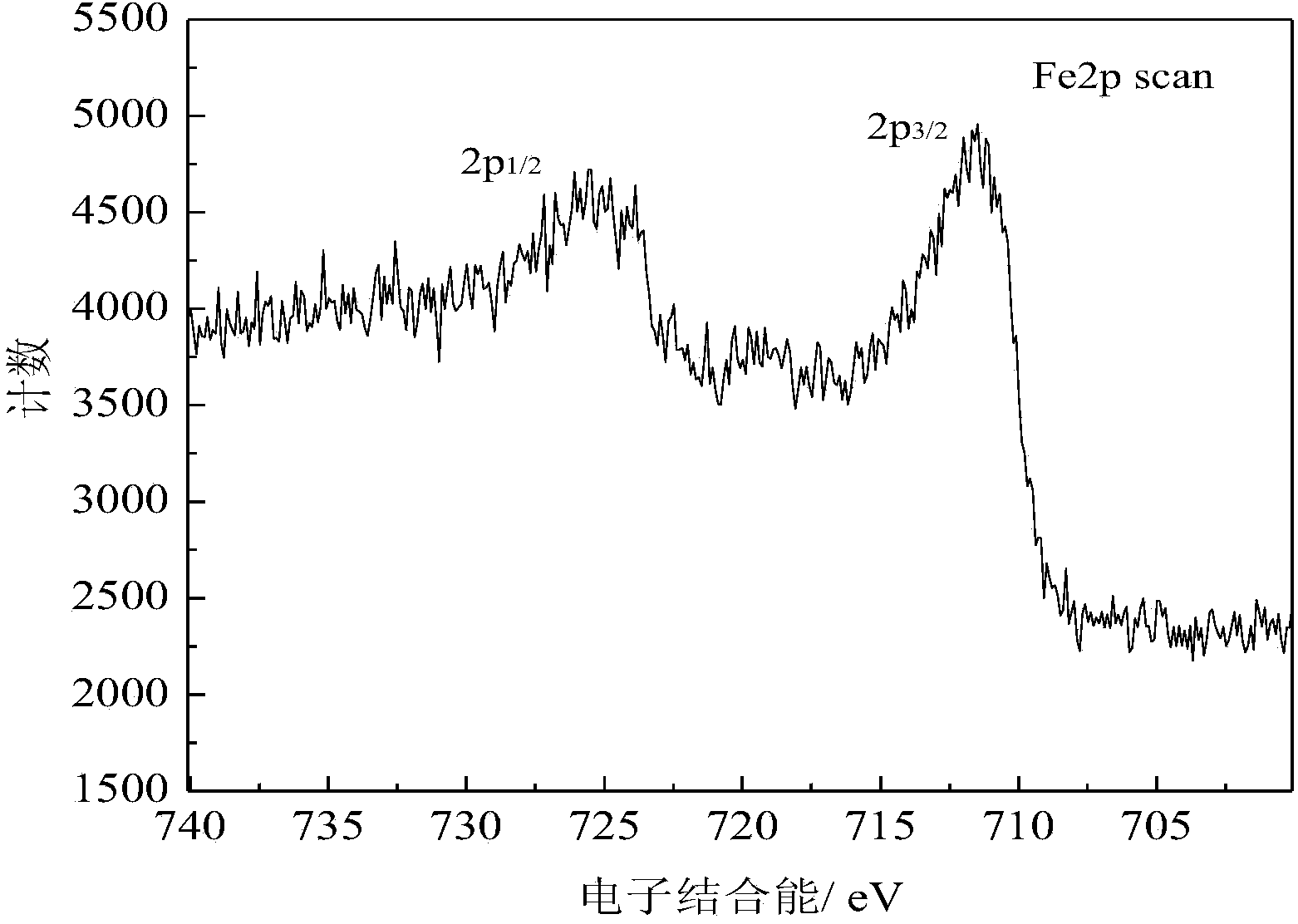
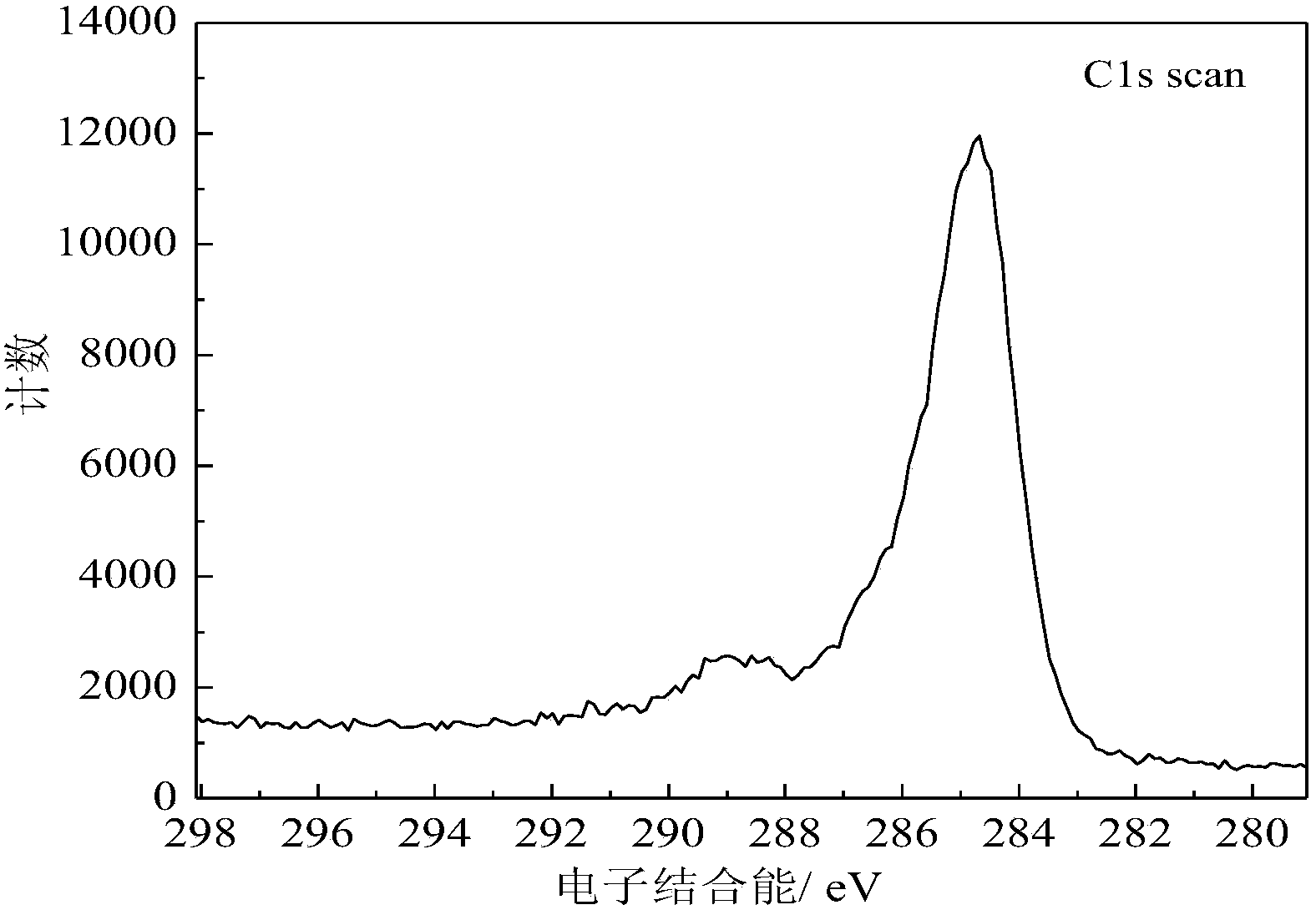
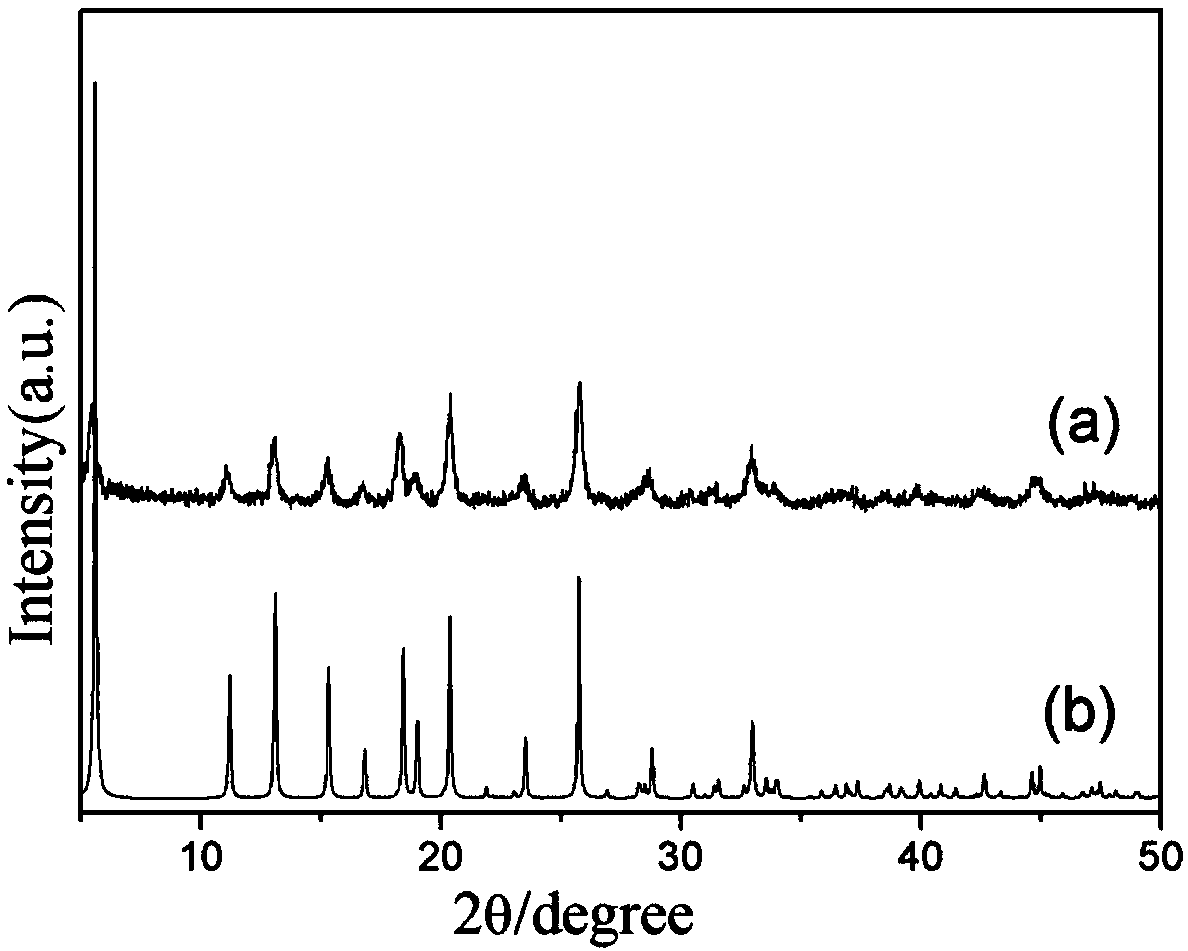
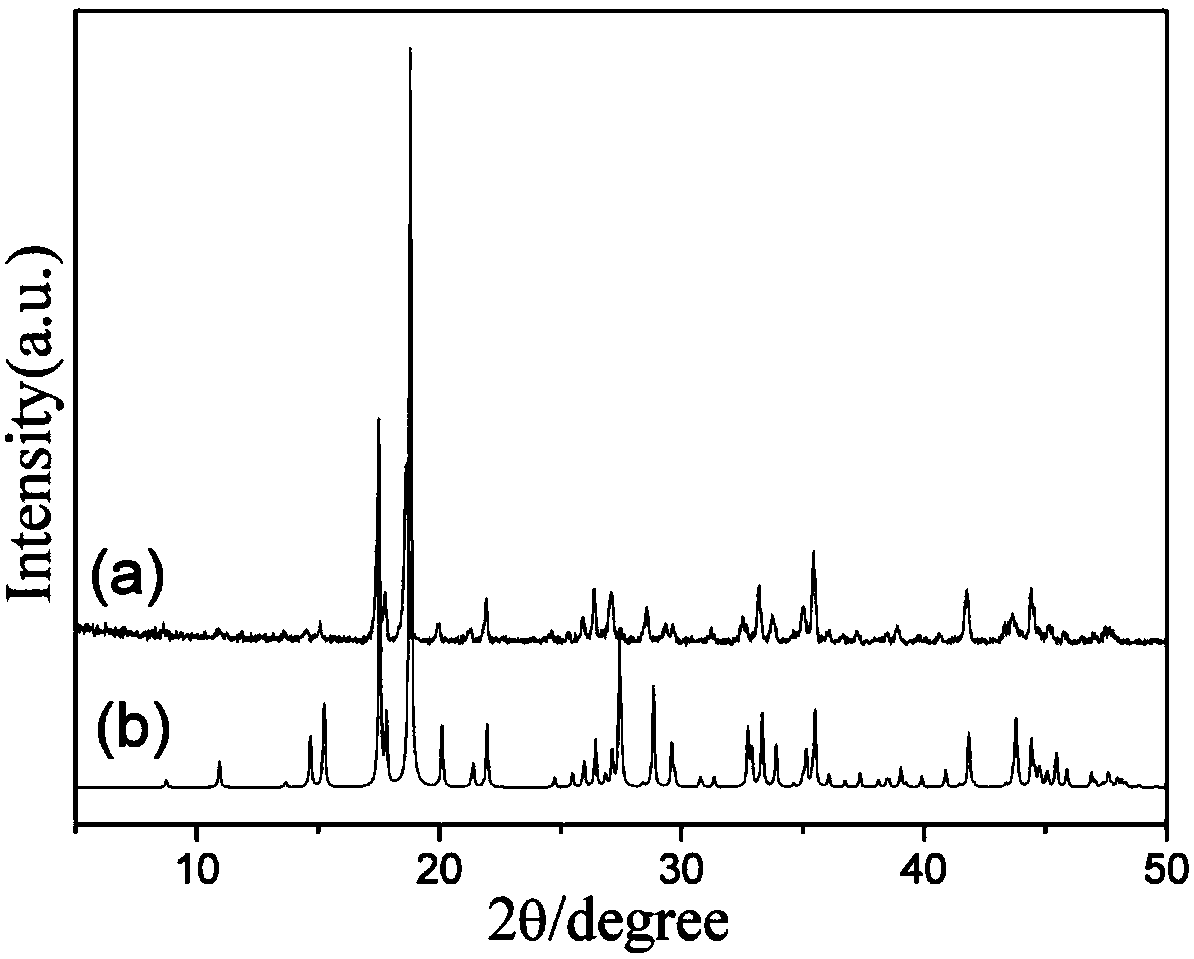
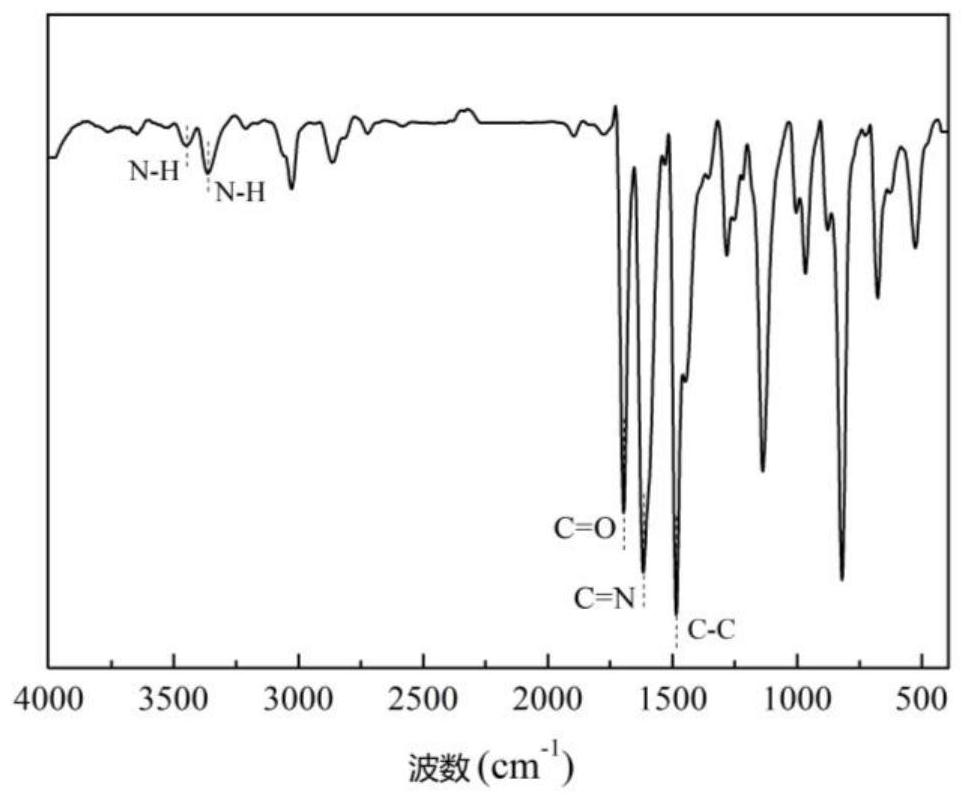
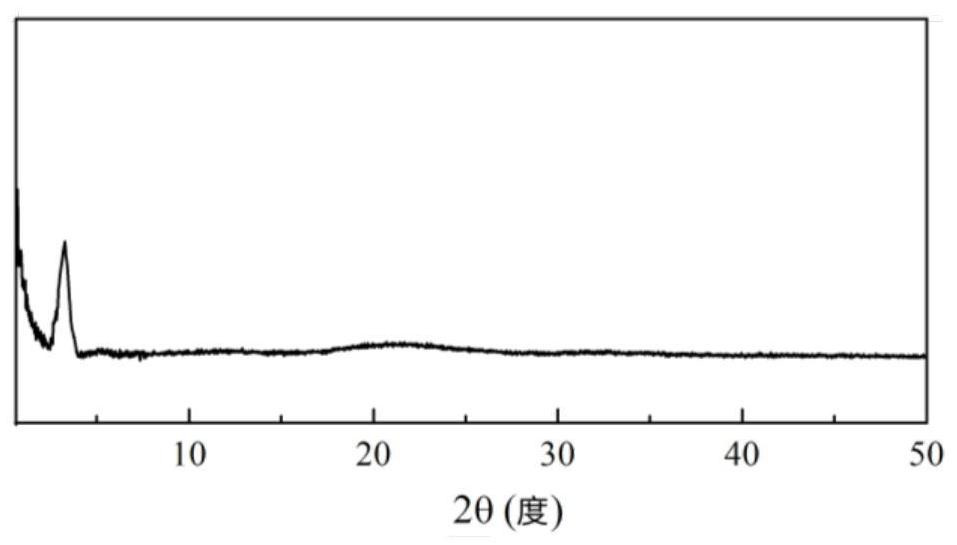
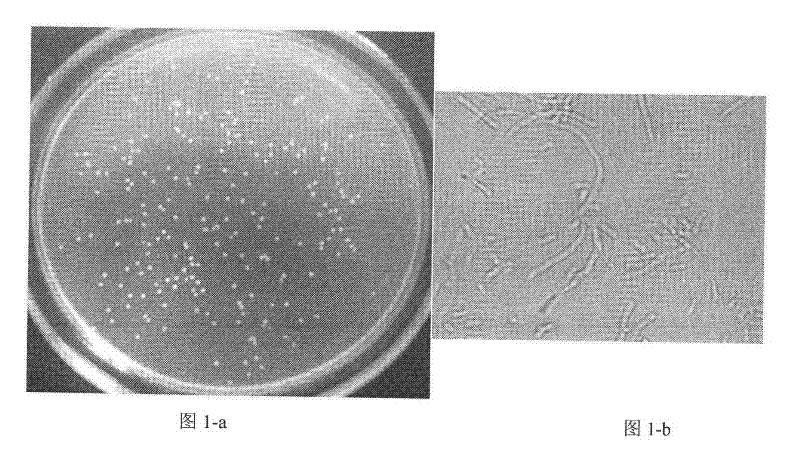
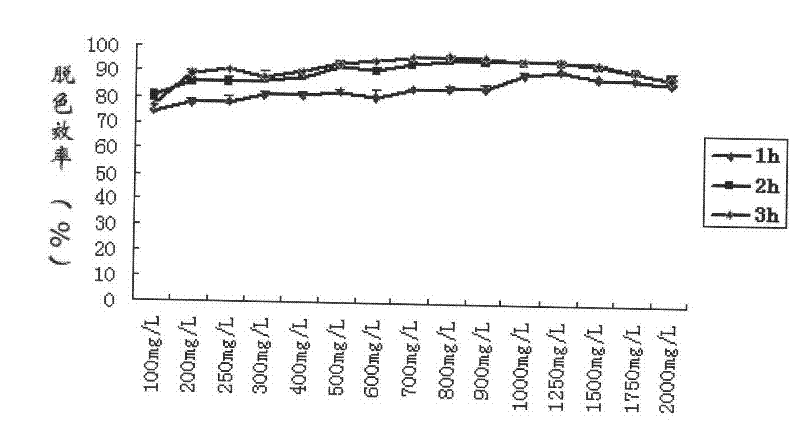
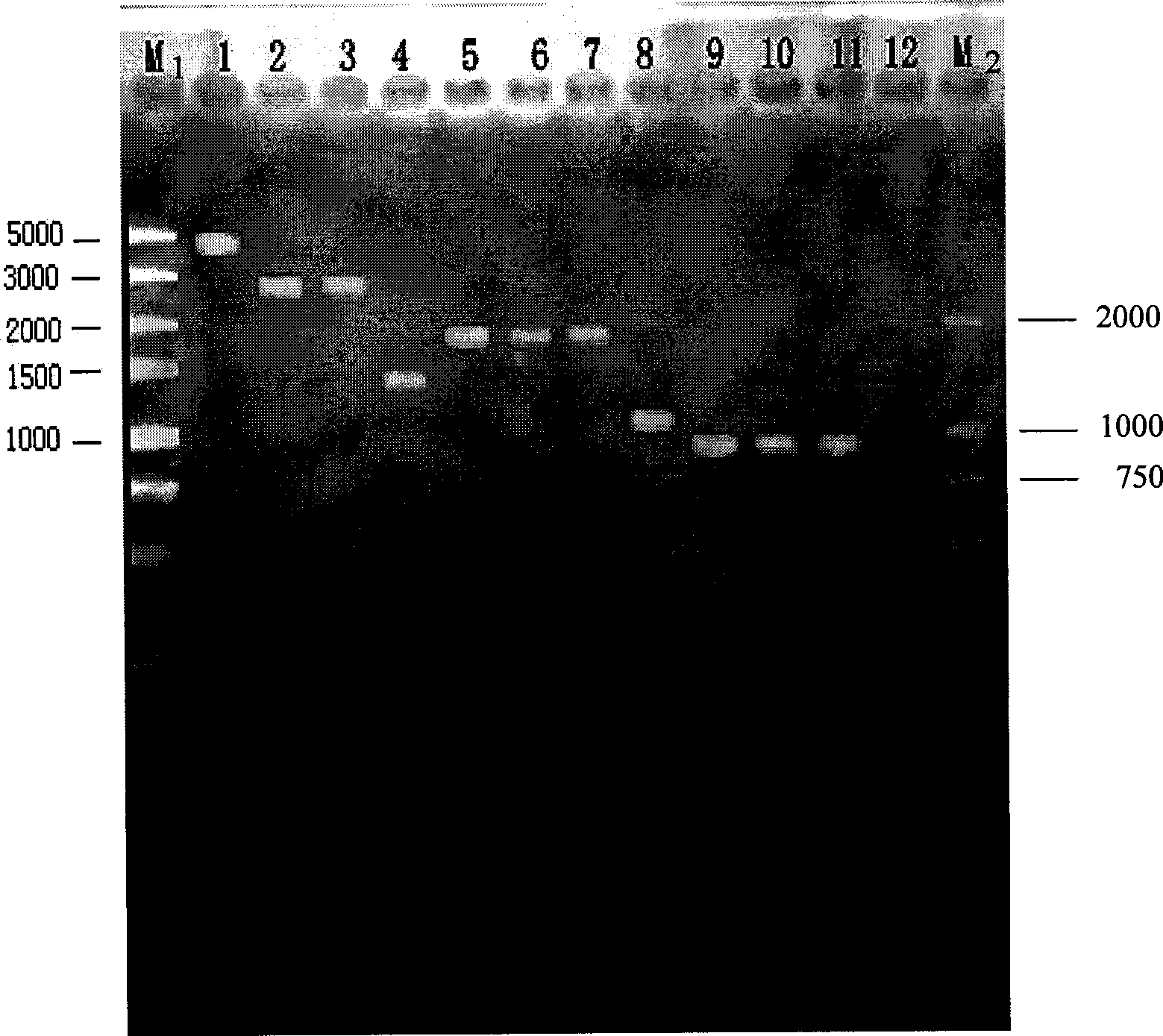
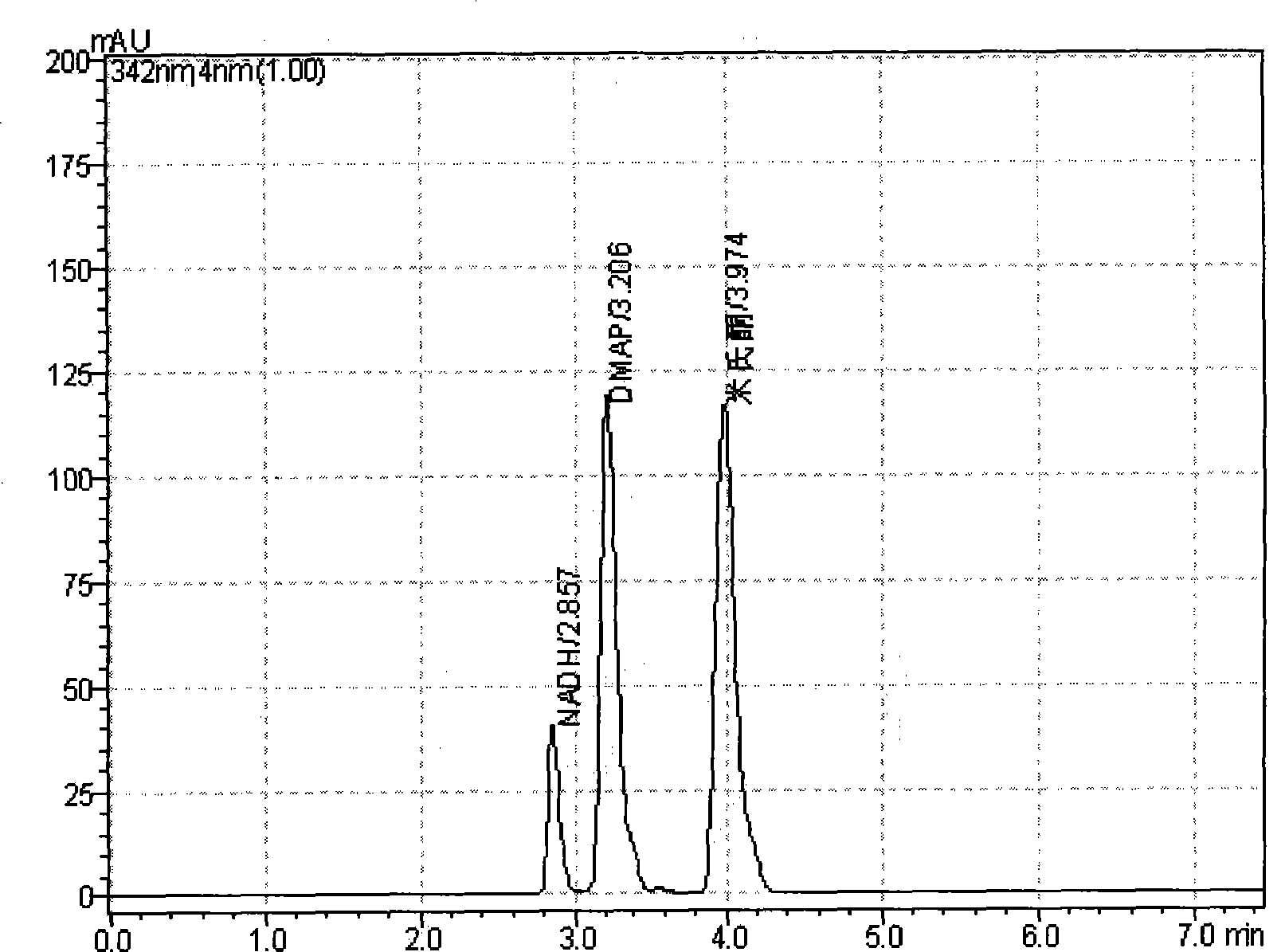
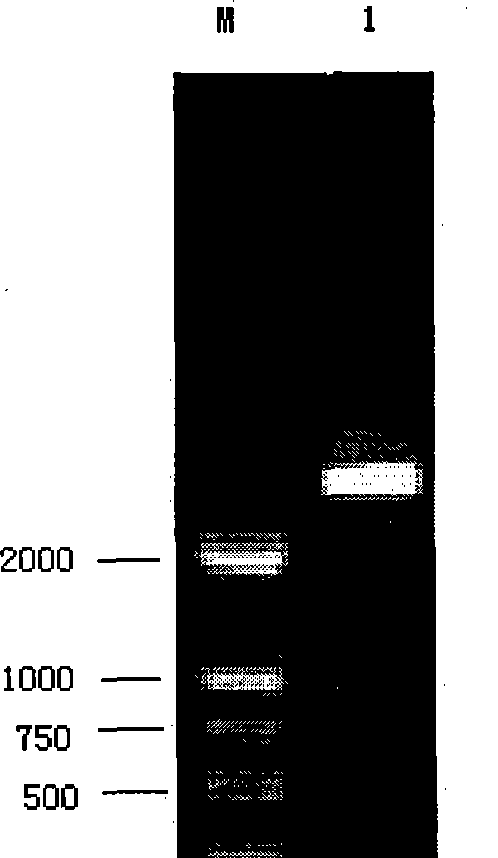
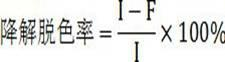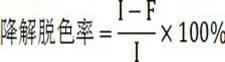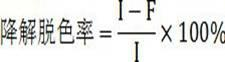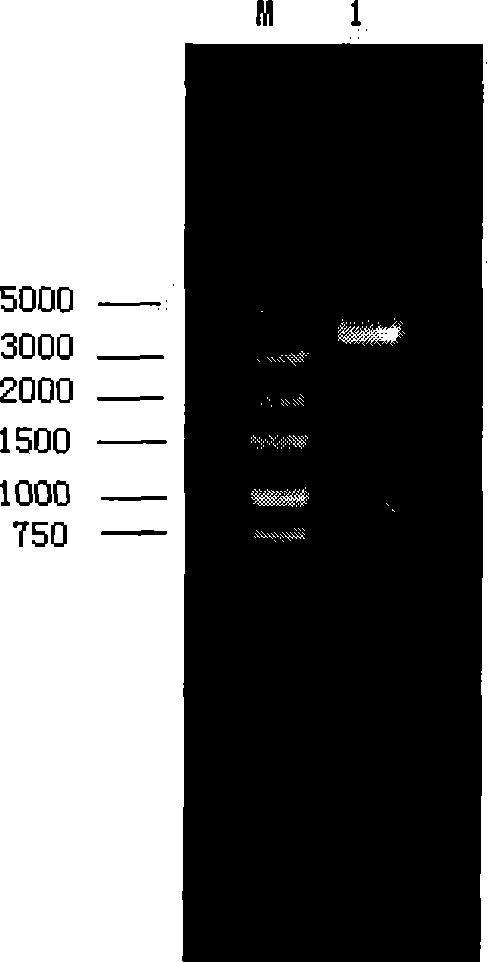Patents
Literature
80 results about "Triphenylmethane dye" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
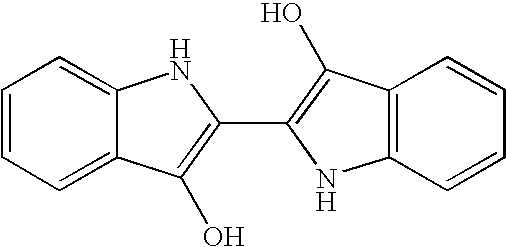
Triphenylmethane dye, any member of a group of extremely brilliant and intensely coloured synthetic organic dyes having molecular structures based upon that of the hydrocarbon triphenylmethane.
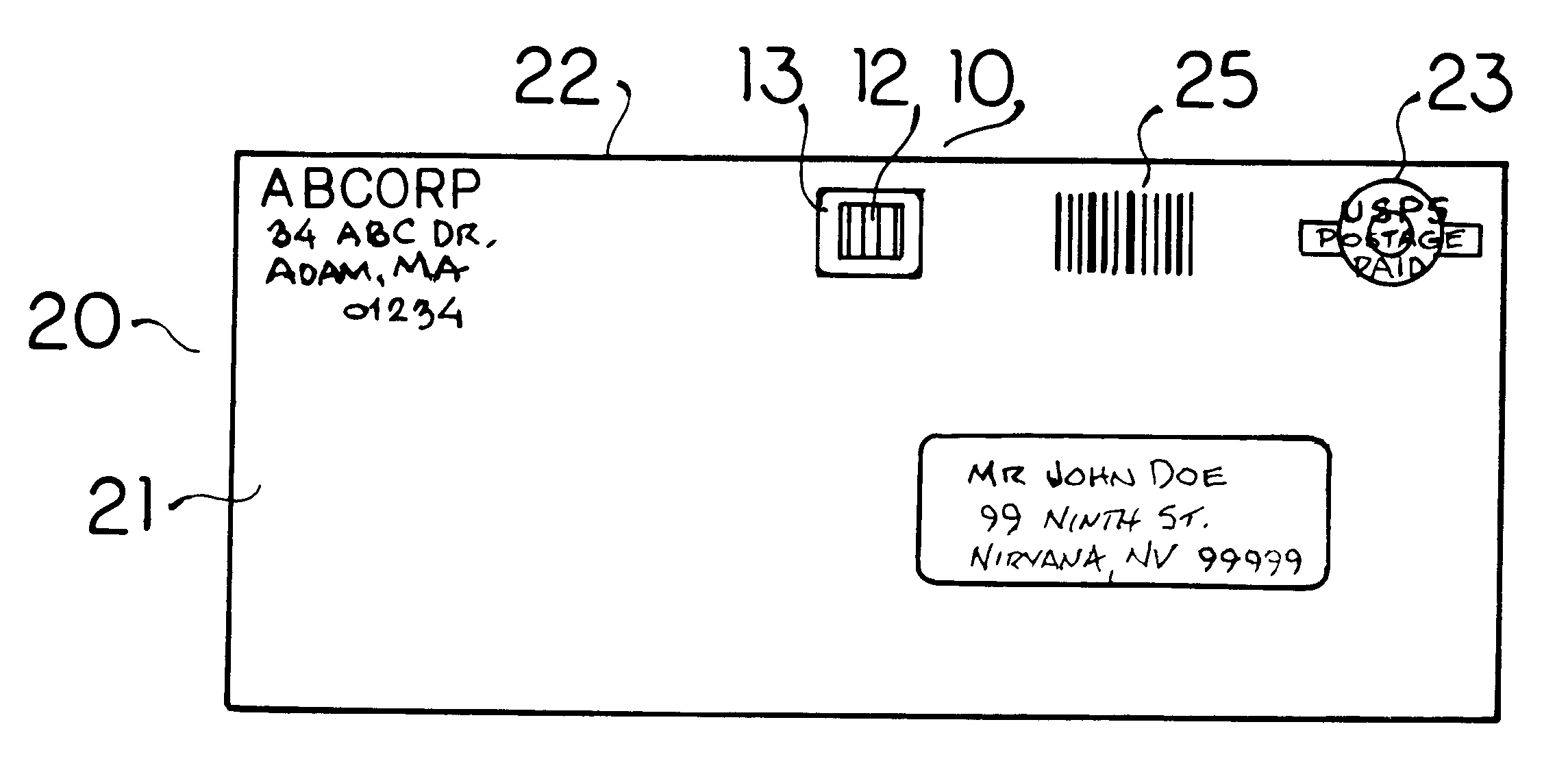
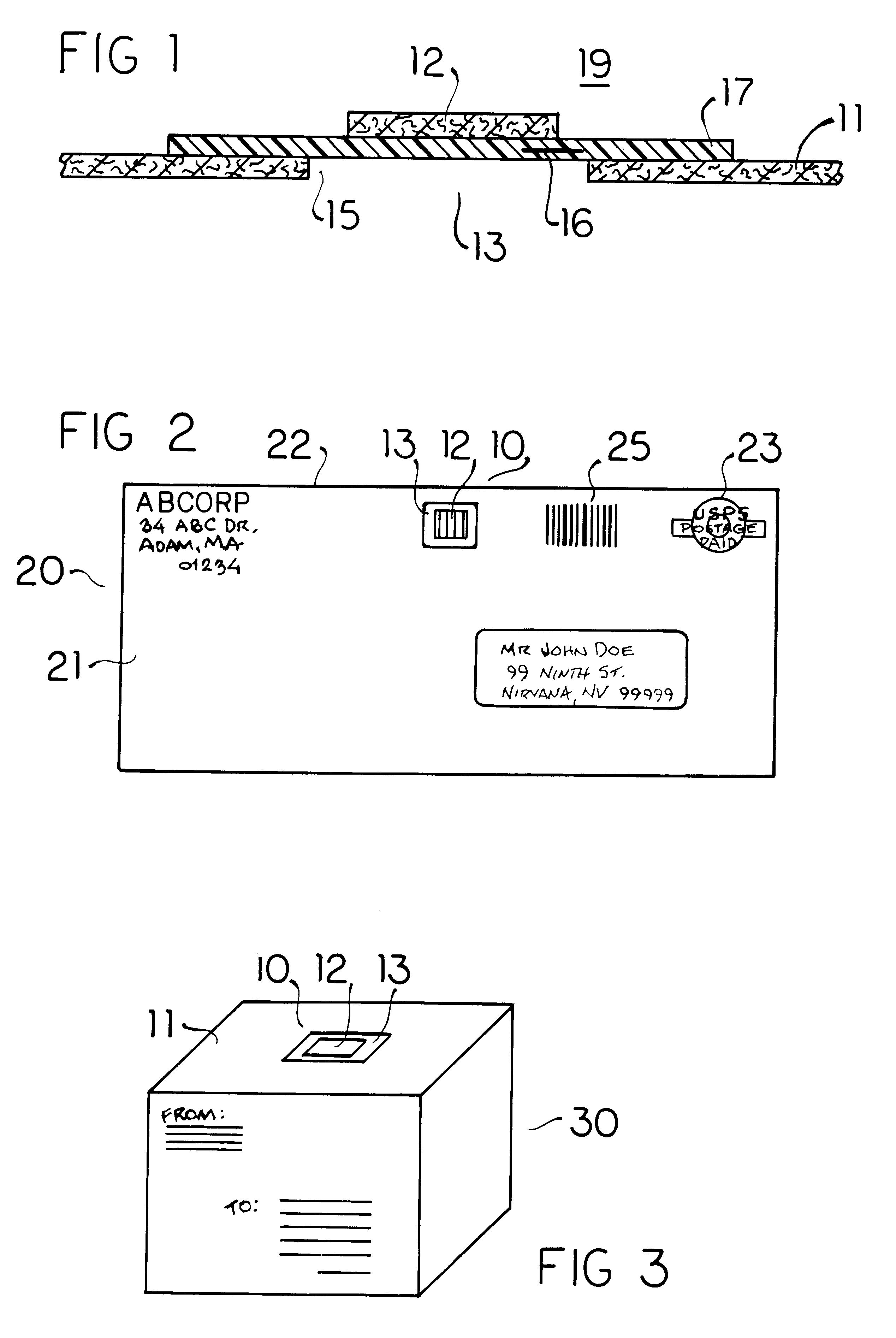
Biological toxin detection system for mailed materials
InactiveUS6524846B1Easy to manufactureReadily adheres to paperBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsPorous substrateQuarantine
Envelopes and other containers intended for mail transportation possess a biological agent / toxin indicator operative upon the interior in detection of volatile bases including gaseous amines released from bacterial biological agents including Bacillus antracis, i.e. anthrax. The biological agent indicator has an acidic acid-base indicator compound that irreversibly changes color when neutralized by volatile bases. The compound is applied in liquid form to an appropriately porous substrate. A polymeric matrix is specifically suggested for this substrate. Irreversible indication of the presence of volatile bases including amines produced by live bacterial agents as toxins at temperate ambient conditions down to below freezing is provided. An indicator compound having a pH of 2-5 is recommended. Halogenated xanthene, sulphonated azo, and sulphonated hydroxy-functional triphenylmethane dyes are suggested. The presence of toxins produced by live bacterial biological agents within a package or container upon which the indicator is mounted is indicated by a slowly reversible color change. Primary public use envelopes and collection containers, secondary transportation and stationary quarantine enclosures, and articles worn inside a room with mail and when handling mail including a badge and gloves are specifically suggested.
Owner:ROBINSON JR WILLIAM L
Method for rapid degradation of triphenylmethane dye waste water
InactiveCN101560027AStrong oxidation abilityImprove applicabilityWater contaminantsMultistage water/sewage treatmentExternal energyPollution
The invention discloses a method for rapid degradation of triphenylmethane dye waste water. The method firstly removes impurities by a grill, stands for precipitation and regulates pH, wherein, the pH value of the triphenylmethane dye waste water is controlled to be about 7-10; the waste water is introduced into a simple reaction container, then a mixture consisting of sodium bismuthate and silver nitrate is added, the multi-phase uniform mixing reaction is kept under the action of stirring, the temperature of the dye waste water during the process is kept at room temperature, the pressure is normal pressure, and the waste water is discharged. The treatment method can high-efficiently degrade triphenylmethane dye which is typically difficult to biodegrade, the catalytic reaction can be realized without the use of any light source or other external energy, such as microwave and the like, and the treatment method has very low requirements on equipment, less energy consumption, low operation cost, convenient operation and no secondary pollution, thereby being the method which can realize the degradation at the room temperature.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Printing and dyeing wastewater adsorbent and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN102211015AImprove adsorption capacityRaw materials are readily availableOther chemical processesWater/sewage treatment by sorptionPhthalocyanine dyeStrong acids
The invention discloses a printing and dyeing wastewater adsorbent, which is characterized by being a cyclodextrin functionalized graphene nanomaterial. A preparation method comprises the following steps of: treating graphite powder with strong acid and a strong oxidizer, and performing ultrasonic exfoliation to obtain graphene oxide; and adding cyclodextrin, and reducing to obtain the cyclodextrin functionalized graphene. The adsorbent is used for treating printing and dyeing wastewater, and the removal rate of dyes in the printing and dyeing wastewater is over 96 percent. The adsorbent has the advantages of readily available raw materials, low cost and simple process, and is suitable for treating the printing and dyeing wastewater generated by azo dyes, active dyes, a triphenylmethane dye, a phthalocyanine dye or an anthraquinone dye, and also can be used for treating aromatic organic chemical wastewater.
Owner:SHANXI UNIV
Curable composition and curable mortar composition
The invention is accomplished with a curable composition, which contains a resin component A with a subsidiary component a, a resin, which can be polymerized by free radicals, and a curing agent component B with a subsidiary component b, a peroxide curing agent. Before use of the curable composition, the components A and B are kept spatially separated and curing takes place only after components A and B have been mixed. To improve such curable compositions, it is proposed that a subsidiary component c, the leuco form of a dye, especially of a triphenylmethane dye, be added to component A. By following such a procedure, it is achieved that the peroxide activity and the progress of the mixing are monitored simultaneously without delaying the curing of the composition.
Owner:HILTI AG
Triphenylmethane polymeric colorant having sterically hindered amine counter ion
Novel triphenylmethane dyes or colorants with sterically hindered fugitive amine counter ions are provided as durable, storage-stable, and excellent coloring and shading printing inks. Ink compositions are disclosed which provide improvements in long-term storage capabilities, particularly within alkaline environments, extremely effective colorations of cellulose-based substrates, and lower cost over those of the prior art. The preferred dyes or colorants are triphenylmethane polymeric colorants which are capped with cyclic anhydride and the preferred sterically hindered amine counter ions are those based on low molecular weight fugitive tertiary amines, such as N,N-dimethylethanolamine. Compositions comprising water soluble or emulsion resins as diluents for lowered viscosity and lower overall cost are also contemplated. Furthermore, compositions comprising the inventive colorant and other pigments, dyes, surfactants, preservatives, and other colorants are contemplated. A method of making such an inventive ink composition and a cellulose-based substrate contacted with such an inventive ink composition are also disclosed.
Owner:MILLIKEN & CO
Cyclodextrin supramolecular polymer/Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticle complex
InactiveCN106853363AImprove adsorption capacityEasy to prepareOther chemical processesWater contaminantsMalachite green stainX-ray
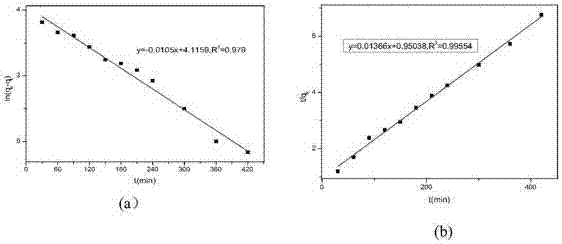
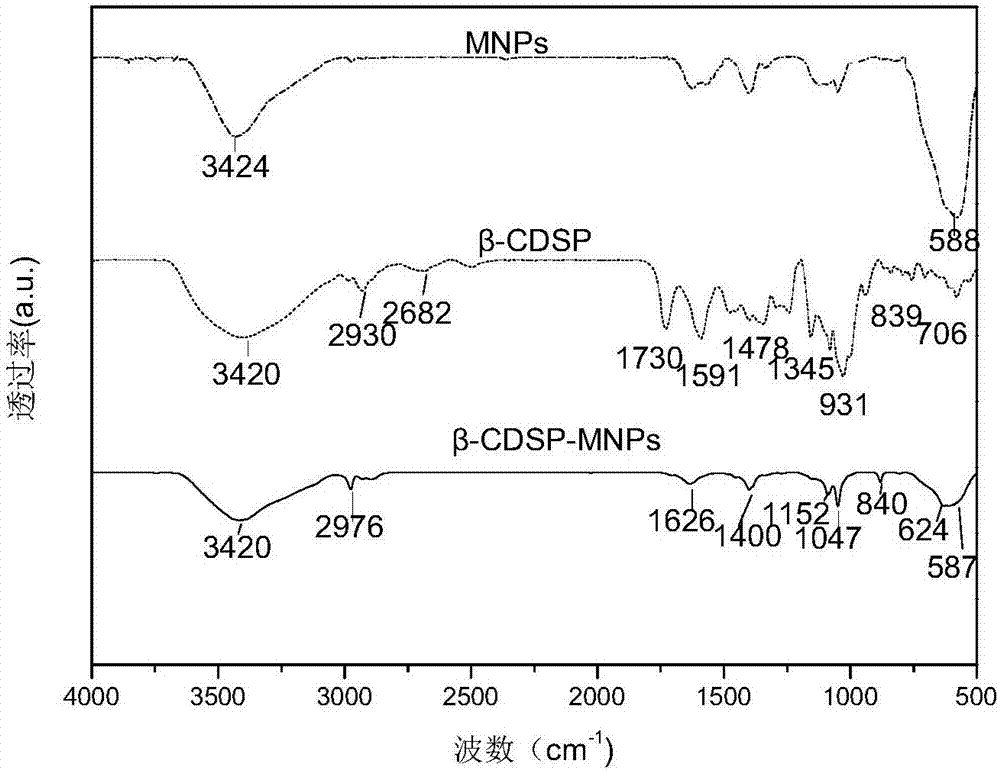
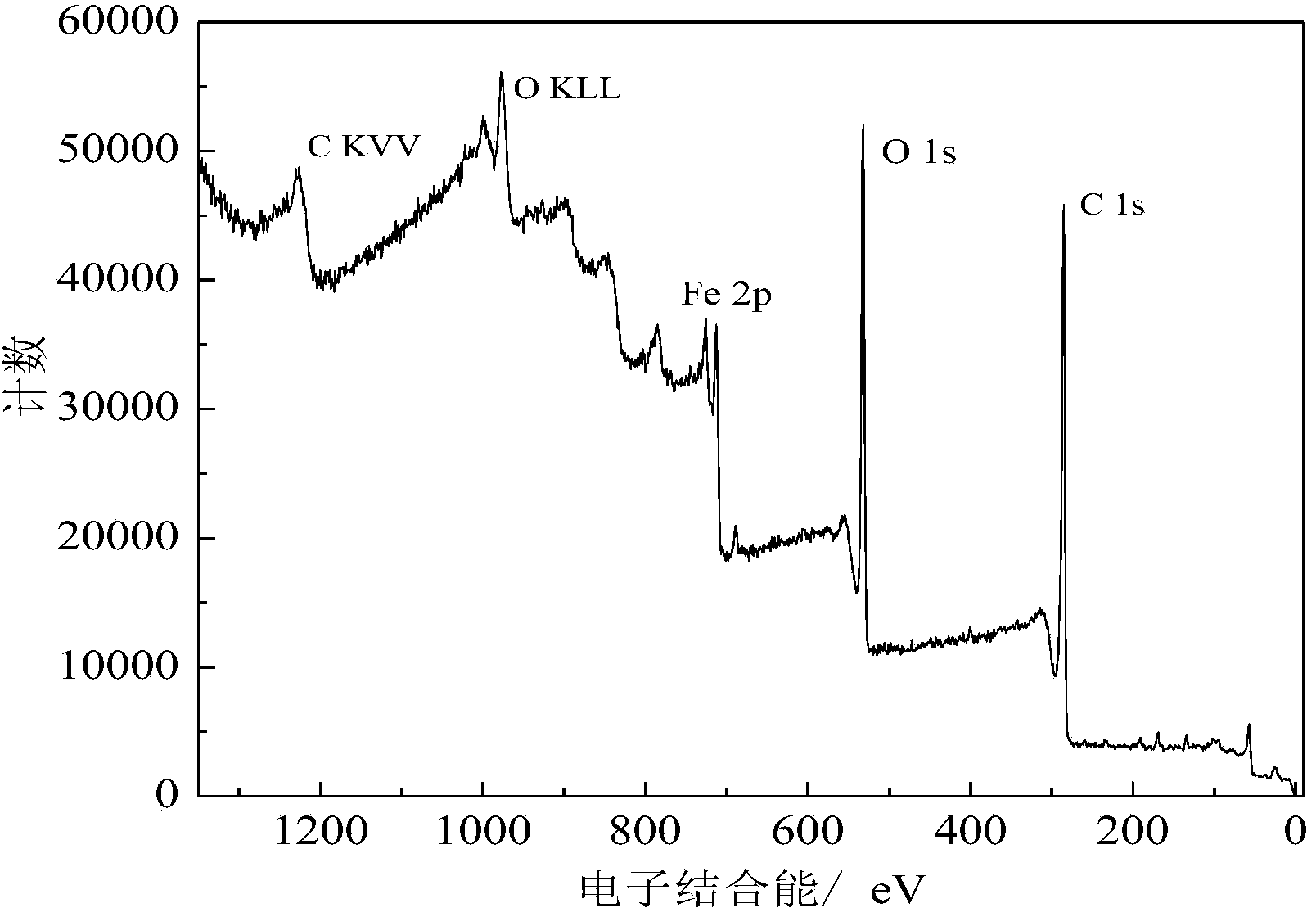
The invention provides a cyclodextrin supramolecular polymer / Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticle complex. The complex is prepared by the following steps: firstly, crosslinking beta-cyclodextrin with pyromellitic dianhydride to synthesize a cyclodextrin supramolecular polymer (beta-CDSP); coprecipitating the beta-CDSP and FeCl3.6H2O and FeCl2.4H2O under an alkaline condition by a one-pot method, so as to obtain the complex. An X-ray diffraction (XRD) method, a transmission electron microscope (TEM) method, a Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) method and a thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) method are applied for characterizing to verify that the beta-CDSP is grafted to Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles. The complex has the advantages of low synthesis cost, environment friendliness, no toxicity, abundant hydroxide radicals, free carboxyl and better magnetic properties, and can be used as an adsorption material for adsorption cation type triphenylmethane dye pollutants; malachite green serves as a model molecule for study on adsorption properties, and results show that the complex has a good adsorption effect on the malachite green and has a potential application prospect on the aspect of the adsorption material of environmental pollutants.
Owner:SHANXI UNIV
Iron ion loaded activated carbon fiber composite cathode, preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN104386784APrevent the occurrenceNo secondary pollutionWater treatment compoundsWater contaminantsFiberSludge
The invention relates to an iron ion loaded activated carbon fiber composite cathode, a preparation method and application thereof. The composite cathode includes iron ion loaded activated carbon fiber. The iron ion loaded activated carbon fiber composite cathode is applied to treatment of humic acid-containing wastewater and triphenylmethane dyes in printing and dyeing wastewater by an Electro-Fenton technique. The method for preparation of the iron ion loaded activated carbon fiber composite cathode includes an inner layer adsorption process and a precipitation process. Iron ions are loaded on activated carbon fiber, the treatment process is simplified, production of sludge is completely eradicated, and no secondary pollution exists; the iron ions loaded on the activated carbon fiber can react with H2O2 generated by electroreduction of dissolved oxygen on the composite cathode surface, thus reinforcing reaction on the composite cathode surface and strengthening the reaction efficiency; iron ions and acidic groups on the surface of the activated carbon fiber undergo inner layer adsorption, so that the iron ions are not easy to fall off during use, and the life of the composite cathode is increased. After repeated use of the composite cathode 4 times, the decolorization rate of the target pollutant is still above 93%.
Owner:XI'AN UNIVERSITY OF ARCHITECTURE AND TECHNOLOGY
Preparation method of MOF (metal-organic framework)-derived cobalt/carbon nanocomposite
InactiveCN108176364AEasy to operateEasy to controlOther chemical processesWater contaminantsArgon atmosphereMetal-organic framework
The invention provides a preparation method of an MOF (metal-organic framework)-derived cobalt / carbon nanocomposite. The method comprises the following steps: dissolving biphenyl-4,4'-dicarboxylic acid or trimesic acid in an aqueous solution containing potassium hydroxide or sodium hydroxide, adding an aqueous solution of a soluble cobalt salt, performing mixing and stirring at room temperature for a reaction, and performing centrifugal washing and drying to obtain a cobalt-based MOF precursor; calcining the obtained precursor in a nitrogen or argon atmosphere to obtain the cobalt / carbon nanocomposite. The preparation method of the cobalt-based MOF precursor has the advantages of being operated at room temperature, saving energy, adopting water as a solvent and being environmentally friendly; the synthesized magnetic cobalt / carbon nanocomposite has excellent selective adsorption capacity on triphenylmethane dyes and can be separated simply and rapidly by means of the magnetism.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Environmentally friendly chromotropic paint with warning function and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN106905833ARealize monitoringEffective peracid-base changeAnti-corrosive paintsPolyurea/polyurethane coatingsEnvironmental resistanceTriphenylmethane
The invention provides an environmental friendly chromotropic paint with warning function and a preparation method thereof. The paint comprises the following components in parts by weight: 10-30 parts of a polyurethane resin material, 20-40 parts of ethanol, 0.01-0.03 parts of an antishrinking agent, and 0.03-2 parts of triphenylmethane dyes or fluorane dyes. The preparation method comprises the following steps: adding polyurethane resin in triphenylmethane dyes or fluorane dyes dissolved by absolute ethyl alcohol, thoroughly dissolving the materials for dissolution; adding the antishrinking agent into a mixed solution, and stirring the materials to obtain the product. The most important feature of the paint is that the paint can effectively warn the superacid or superbasic environment which is harmful to human health, can keep the air circulation of working environment in time, and takes active protective measurements. The paint has the advantages of simple formula, low cost and easy production with a large scale.
Owner:SHANXI UNIV
Aqueous degradable environment-friendly ink and decoloring agent thereof
InactiveCN102838900ASafe to useStable in natureChemical paints/ink removersInksSodium dithioniteOrganic solvent
The invention provides aqueous degradable environment-friendly ink for printing, a special decoloring agent and a preparation method of the ink. The degradable environment-friendly ink contains dye, wherein the dye is azo-dye or triphenylmethane dye, or macromolecular dye synthesized by one of azo-dye or triphenylmethane dye, and aqueous macromolecular material. The preparation method of the degradable environment-friendly ink comprises the steps of dispersing, grinding and filtering aqueous acrylic resin, dye, de-ionized water, an antifoaming agent, a flatting agent, surfactant and amine materials in a high-speed disperser and a sand mill in sequence. The special decoloring agent is sodium dithionite or 2Na2CO3.3H2O2. The ink has the advantages of environment friendliness, no harmfulness, good safety, stable performance and good printing effect. When waste papers is recycled, the ink can be decoloured quickly under the action of the matching decoloring agent, and therefore, the problems that organic solvent in the oily ink volatilizes, the waste paper is difficult to deink and sewage pollution is serious are solved.
Owner:SHANXI UNIV
Single dye type bright acidic copper plating additive and preparation method and application thereof
The invention discloses a single dye type bright acidic copper plating additive and a preparation method and application thereof. The additive is prepared from a polymeric phenazine dye, a triphenylmethane dye, a thiazine dye, a surfactant and polysulfide serving as main raw materials; when the additive is applied to copper plating solution for copper plating, the using effect can reach that of a three-dose additive; the entire plated sheet is bright; the additive is simple to manage and the maladjustment of the plating solution additive is not caused; and even if the concentration of the additive is over-high, the plating solution can be continuously used after the plating solution is slightly diluted.
Owner:济南德锡科技有限公司
System for treating dye wastewater and method for treating triphenylmethane dye wastewater
ActiveCN102358636AIncrease concentrationImproving the technical status quo of substandard effluentWater/sewage treatment with mechanical oscillationsWater contaminantsCyclic processDyeing wastewater
The invention provides a system for treating dye wastewater and a method for treating triphenylmethane dye wastewater separately and relates to a device for treating dye wastewater and a method for treating dye wastewater. The system and the method can be used for solving the technical problem that by adopting the existing chemical advanced oxidation method for treating dye industrial wastewater,the energy consumption is large and the cost is high. The system consists of a sieve-plate tower, an ultrasound system, an ozone generator and an ozone tail gas treatment device; and an ultrasonic probe is arranged under the first sieve plate of a sieve-plate tower top meter, the ozone generator is communicated with the gas inlet of the sieve-plate tower, and the gas outlet of the sieve-plate tower is communicated with an ozone tail gas treatment device. The method comprises the following steps: adding triphenylmethane dye wastewater into the sieve-plate tower through a water inlet, simultaneously starting an ultrasonic generating device and the ozone generator, circulating the water flowing from the water outlet of the sieve-plate tower once, and finishing the treatment of wastewater after 4-6 cycles. The device and method provided by the invention have the advantages of low energy consumption and high treatment speed, and can be used in the field of wastewater treatment.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
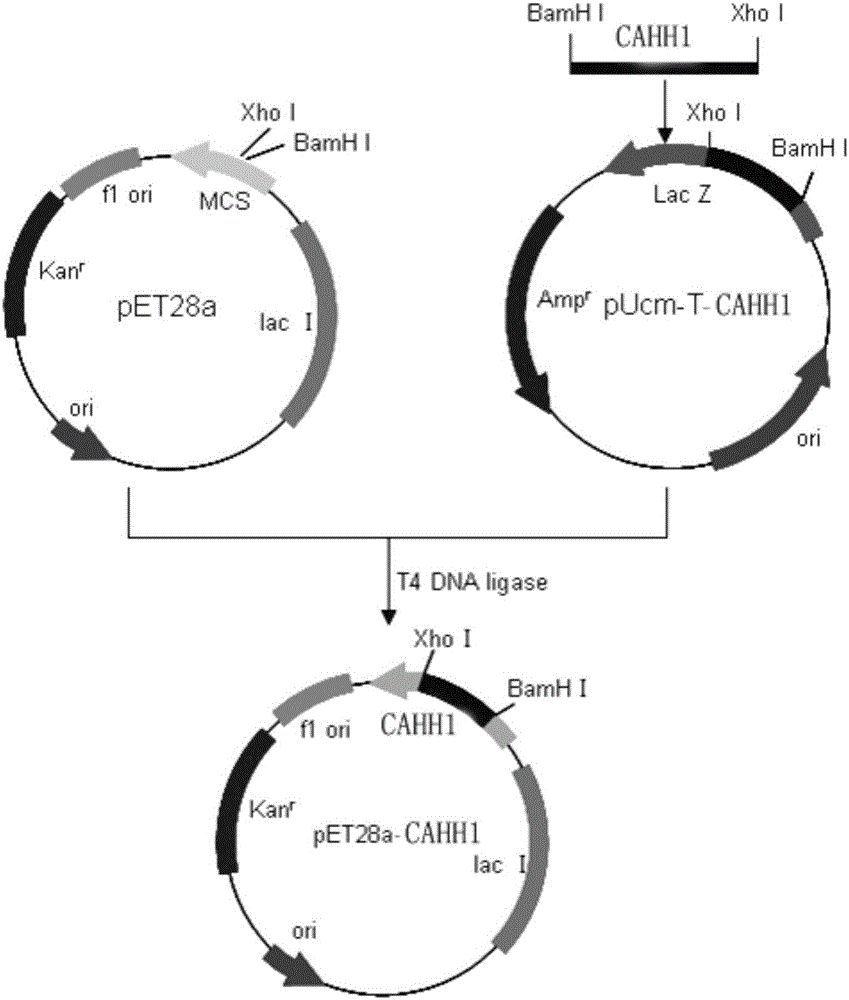
Bacillus subtilis ZNXH1 sourced bacterial laccase gene, bacterial laccase and application thereof
The invention provides a bacillus subtilis ZNXH1 sourced bacterial laccase gene, bacterial laccase and application thereof, belongs to the technical field of biology, and particularly relates to a bacillus subtilis ZNXH1 sourced bacterial laccase gene cahh1, bacterial laccase CAHH1 expressed by the gene and application of the bacterial laccase CAHH1 in the fields of textile industry, environmental protection and the like. Compared with traditional laccase, the bacterial laccase CAHH1 has the advantages of remarkable application stability and broad spectrum effect, mainly including that (1) the bacterial laccase CAHH1 has better pH stability in a range of 3-9; (2) the bacterial laccase CAHH1 has better temperature stability in a range of 30-90 DEG C; and (3) the bacterial laccase CAHH1 has a strong decolorizing effect on indigo dye, azo dye and triphenylmethane dye. The bacterial laccase can be used for decolorizing industrial dye, has wide application prospects, can easily realize engineering preparation and has higher practical values.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
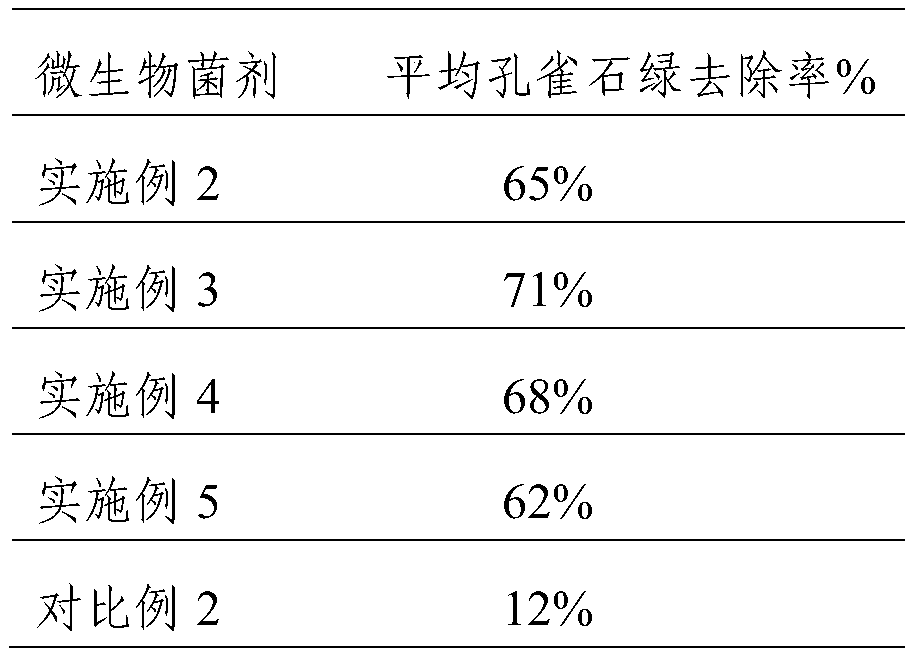
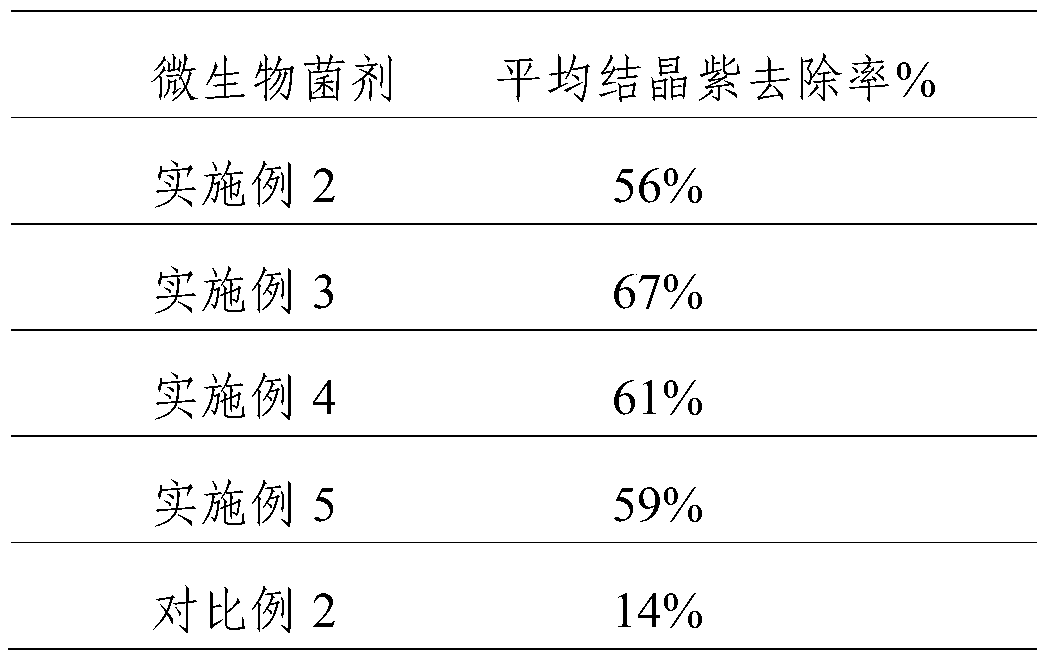
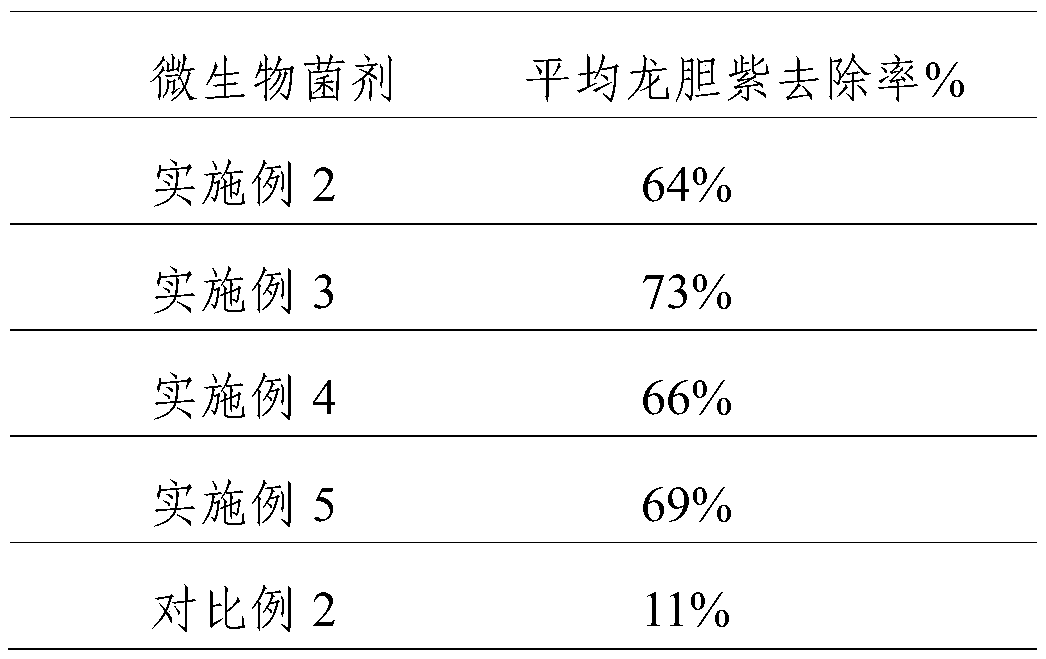
Method for efficiently removing typical triphenylmethane dye from water
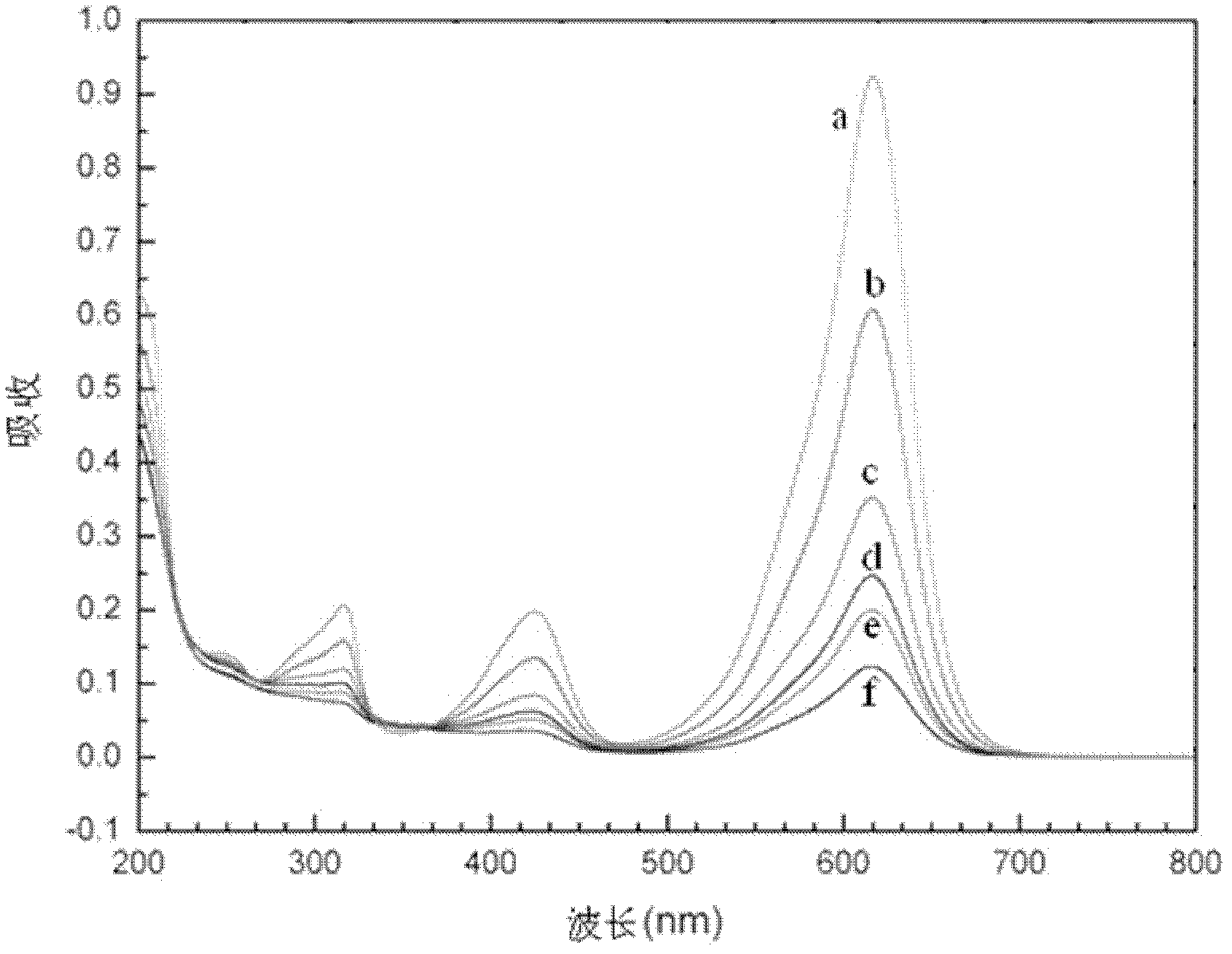
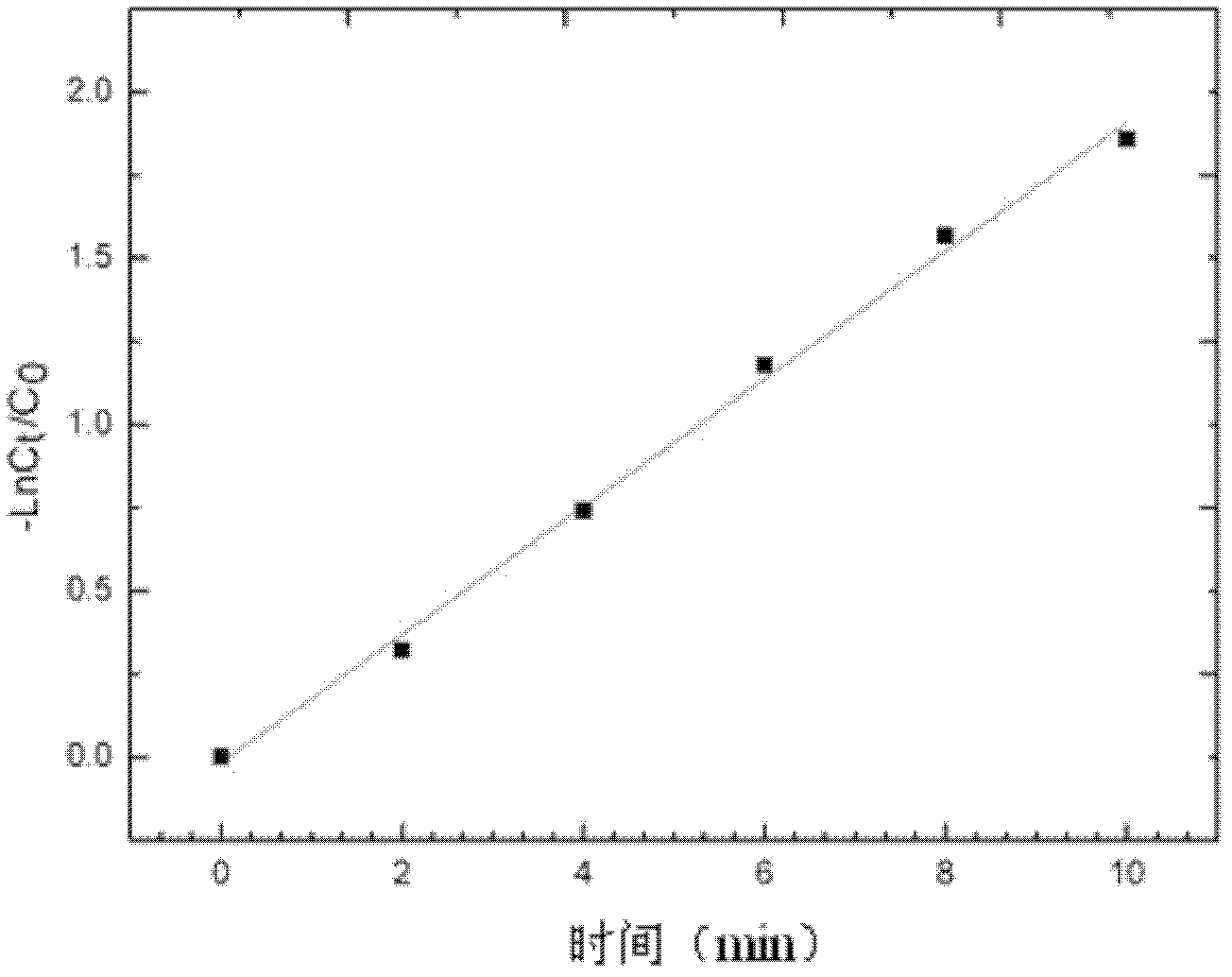
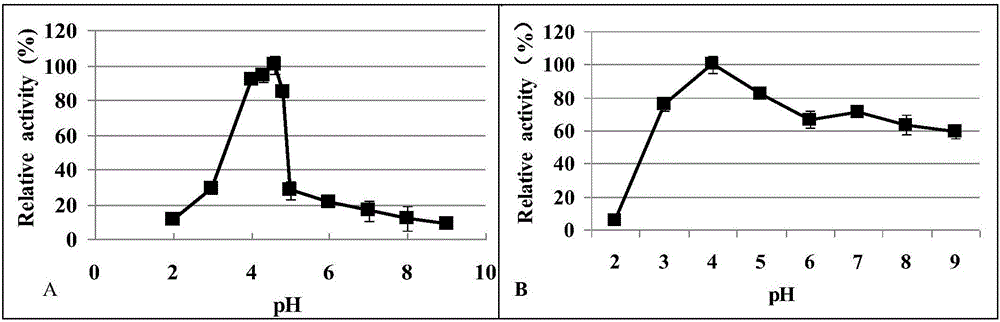
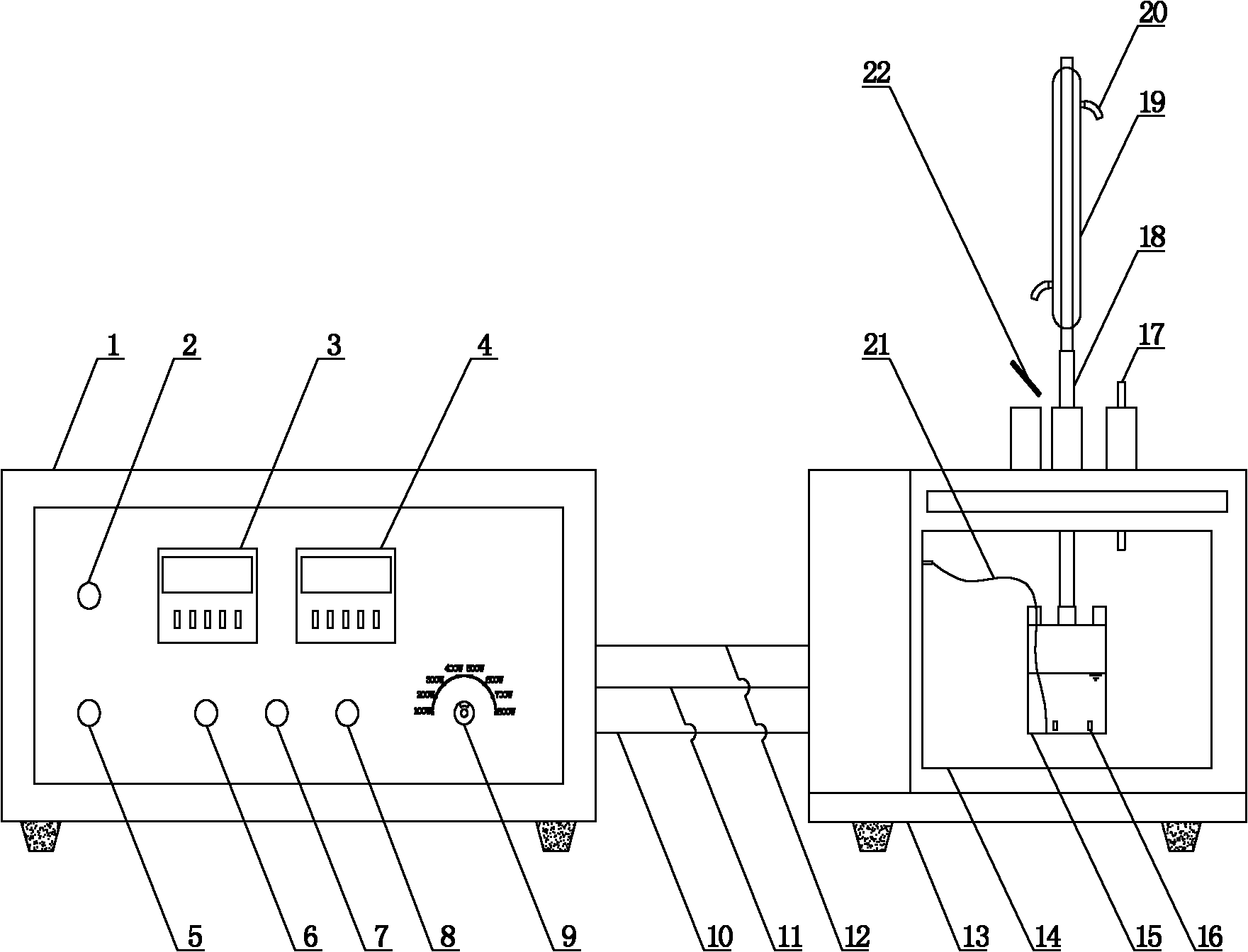
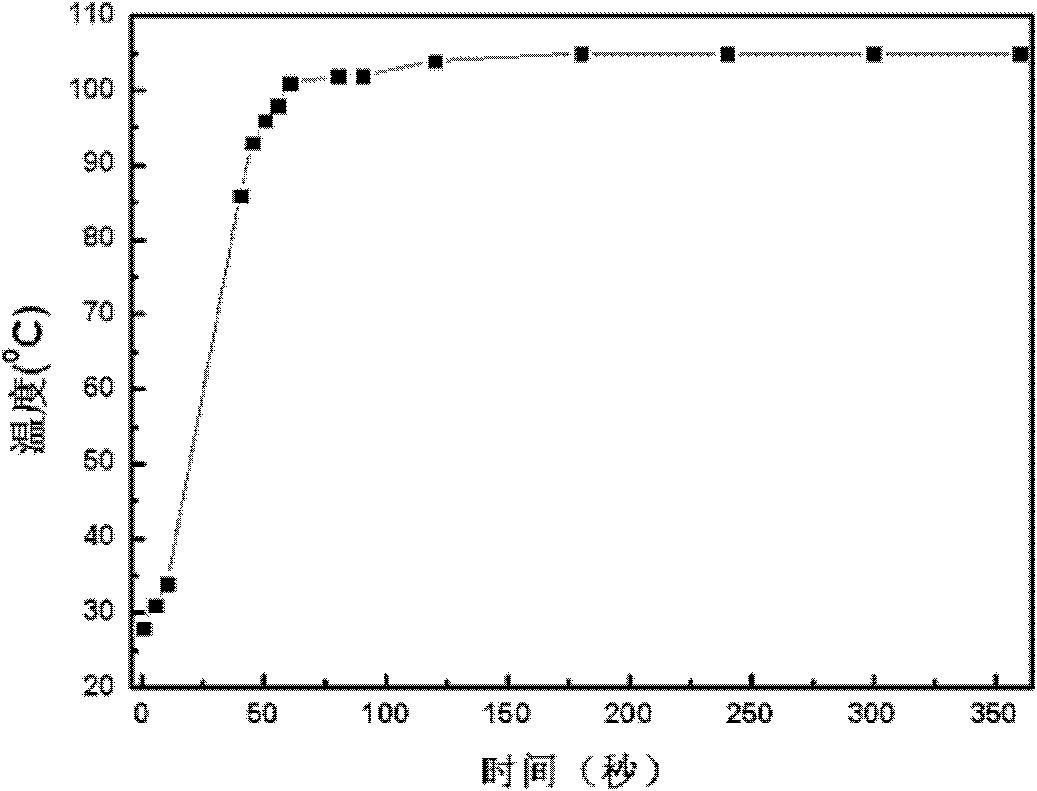
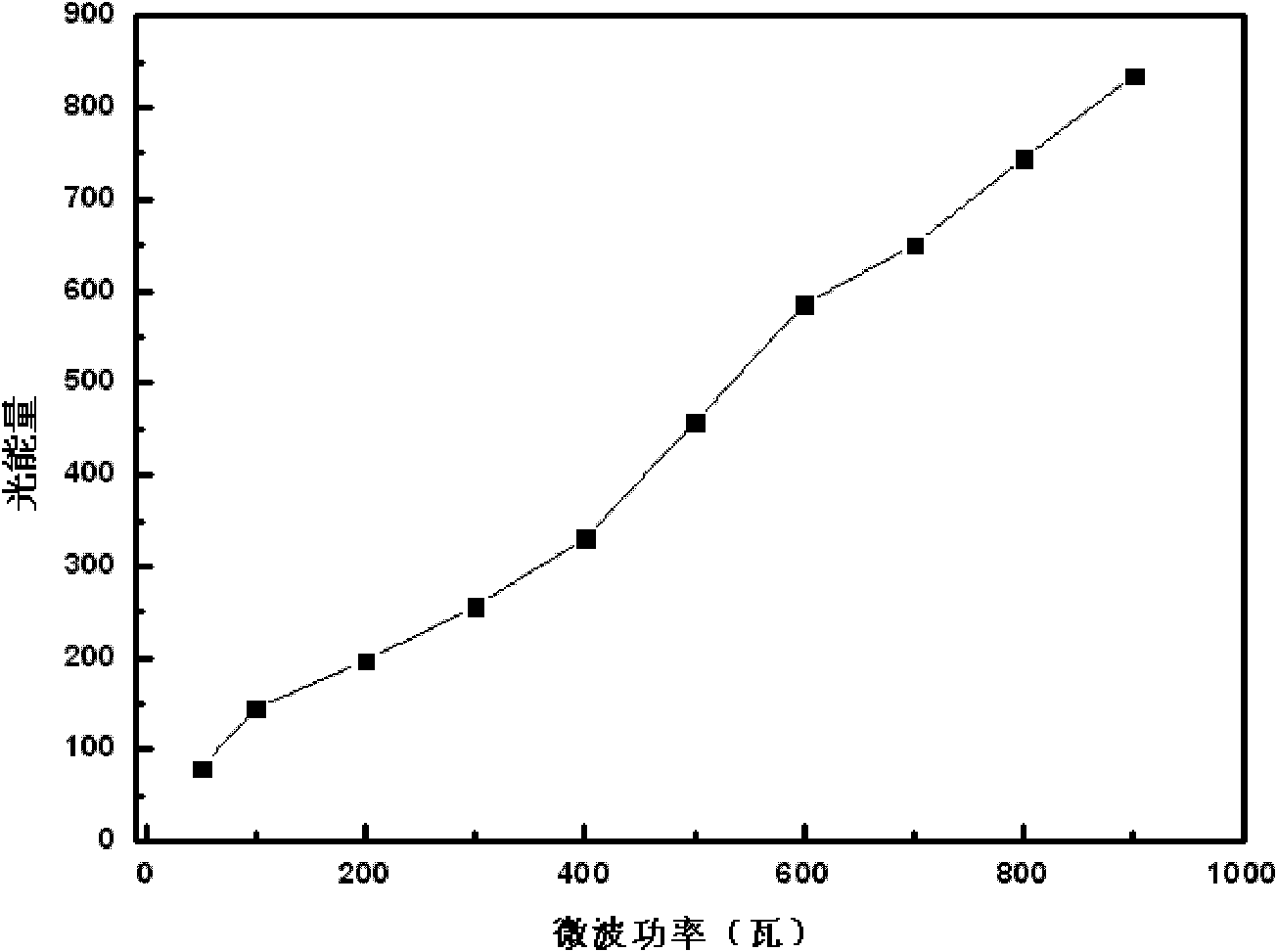
InactiveCN101885530AEfficient degradationEasy to degradeWater/sewage treatment by irradiationWater/sewage treatment by oxidationChemical reactionMalachite green stain
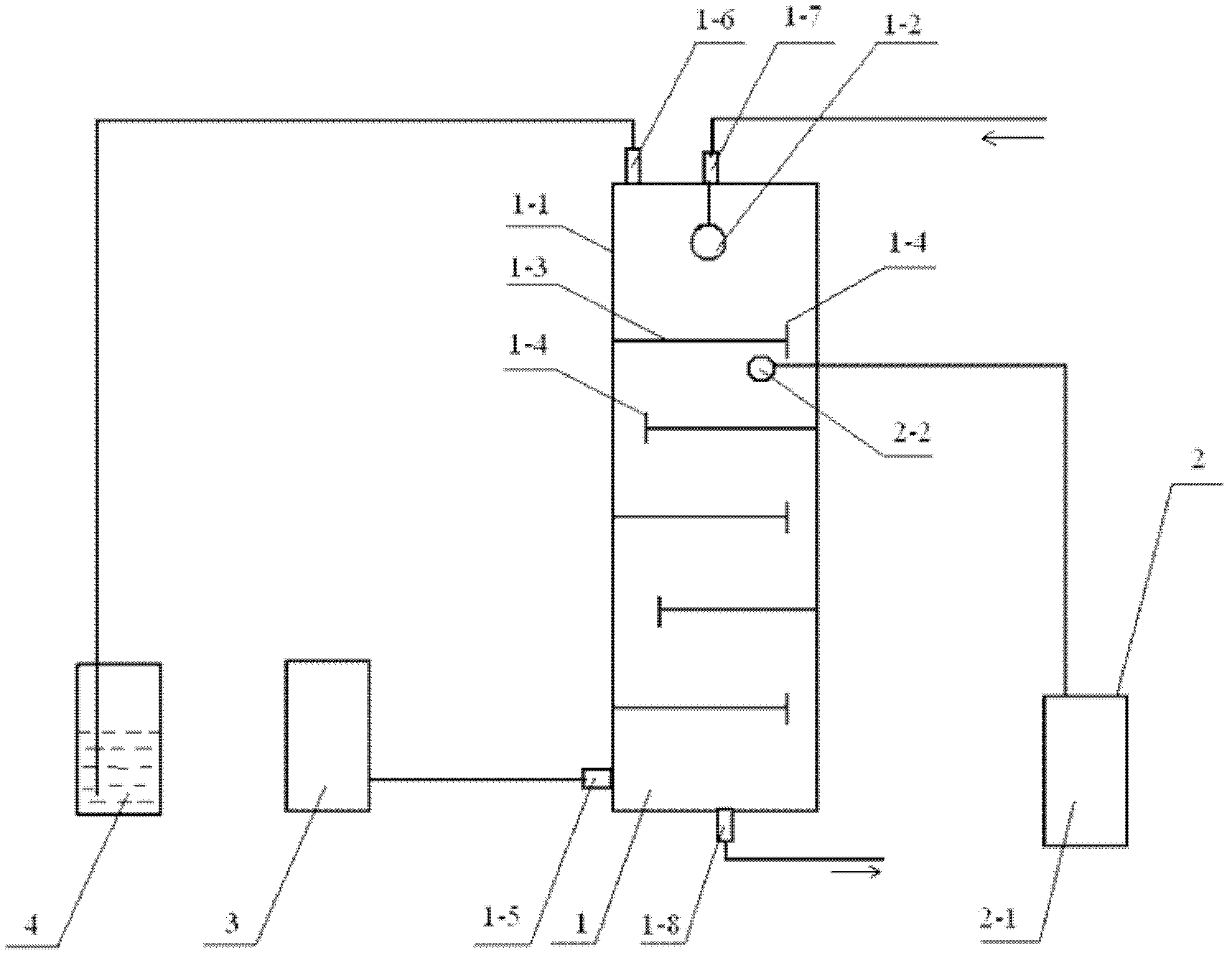
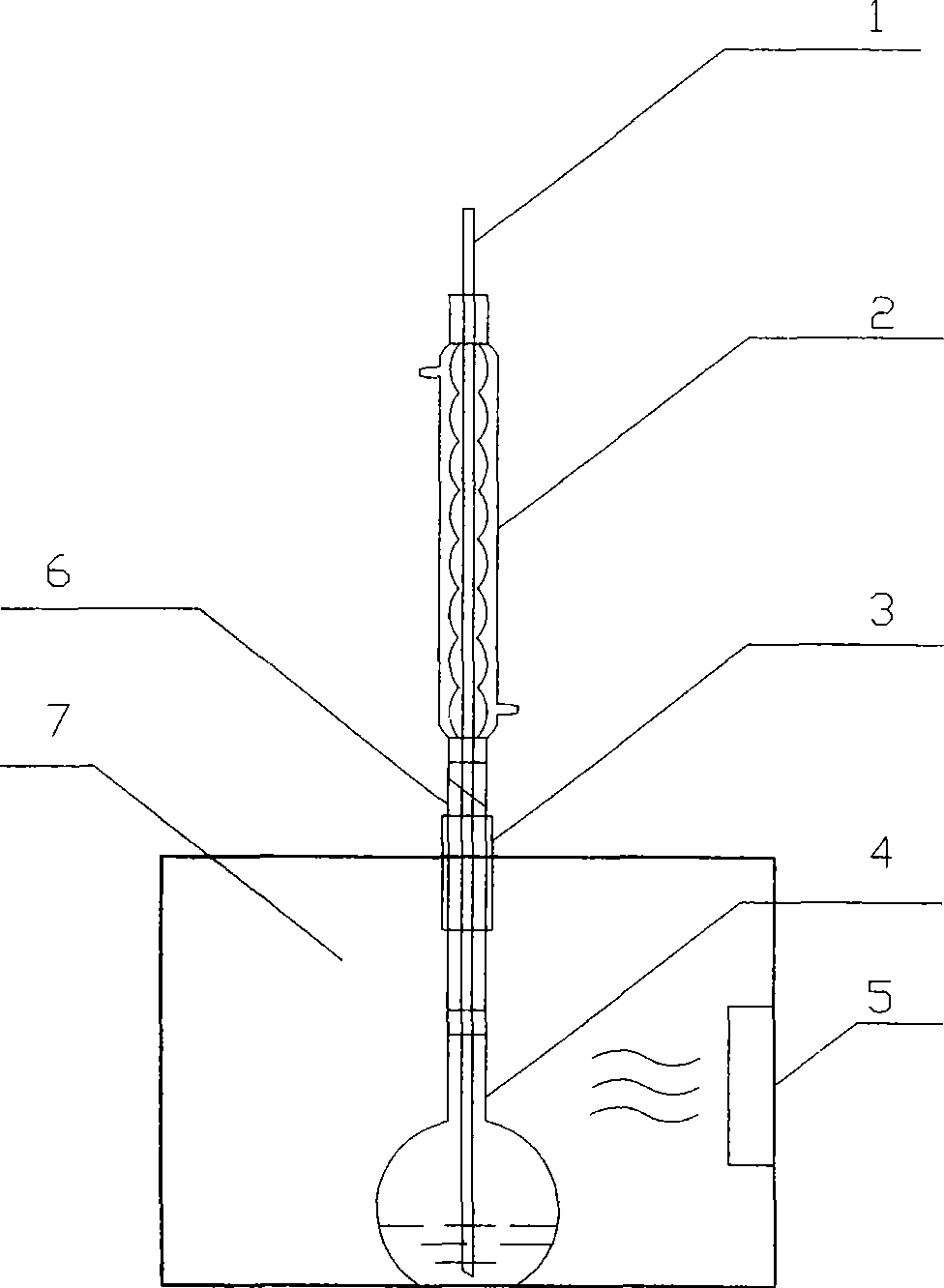
The invention discloses a method for efficiently removing typical triphenylmethane dye from water, and belongs to the field of wastewater treatment. Microwave is utilized to excite an electrodeless lamp to generate ultraviolet-visible light to respectively initiate TiO2 photo-catalysis decomposition and H2O2 non-catalytic oxidation decomposition of malachite green and crystal violet typical triphenylmethane dye wastewater. The used microwave radiation is generated by a microwave generation device, wherein the microwave generation device mainly comprises a microwave power source (1), a reaction chamber (13), a glass reactor (15), the electrodeless lamp (16), a condenser pipe (19) and a temperature probe (21). By improving a conventional microwave chemical reaction device, the reaction device can work for a long time, accurately measure the temperature of the reaction system, the emission spectrum of the electrodeless lamp and the like, and treat the malachite green wastewater and the crystal violet wastewater caused by the triphenylmethane dye; and thus the method has the advantages of high efficiency, simple process, strong controllability, mild reaction conditions, simple and convenient operation and the like.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA INST OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCI MEP
Bacterial laccase gene from bacillus subtilis ZXN4, bacterial laccase and application thereof
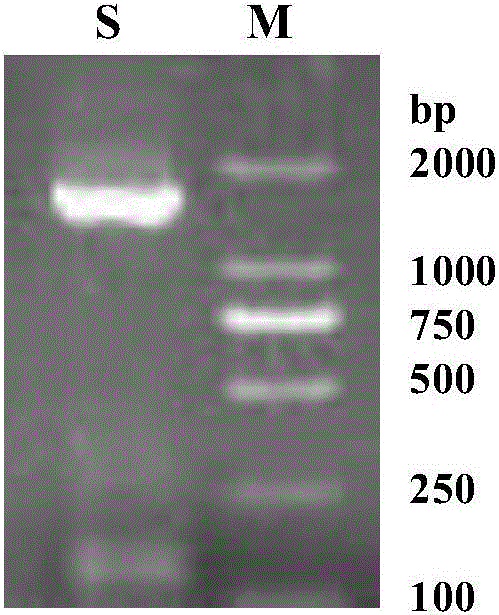
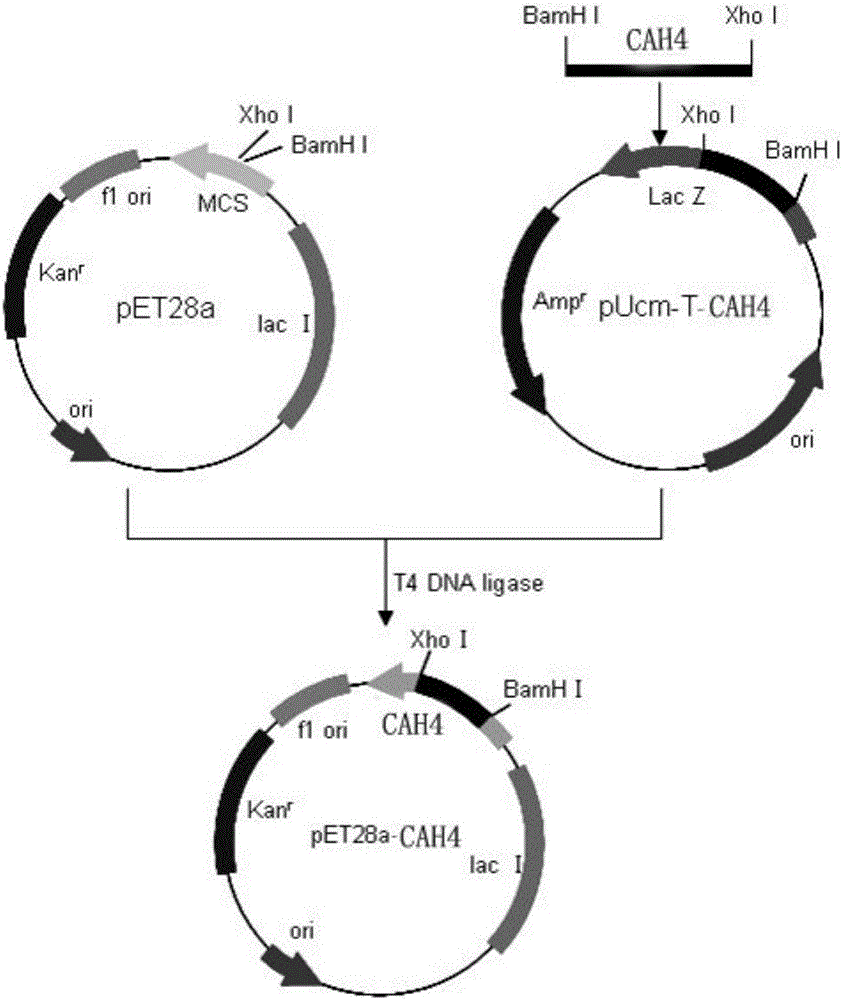
The invention discloses a bacterial laccase gene from bacillus subtilis ZXN4, bacterial laccase and an application thereof, belongs to the technical field of biology, and particularly relates to a bacterial laccase gene cah4 from the bacillus subtilis ZXN4, bacterial laccase CAH4 expressed by the bacterial laccase gene cah4 and the application of the bacterial laccase CAH4 to the fields of textile industry, environment protection and the like. Compared with traditional laccase, the bacterial laccase CAH4 has the advantages of being obvious in application stability and effect wide spectrum, and mainly has the advantages that the bacterial laccase CAH4 has the good acidic and alkaline stability within the range of pH equal to 3 to 7, the good temperature stability within the temperature range of 30 DEG C to 90 DEG C and the high decoloration effect on indigo blue dye, azo dye and triphenylmethane dye, can be used for decoloration of industry dye, and has broad application prospects, engineering preparing is easy to achieve, and the bacterial laccase CAH4 has the high practical value.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Rhodococcus and method for degrading and decoloring triphenylmethane dyes by utilizing rhodococcus
ActiveCN102618462AGood decolorization effectGood decolorizationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesResistSolid component
There is disclosed a chemically amplified positive resist composition to form a chemically amplified resist film to be used in a lithography, wherein the chemically amplified positive resist composition comprises at least, (A) a base resin, insoluble or poorly soluble in an alkaline solution, having a repeating unit whose phenolic ydroxyl group is protected by a tertiary alkyl group, while soluble in an alkaline solution when the tertiary alkyl group is removed; (B) an acid generator; (C) a basic component; and (D) an organic solvent, and a solid component concentration is controlled so that the chemically amplified resist film having the film thickness of 10 to 100 nm is obtained by a spin coating method. There can be provided, in a lithography, a chemically amplified positive resist composition giving a high resolution with a suppressed LER deterioration caused by film-thinning at the time of forming a chemically amplified resist film with the film thickness of 10 to 100 nm, and a resist patterning process using the same.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Preparation method and application of magnetic covalent organic framework compound for adsorbing triphenylmethane dyes
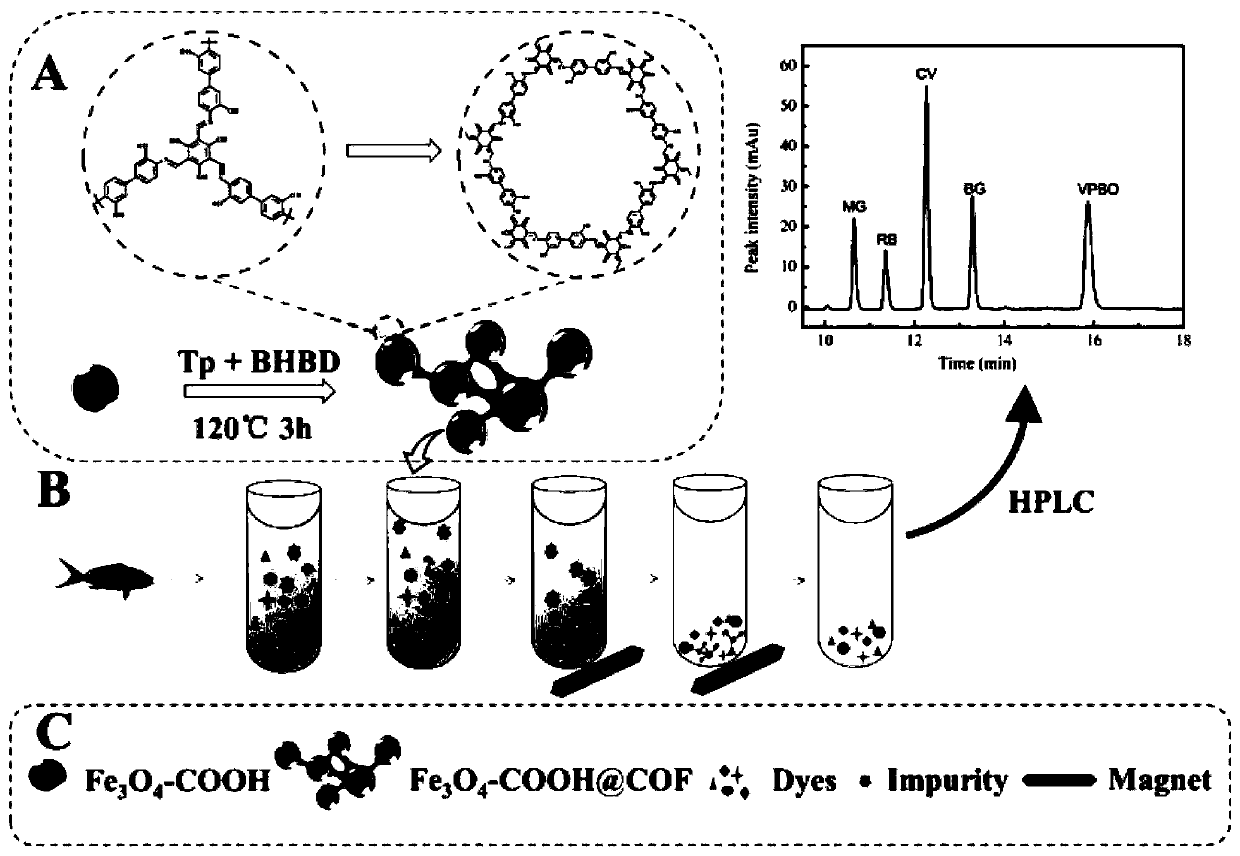
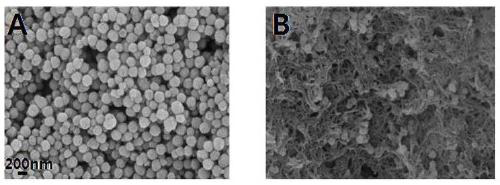
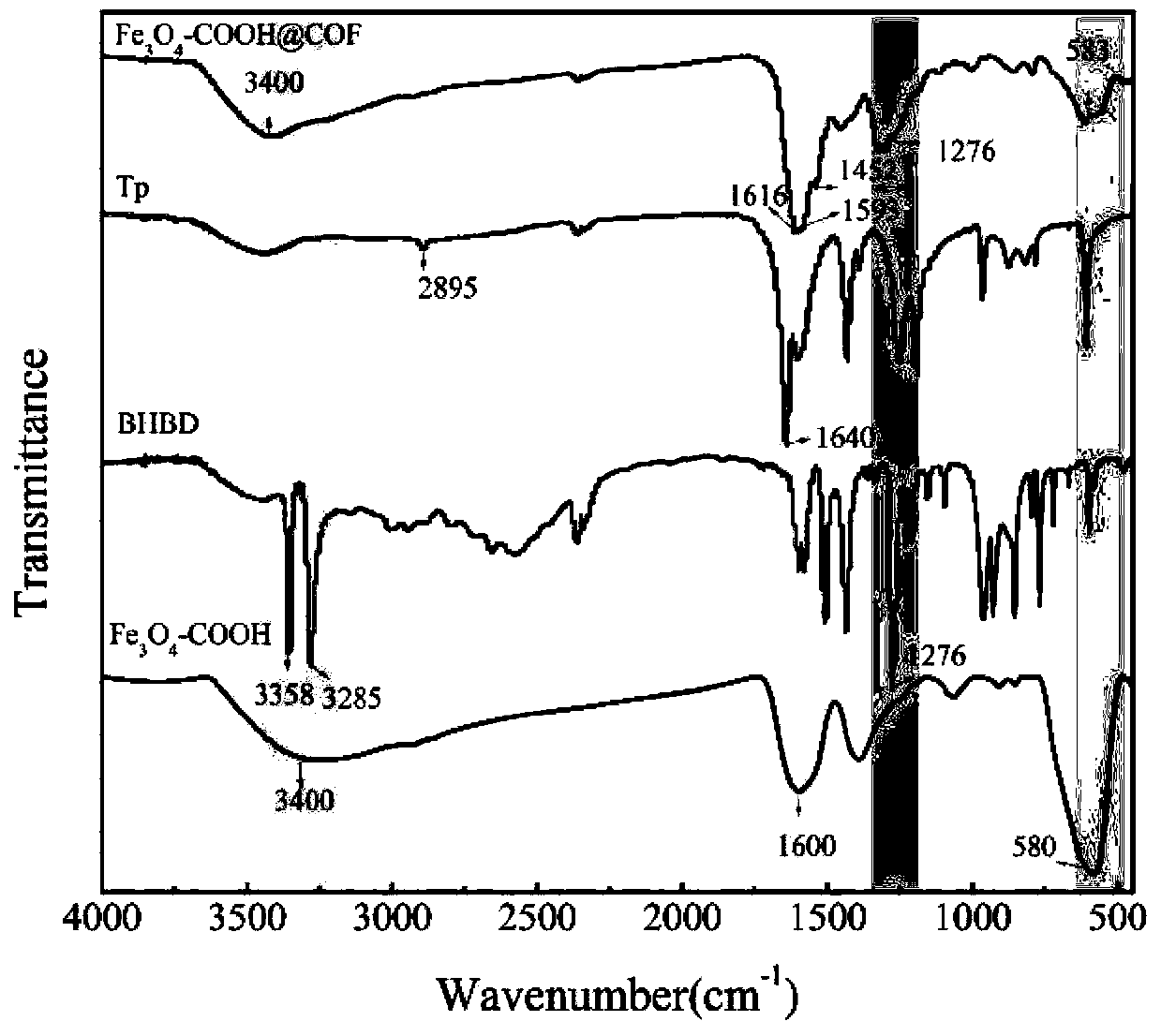
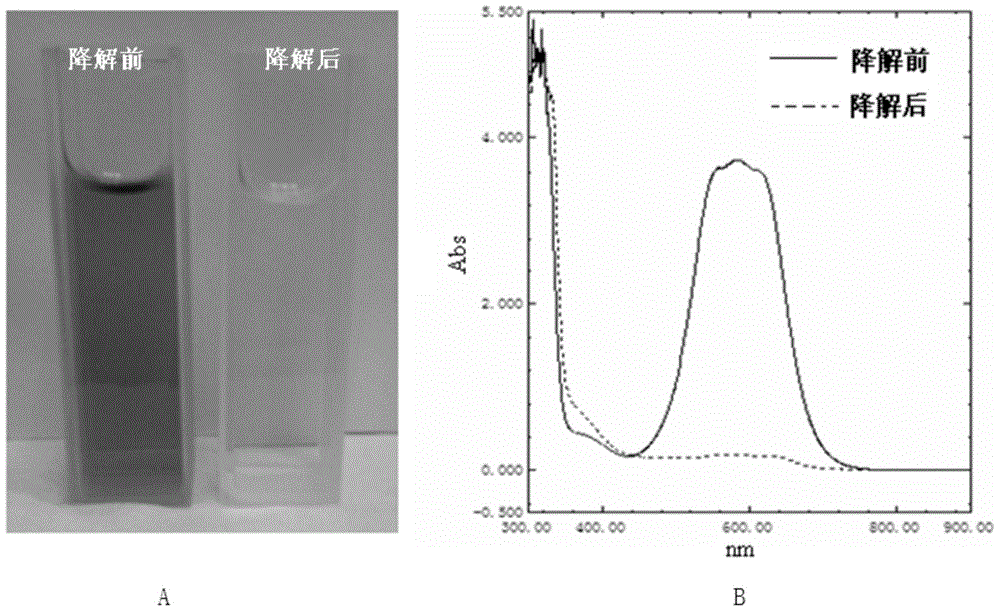
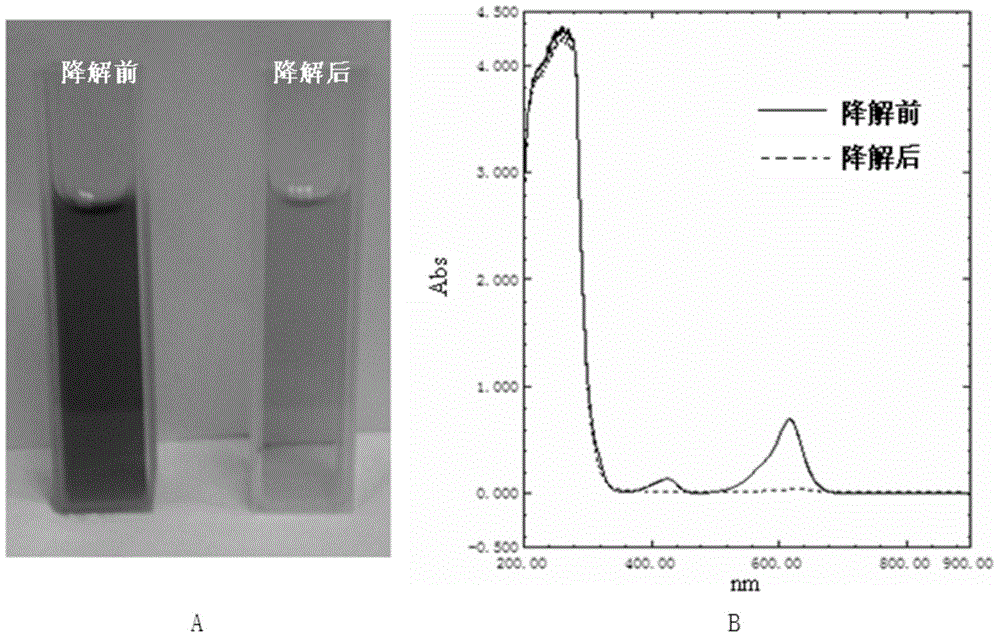
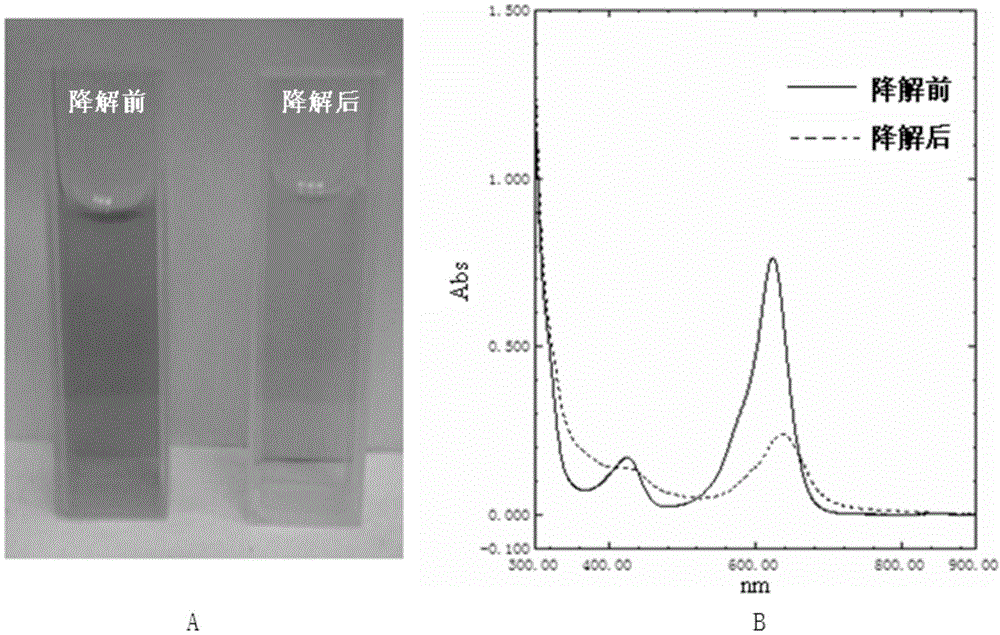
ActiveCN111450803AThe synthesis process is simpleEasy to prepareOther chemical processesWater contaminantsTriphenylmethaneMaterials science
The invention discloses a preparation method and application of a magnetic covalent organic framework compound for adsorbing triphenylmethane dyes. The invention belongs to the field of preparation ofmagnetic covalent organic framework compounds. The invention aims to solve the technical problems of complex operation and long reaction time of the existing method for synthesizing the covalent organic frameworks (COFs). The method comprises the following steps of: 1) preparing carboxylated magnetic nano (Fe3O4-COOH); and 2) synthesizing a magnetic covalent organic framework (Fe3O4-COOH(at)COF)on the surface of the magnetic nano material through a Schiff base reaction. The preparation method is simple, the synthesis time is short, and the synthesis only takes 3 hours at high temperature of120 DEG C. The prepared Fe3O4-COOH (at) COF has magnetic responsiveness, high specific surface area, high thermal stability and high adsorption performance (42.8 mg / g-500mg / g). According to the method, the triphenylmethane cationic dyes can be rapidly extracted from a complex sample within 10 minutes, so that multi-residue detection of the triphenylmethane cationic dyes can be realized, the pretreatment process of the complex sample is simplified, and the separation efficiency is greatly improved.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Method for degrading triphenylmethane dye by utilizing recombinational lipoxygenase
InactiveCN104591407AEfficient productionCatalytic degradationWater contaminantsMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliHeterologous
The invention discloses a method for degrading a triphenylmethane dye by utilizing recombinational lipoxygenase and application of the recombinational lipoxygenase rLOX-27853 in degrading the triphenylmethane dye. The amino acid sequence of the recombinational lipoxygenase rLOX-27853 is as shown in SEQ ID NO.2. The method for degrading the triphenylmethane dye by utilizing the recombinational lipoxygenase comprises the following steps: adding the recombinational lipoxygenase rLOX-27853 to a medium which contains sodium linoleate and the triphenylmethane dye to degrade the medium. The method disclosed by the invention obtains a novel prokaryotic lipoxygenase gene LOX-27853 by cloning from a pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC27853 strain genome and realizes the heterogenetic high-efficiency expression of host bacteria in escherichia coli by utilizing a fermentation culture method, thereby efficiently catalyzing the degradation of the triphenylmethane dyes, namely aniline blue, malachite green and brilliant green.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Method for microwave induced catalytic degradation of triphenyl methane dye waste water
InactiveCN101372368AImprove removal efficiencyNo secondary pollutionWater/sewage treatment by irradiationWater contaminantsPollutionPhotochemistry
The invention discloses a method for degrading triphenylmethane dye wastewater by the method of microwave induced catalysis. The microwave induced catalysis method is adopted, and nano NiO is taken as a catalyst to degrade triphenylmethane dyes in a microwave device. The dosage of the nano NiO is 0.4-1.0g / L, and the initial concentration of the triphenylmethane dyes is 30-100mg / L. A reaction solution is aerated for 30 minutes at first, put into the microwave device for reaction, and kept aerated in the course of the reaction. The method adopts a microwave induced catalysis system, and catalytic reaction is carried out without any light source, which overcomes the defects of low light utilization rate and low light quantum efficiency of the photocatalysis technology. The experimental device adopted by the method is simple and convenient to be operated, and the reaction can be carried out at normal temperature and normal pressure, thus achieving the effects of saving energy and lowering energy consumption. By adopting the method, typical triphenylmethane dyes which are difficult to be biodegraded can be effectively degraded, which causes no secondary pollution, and has high TOC removing efficiency, and the method is characterized by high speed and high efficiency.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Foam material based on heteroporous covalent organic framework as well as preparation method and application thereof
PendingCN112316907AQuick snapImprove adsorption capacityOther chemical processesWater contaminantsSodium bicarbonateMalachite green stain
The invention belongs to the technical field of material preparation, and particularly relates to a foam material based on a heteroporous covalent organic framework as well as a preparation method andapplication of the foam material. According to the invention, benzidine, p-toluenesulfonic acid and benzenetricarboxaldehyde are mixed and ground according to a certain ratio, and sodium bicarbonateand a small amount of deionized water are added in batches for grinding to help raw materials expand so as to form nonuniform gaps; and then through freezing, drying, heating and other methods, moisture is removed and redundant carbon dioxide released in reaction is released until the foam material based on the heteroporous covalent organic framework is generated through crystallization. Due to the porosity of the material, triphenylmethane dyes (malachite green and crystal violet) can be quickly, efficiently and massively captured and adsorbed, the material has very high thermal stability andreusability, and the practicability of the material is reflected in that the material can be applied to the field of sewage treatment and particularly can be massively applied to adsorption of the triphenylmethane dyes.
Owner:SHAANXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Achromobacter xylosoxidans MG1 strain and application thereof
InactiveCN102181379AStrong decolorization efficiencyHigh decolorization rateBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBacteroidesMalachite green stain
The invention relates to an achromobacter xylosoxidans MG1 strain and application thereof, and belongs to the field of environmental application of microorganisms. The achromobacter xylosoxidans MG1 strain is prepared by screening bacteria obtained by separating printing and dyeing wastewater by the conventional method, and was collected in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on December 15, 2010; and the collection number is CGMCC NO.4476. The achromobacter xylosoxidans MG1 strain has ultrastrong efficiency of decoloration on malachite green in triphenylmethane dyes, and the decolorization rate at 1 hour is up to 86+ / -1 percent when the concentration of the malachite green is up to 2,000mg / L. In addition, the MG1 strain also has a better effect of decolorizing crystalviolet, and can be applied to the preparation of biological decoloring agents. The achromobacter xylosoxidans MG1 strain has the advantages that: the range of strains which can degrade dyes can be broadened, so that an additional artificial degradation way is provided for the malachite green and the crystal violet in the environment, and the treatment cost for environmental pollution is reduced.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
Electroplate liquid for acid copper plating of triphenylmethane dye system and electroplating method
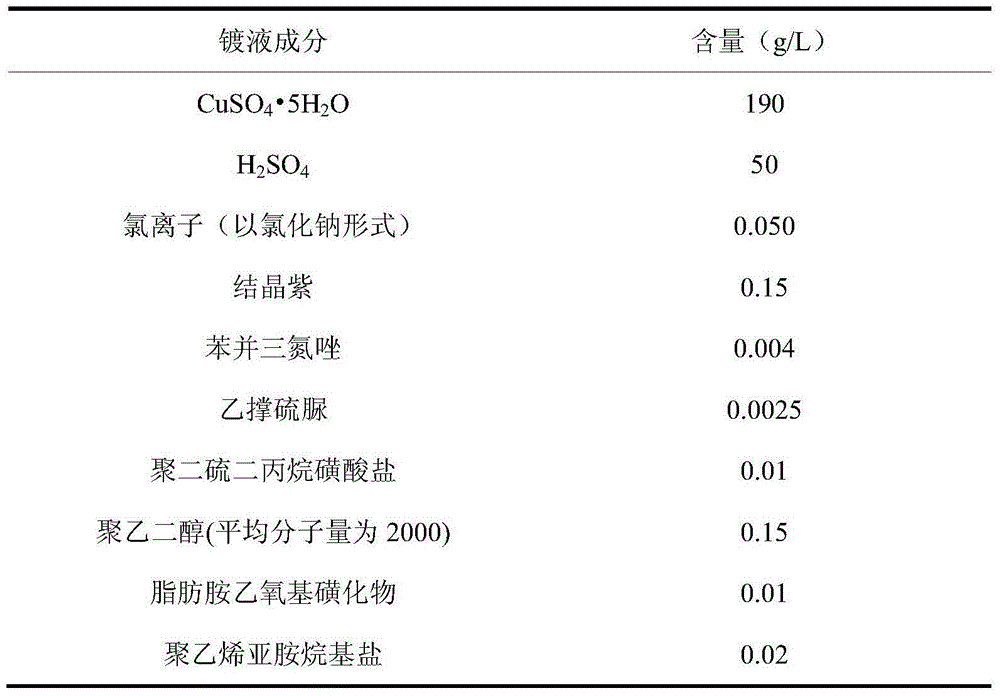
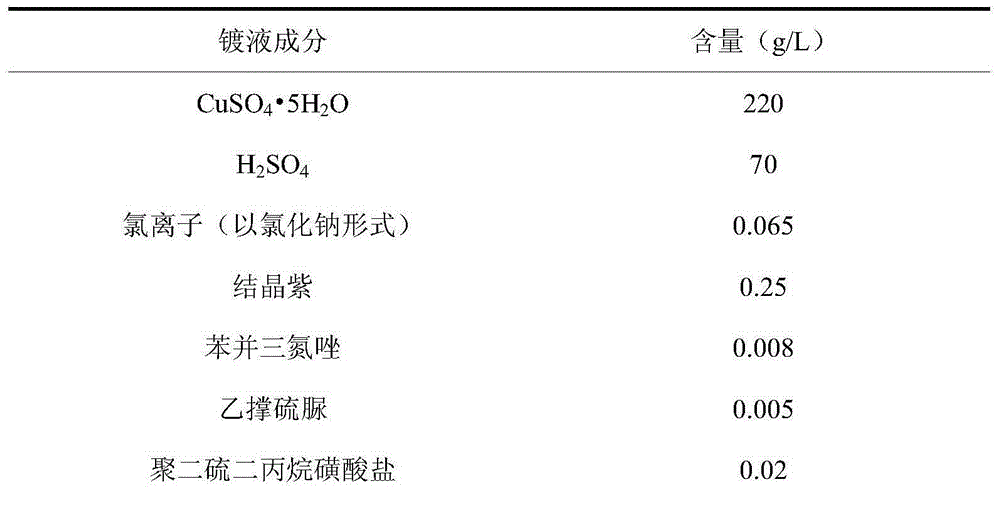
The invention discloses electroplate liquid for acid copper plating of a triphenylmethane dye system and an electroplating method. The electroplate liquid comprises 190-220 g / L of CuSO4 5H2O, 50-70 g / L of H2SO4, 0.050-0.080 g / L of chloridion, 0.15-0.25 g / L of triphenylmethane dye, 0.004-0.008 g / L of benzotriazole, 0.0025-0.005 g / L of ethylene thiourea, 0.01-0.02 g / L of sodium 3,3'-dithiodipropane sulfonate, 0.15-0.30 g / L of polyethylene glycol, 0.01-0.02 g / L of aliphatic amine ethyoxyl sulfonated body and 0.01-0.02 g / L of polyethyleneimine alkyl salt. Triphenylmethane dye serves as a leveling agent of the electroplate liquid, benzotriazole and ethylene thiourea are compounded as a brightener, sodium 3,3'-dithiodipropane sulfonate serves as a grain refiner, polyethyleneimine alkyl salt and aliphatic amine ethyoxyl sulfonated body are compounded as an extension agent, polyethylene glycol serves as a wetting agent, and therefore the electroplate liquid has good stability; and a coating obtained through electroplating of the electroplate liquid under the acid condition is good in leveling performance and high in phototaxis.
Owner:无锡永发电镀有限公司
Fluorescent tracing multifunctional decoloring Shewanella engineered decolorationis and construction method thereof
ActiveCN101486989AWide range of decolorizationHas a decolorizing effectBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescenceModifier Genes
The invention discloses a discoloring Shiva engineering bacterium with multiple functions of fluorescent tracing and discoloring and a construction method of the discoloring Shiva engineering bacterium, and aims at providing a genetic engineering bacterium that has high-efficiency discoloring capability of three major dyes including azo, anthraquinone and triphenylmethane as well as the fluorescent tracing function. The invention adopts the technical proposal that combines a foreign fusion gene SPrtpmD' into a discoloring Shiva bacterium S12; wherein, the fusion gene SPrtpmD' is formed by connecting a discoloring enzyme modifier gene tpmD' of the triphenylmethane dye after a NAD(P)H dehydrogenase gene initiator sequence of the discoloring Shiva bacterium S12, and the discoloring enzyme modifier gene tpmD' of the triphenylmethane dye is formed by adding an SD sequence before a 5'-end initiation codon of the discoloring enzyme modifier gene tpmD' of the triphenylmethane dye and adding a small label that can chelate 6 encoding amino acids of a diarsenic fluorescent dye before a 3'-end termination codon. The discoloring Shiva engineering bacterium with multiple functions of fluorescent tracing and discoloring can be used for environmental reparation and administration.
Owner:GUANGDONG INST OF MICROORGANISM
Transgenic Pichia yeast engineering strain and construction method thereof
The invention discloses a transgenic Pichia pastoris engineering strain and a construction method thereof, and aims to provide an engineering strain which can safely perform extracellular secretory expression on phenylmethane dye decolorizing enzyme in a large amount. The technical proposal of the invention comprises that a triphenylmethane dye decolorizing enzyme TpmD gene is cloned from Aeromonas hydrophlla subsp DN322; the triphenylmethane dye decolorizing enzyme TpmD gene is connected with an expression vector, namely a pPICZaA vector to construct a plasmid pPICZaA-tpmD; the constructed plasmid pPICZaA-tpmD is subjected to enzyme digestion linearization and then is led into Pichia pastoris X-33; and the transformation of the triphenylmethane dye decolorizing enzyme TpmD gene into the Pichia pastoris X-33 is determined, thereby obtaining the transgenic Pichia pastoris engineering strain. The transgenic Pichia pastoris engineering strain is mainly used for environmental remediation and treatment.
Owner:GUANGDONG INST OF MICROORGANISM
Pseudomonas veronii composition and application thereof in treatment of materials containing dyes
ActiveCN110172414AEasy to handleHigh removal rateBacteriaWater contaminantsBacillus licheniformisTreatment effect
The embodiment of the invention discloses a pseudomonas veronii strain. The pseudomonas veronii strain is preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC) on April 4th, 2019, the preservation number is CGMCC No. 17523, and the preservation address is No. 3, No. 1 Yard, Beichen West Road, Chaoyang District, Beijing. The embodiment of the invention further provides a microbial agent. The microbial agent comprises kurthia huakui, bacillus licheniformis and pseudomonas veronii in claim 1. On the other hand, the embodiment of the invention further provides a process of treating sewage and soil which contain triphenylmethane dyes by the microbial agent. The pseudomonas veronii disclosed by the embodiment of the invention can be used for performing degradation treatment on the triphenylmethane dyes in the sewage and the soil of the triphenylmethane dyes in water bodies or soil, is good in treatment effect, and has very good removal rate especially for malachite green, crystal violet or gentian violet.
Owner:宋金龙
Optimized triphenylmethane reductase gene as well as expression and application thereof
InactiveCN102108362AGrowth impactVerify degradation functionMicroorganism based processesOxidoreductasesEnzyme GeneNucleotide
The invention discloses an optimized triphenylmethane reductase gene as well as an expression and an application thereof. The triphenylmethane reductase gene in citric acid bacillus is transformed by a plant preference codon to get the optimized triphenylmethane reductase gene with the full length of 864bp, the nucleotide sequence of the optimized triphenylmethane reductase gene is as shown in SEQ (sequence) ID (identity) No.1, and the sequence of a coded protein is as shown in SEQ ID No.2. The optimized triphenylmethane reductase gene is constructed into a plant vector, agrobacterium-mediated transformation is further performed, and a transformed arabidopsis thaliana plant can continuously express triphenylmethane reductase and induce the plant to participate in degradation of crystal violet and malachite green, thereby providing broad application prospects for restoring pollution caused by triphenylmethane dyes through the plant.
Owner:SHANGHAI ACAD OF AGRI SCI +1
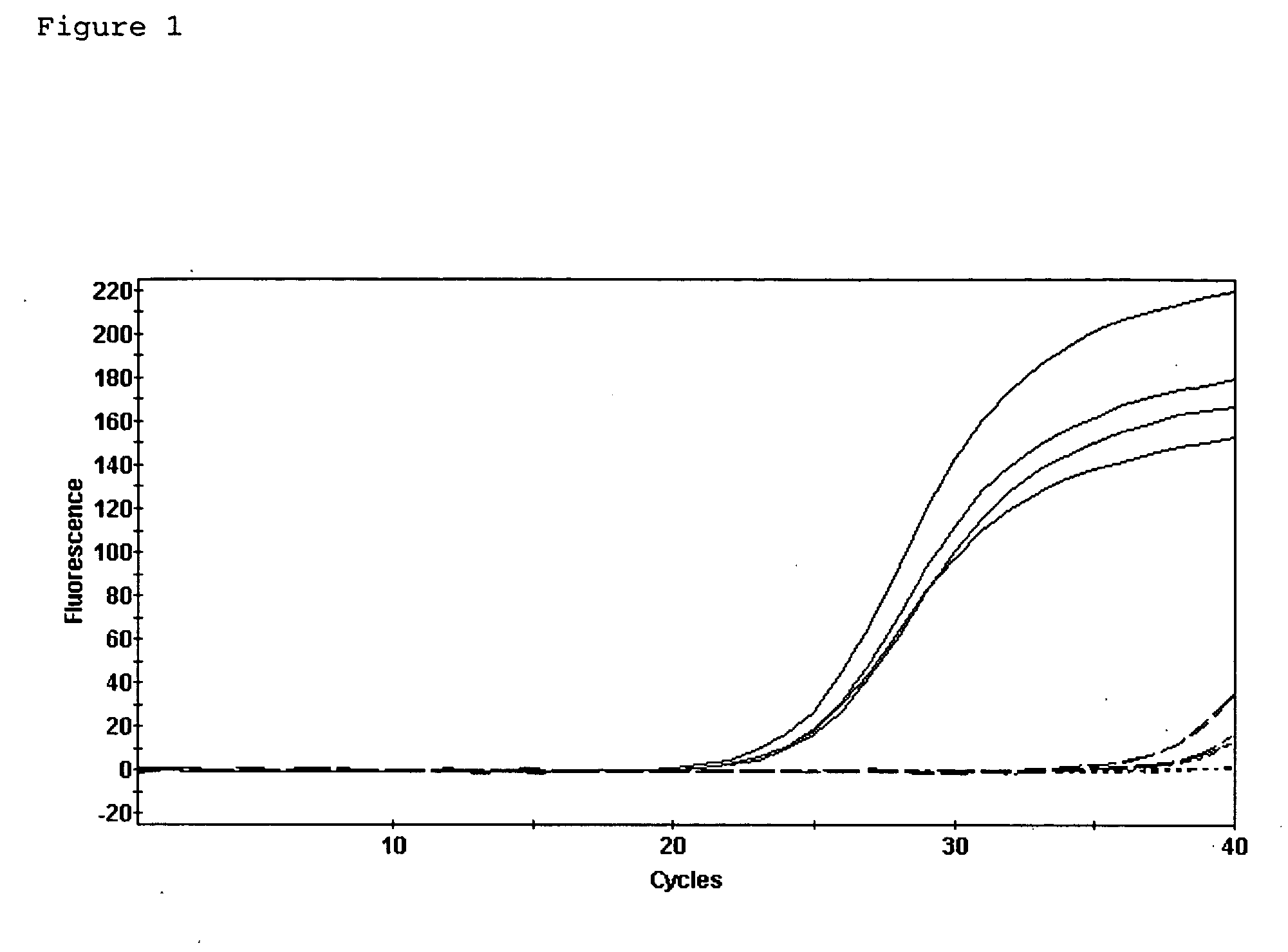
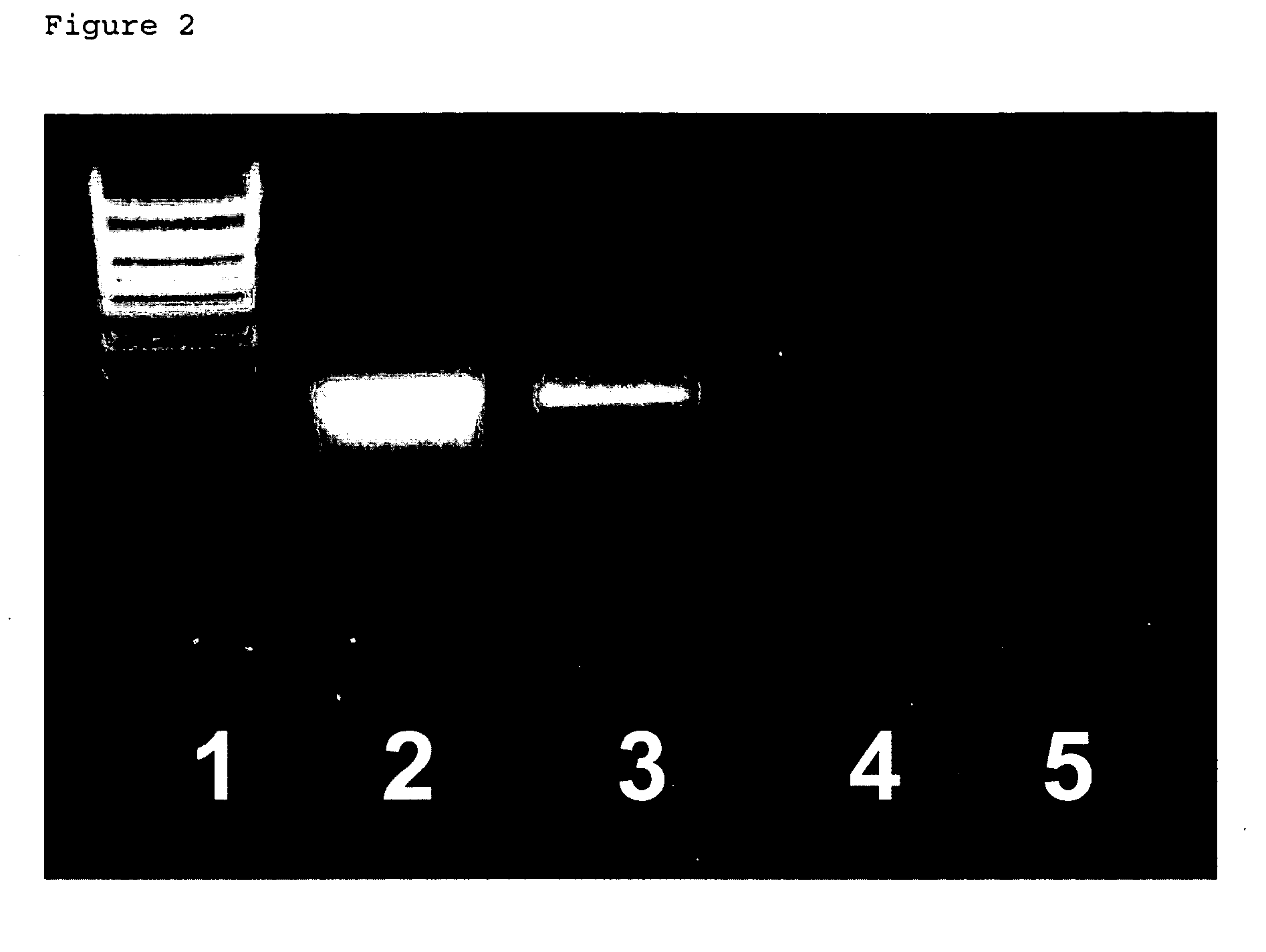
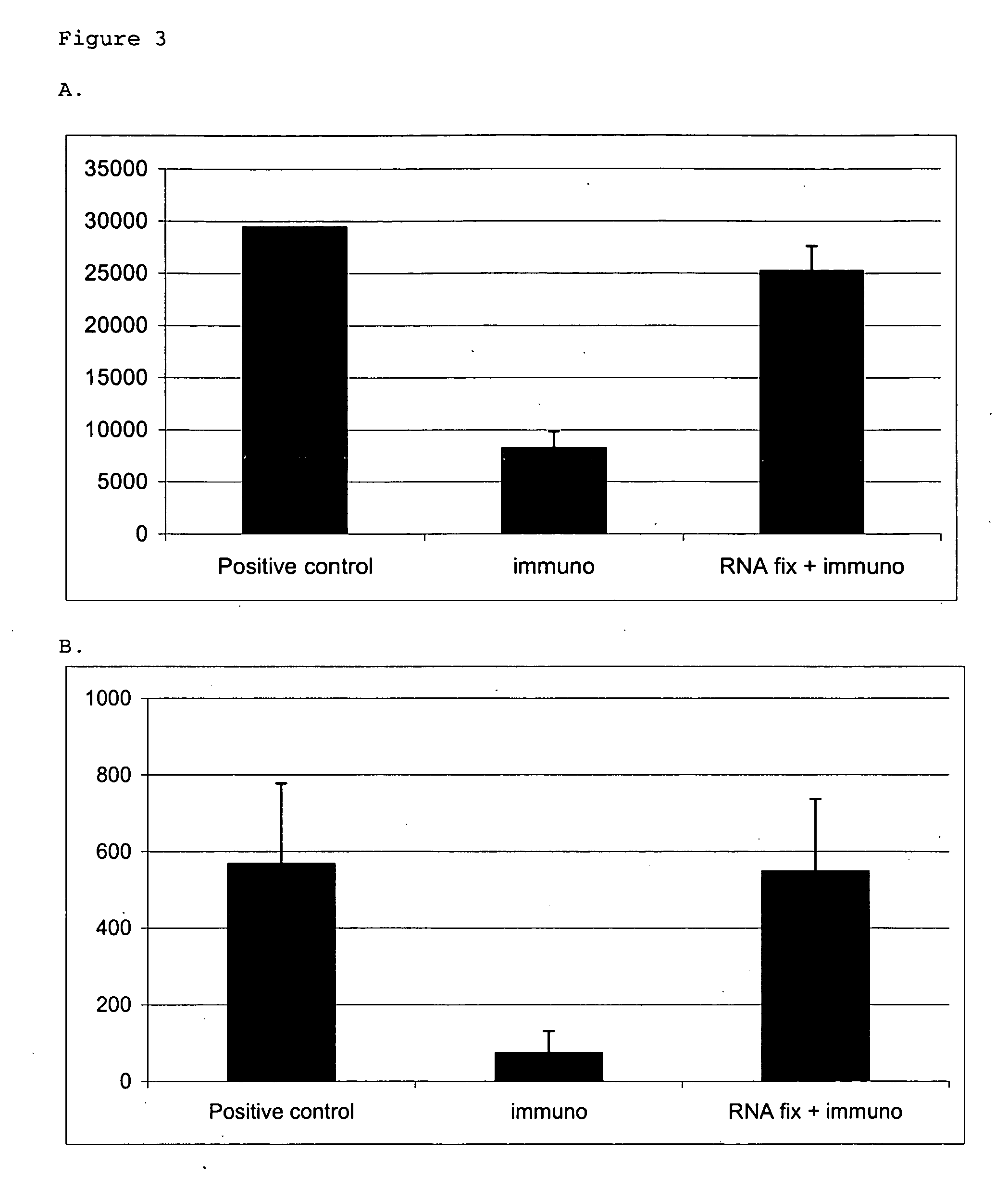
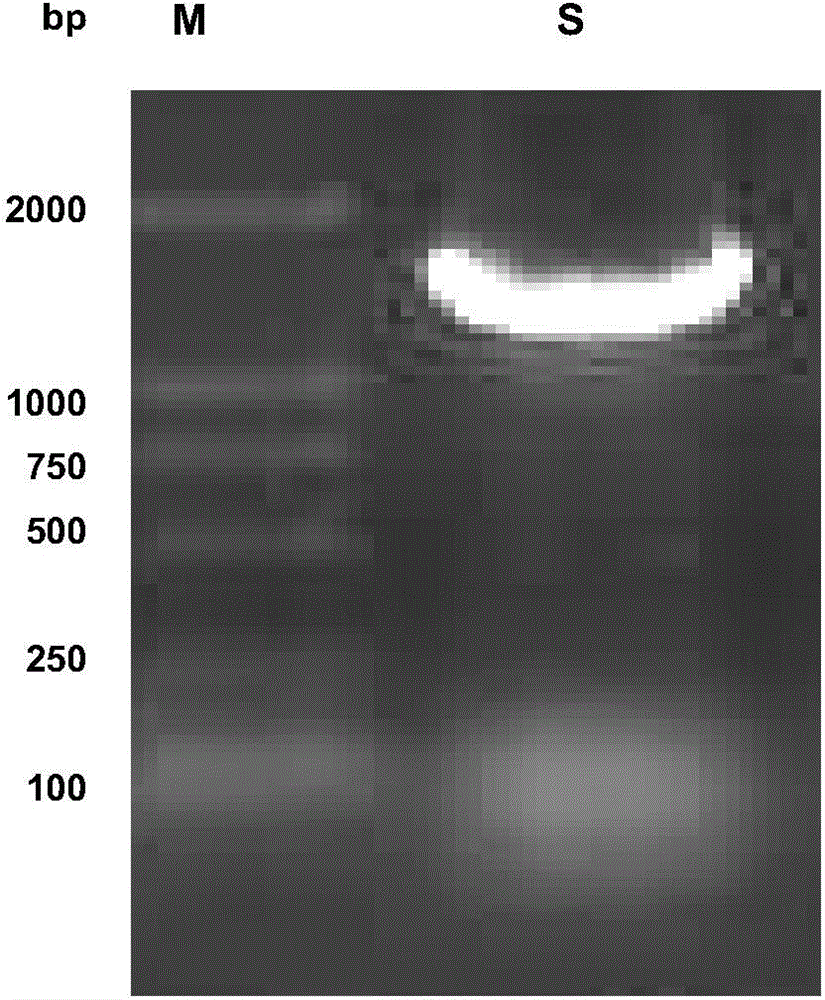
Preservation of RNA in a biological sample
Owner:KAMME FREDRIK +3
Mesophilic laccase gene, mesophilic laccase and application thereof
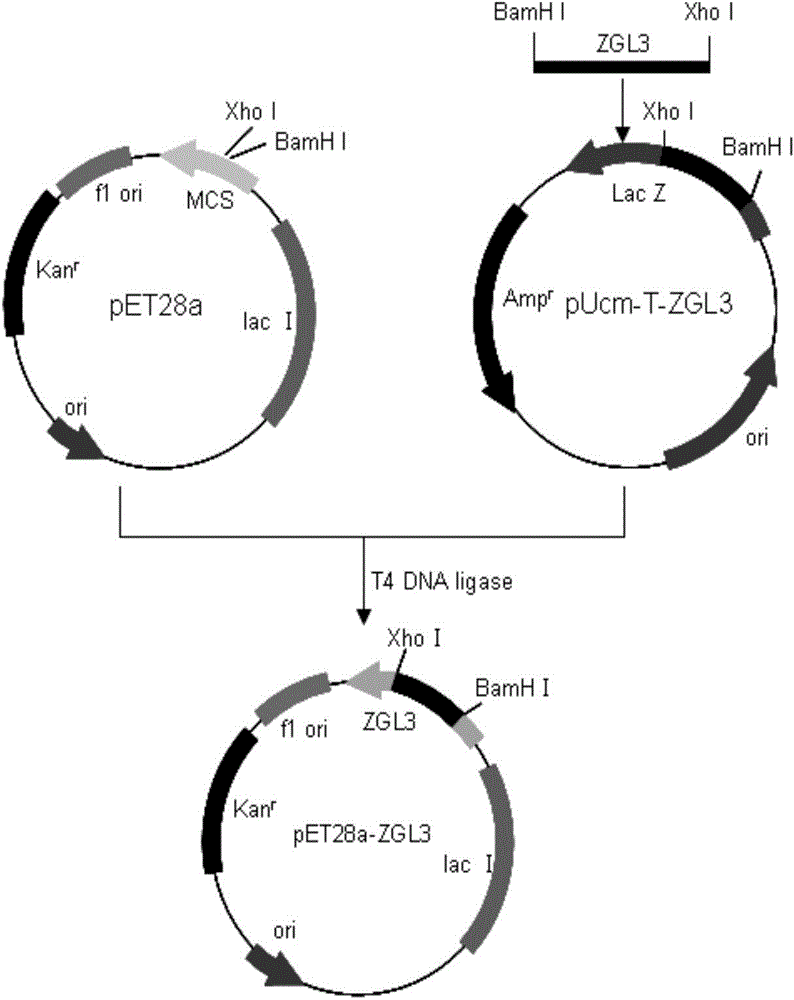
Mesophilic laccase gene, mesophilic laccase and application thereof belong to the field of biotechnology. In particular, the invention relates to a mesophilic laccase gene from mesophilic bacteria ZW2531-1, mesophilic laccase expressed by the gene ZGL3 and application of the mesophilic laccase to the fields of textile industry and environmental protection. More specifically, the invention provides a mesophilic laccase gene derived from a thermophilic bacterium and mesophilic laccase expressed by the gene. The invention also relates to the effective application of the thermophilic laccase to industrial dye degradation, and further relates to the wide application of the mesophilic laccase to the fields of textile industry and environment protection. The mesophilic laccase provided by the invention can safely and effectively realize degradation and decolorization of anthraquinone, azo and triphenylmethane dyes, has broad application prospects, easiness for realizing industrialization preparation and high practical value.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Method for reductively degrading triphenylmethane dye crystal violet wastewater quickly
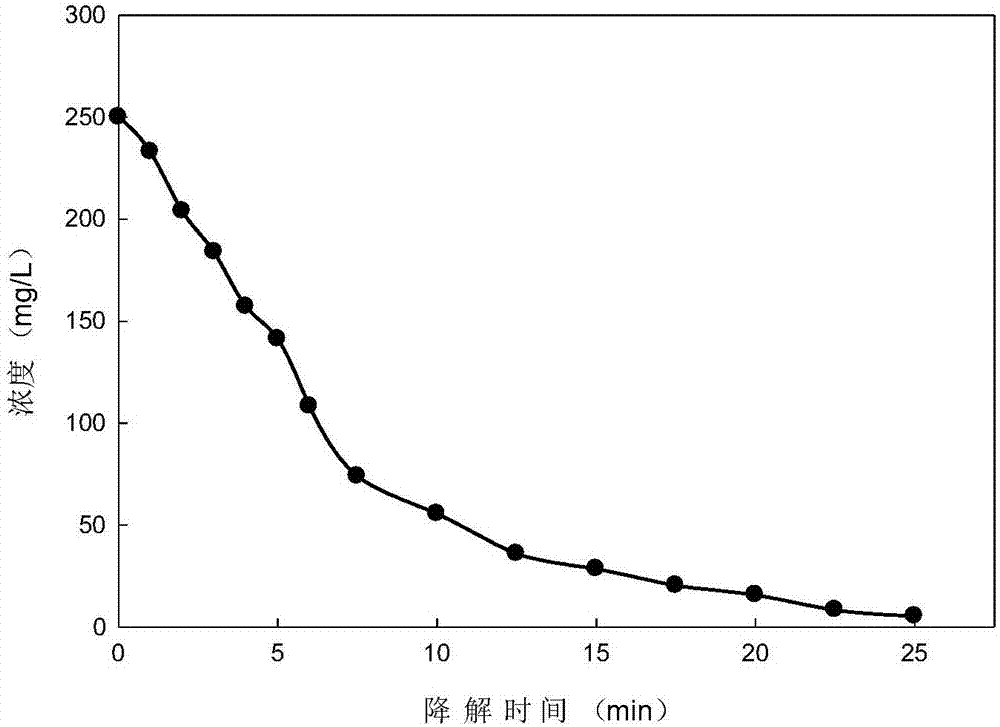
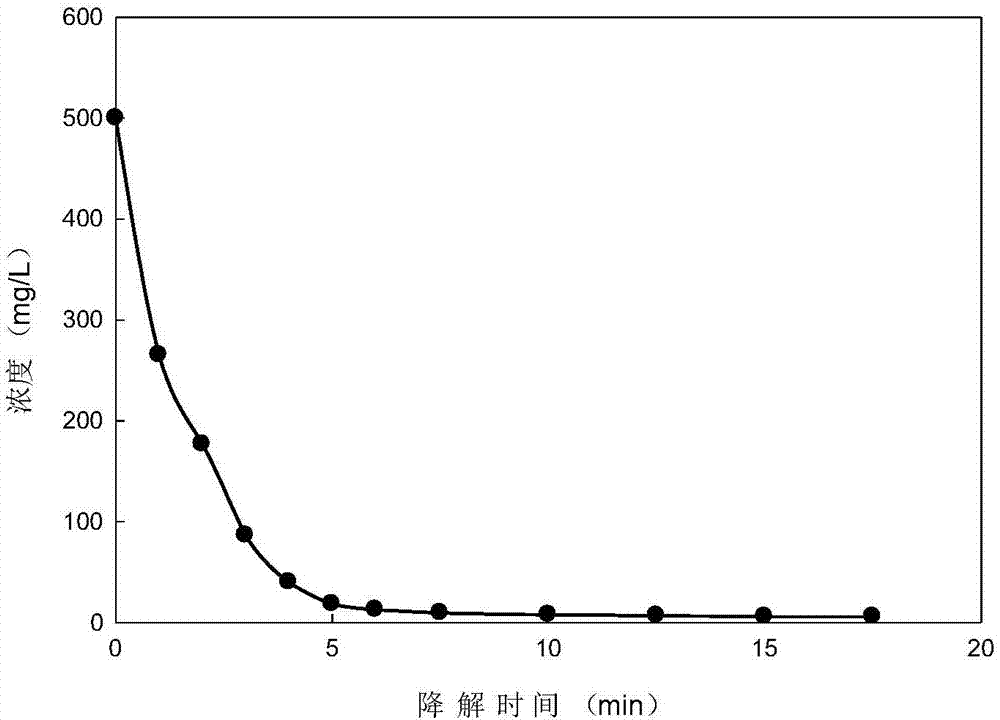
ActiveCN106957099ABroaden your optionsQuick and easy to manufactureGeneral water supply conservationWater contaminantsRoom temperatureDyeing wastewater
The invention discloses a method for reductively degrading triphenylmethane dye crystal violet wastewater quickly and belongs to the field of nano material and dye wastewater treatment. Nano zero-valent iron (perilla seed-nano zero-valent iron) is prepared from a perilla seed extract solution as a stabilizer under a room temperature condition and can be used for reductively degrading triphenylmethane dye crystal violet quickly in a suspension state, wherein the dosage of the perilla seed-nano zero-valent iron is 0.5-2.5g / L, the pH range of the degraded dye wastewater is 2-10, the concentration range is 50-1000mg / L, the perilla seed-nano zero-valent iron at least has the decolorization ratio of 95.49% or over on 50-1000mg / L of triphenylmethane dye crystal violet within 30min and has the removal rate of 90.20% on COD of 500mg / L of triphenylmethane dye crystal violet, and the method is high in environmental adaptability, high in degradation efficiency and thorough in degradation. The method is simple and fast, and the targets of dye decolorization, degradation and removal of organic pollutants of the dye can be achieved within a short period of time.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Pantoea and bacterium manganese mixture and application of bacterium manganese mixture in degradation of malachite green
ActiveCN113528372APromote degradationNo effect on biological growth and developmentBacteriaWater contaminantsTriphenylmethaneMicroorganism
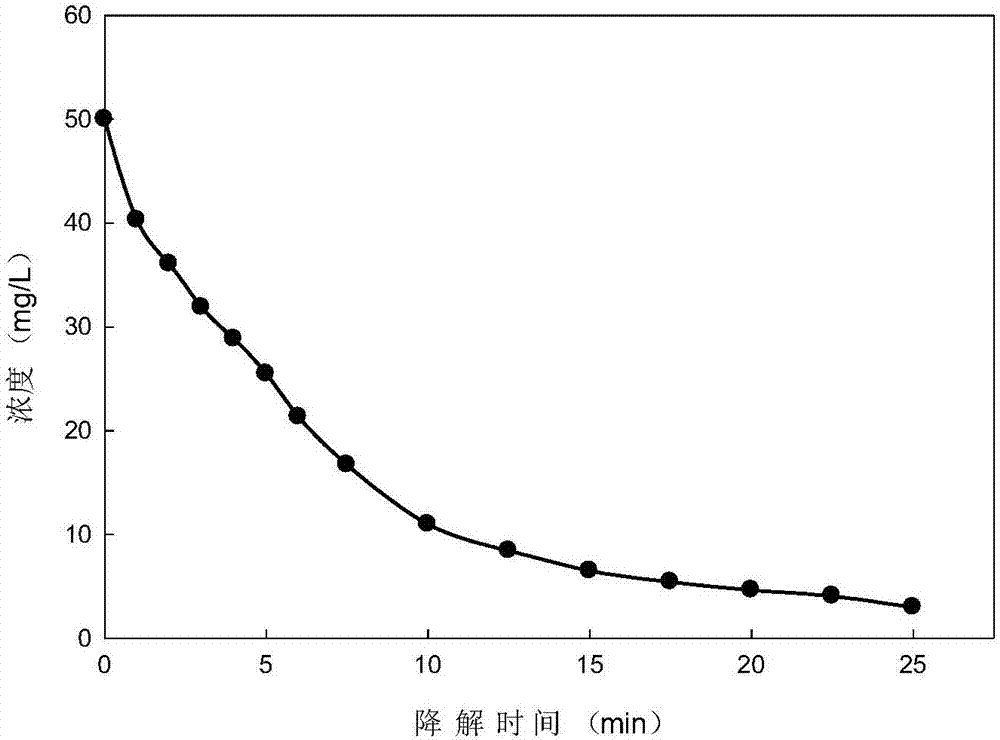
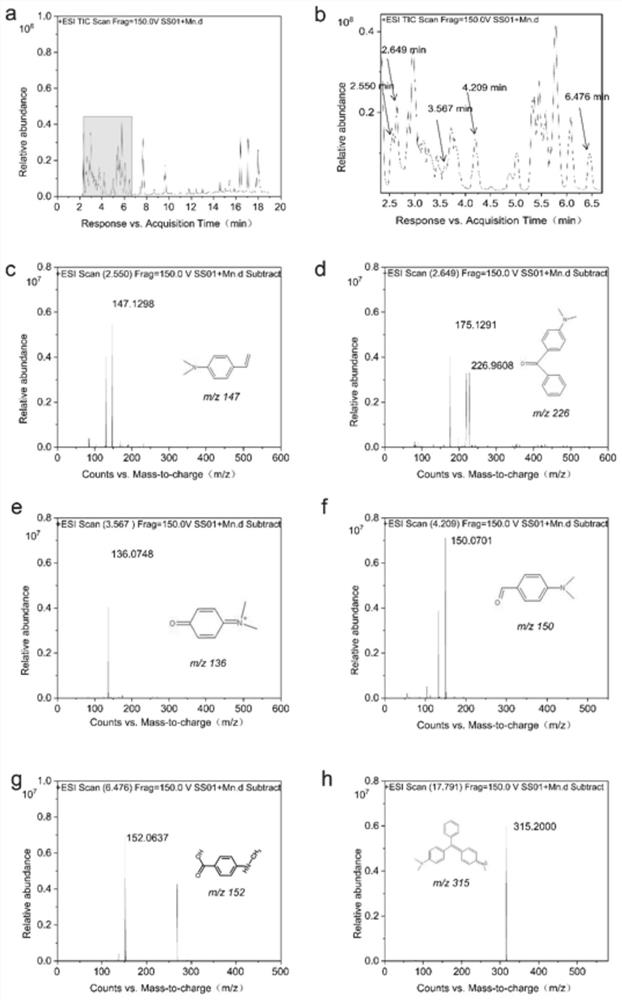
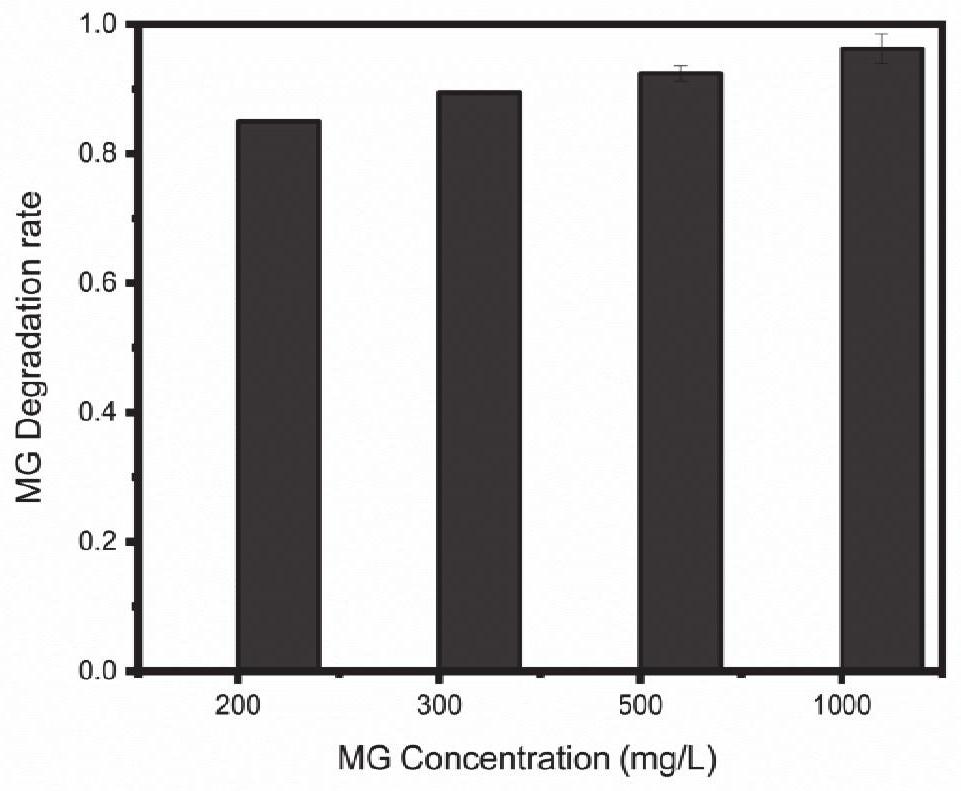
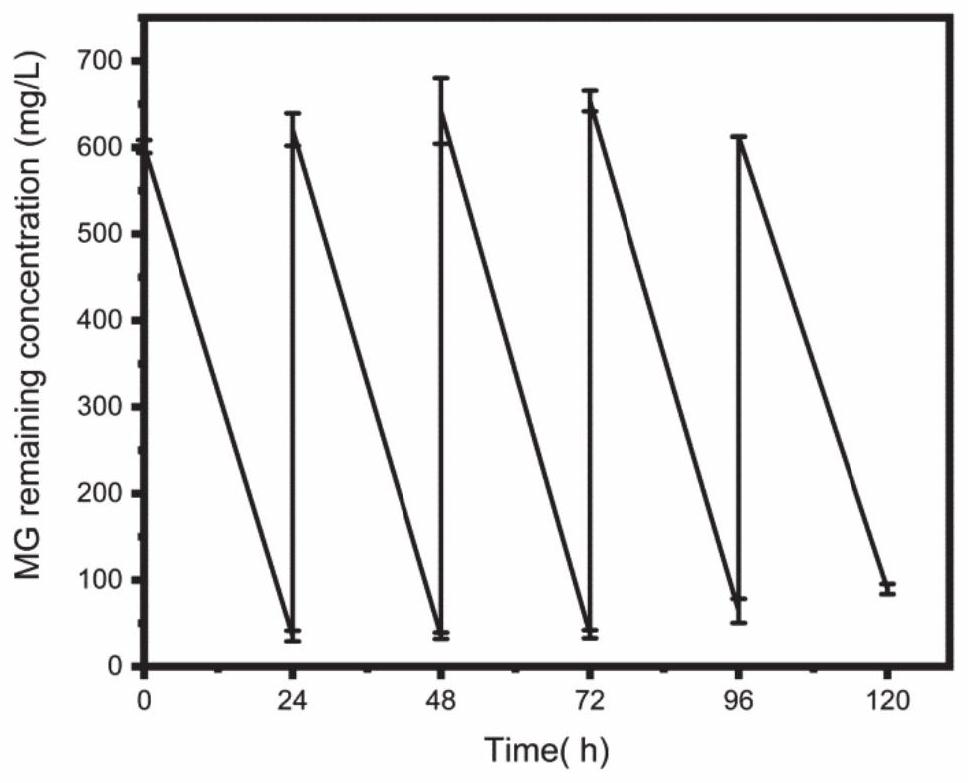
The invention relates to the technical field of environmental microorganisms, in particular to a pantoea, a bacterium manganese mixture and application of the bacterium manganese mixture in degradation of malachite green. The bacterial strain is preserved in the China Center for Type Culture Collection (called CCTCC for short, Luojia mountain on Bayi road, Wuchang District, Wuhan City, Hubei Province) on March 24, 2021, the preservation number is CCTCC M 2021491, the bacterial manganese mixture is formed by mixing Pantoea eucrina SS01 and a manganese oxidation product thereof, the Pantoea eucrina SS01 and a culture solution thereof are mixed with a manganese chloride solution for culture, and the cultured product is dried to obtain the bacterial manganese mixture. The bacteria-manganese mixture can rapidly degrade high-concentration malachite green and can continuously degrade the high-concentration malachite green, degradation products are nontoxic and harmless, the use cost is low, ecological restoration is good, the application prospect is extremely wide, and the practical problem that at present, triphenylmethane dye polluted water is difficult to treat can be solved.
Owner:SHANDONG NORMAL UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com