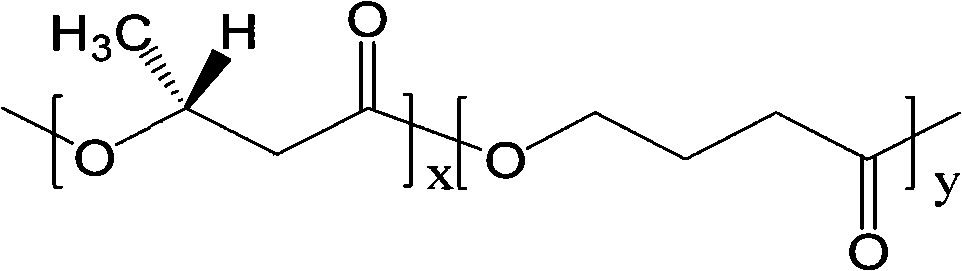
Engineering bacterium containing 2-ketoglutarate decarboxylase gene kgd and application thereof
A technology of engineering bacteria and genes, applied in the field of genetic engineering technology and fermentation, can solve the problems of high price, high cytotoxicity, cumbersome and complicated mixed carbon source fermentation strategy, etc., and achieve the effect of reducing production costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0041] Embodiment 1, construction plasmid pBHR68orfZ
[0042] 1. Double cut plasmid pCK3 with ClaI and EcoRI ( B, Gott schalk G. Mol ecular analysis of the anaerobic succinate degradation pathway in Clostridium kluyveri. J Bacteriol, 1996, 178: 871-880), a 1.8 kb fragment was recovered from the gel, containing the orfZ gene and its promoter sequence.
[0043] 2. Double cut plasmid pBHR68 with ClaI and EcoRI (Spiekermann P, Rehm BHA, Kalscheuer R, et al. A sensitive, viable-colony staining method using Nile red for direct screening of bacteria that accumulate polyhydroxyalkanoic acids and other lipid storage compounds. Arch Microbiol, 1999, 171:73-80), the gel recovered a fragment of 8.1 kb, which contained the phaCAB gene and its promoter sequence, the Amp resistance gene and replicon derived from pBluescript II SK (-).
[0044] 3. Use T4 DNA ligase to ligate the fragments recovered in step 1 and step 2; after the ligation reaction is completed, plasmid pBHR68orfZ is obtaine...
Embodiment 2
[0046] Embodiment 2, construction plasmid pMCS4HB
[0047] 1. Contains pyruvate decarboxylase promoter (referred to as P pdc ) construction of expression vector pPpdc
[0048]人工合成一段双链DNA,其序列如下所示:5′-tgataagaattccctaggactagtttacgctcatgatcgcggcatgtcctgatatttttcctctaaaaaagataaaaagtcttttcgcttcggcagaagaggttcatcatgaacaaaaattcggcatttttaaaaatgcctatagctaaatccggaacgacactttagaggtttctgggtcatcctgattcagacatagtgttttgaatataggatccgagctcaagcttagatctggtacctctagacgcccgccataaactgccaggcatcaaattaagcagaaggccatcctgacggatggcctttttgcgtttctacaaactcttcctgt
[0049] It contains a pyruvate decarboxylase promoter sequence from Mobilemonas, a multiple cloning site, and a transcription termination sequence. It was connected to T vector pMD19-T Simple (purchased from Japan Takara Company) by TA cloning method to obtain expression vector pPpdc.
[0050] 2. Cloning of 4hbD gene and construction of expression vector pPpdc4hbD
[0051] 1) Under standard polymerase chain reaction conditions, the plasmid pCK3 ( B...
Embodiment 3
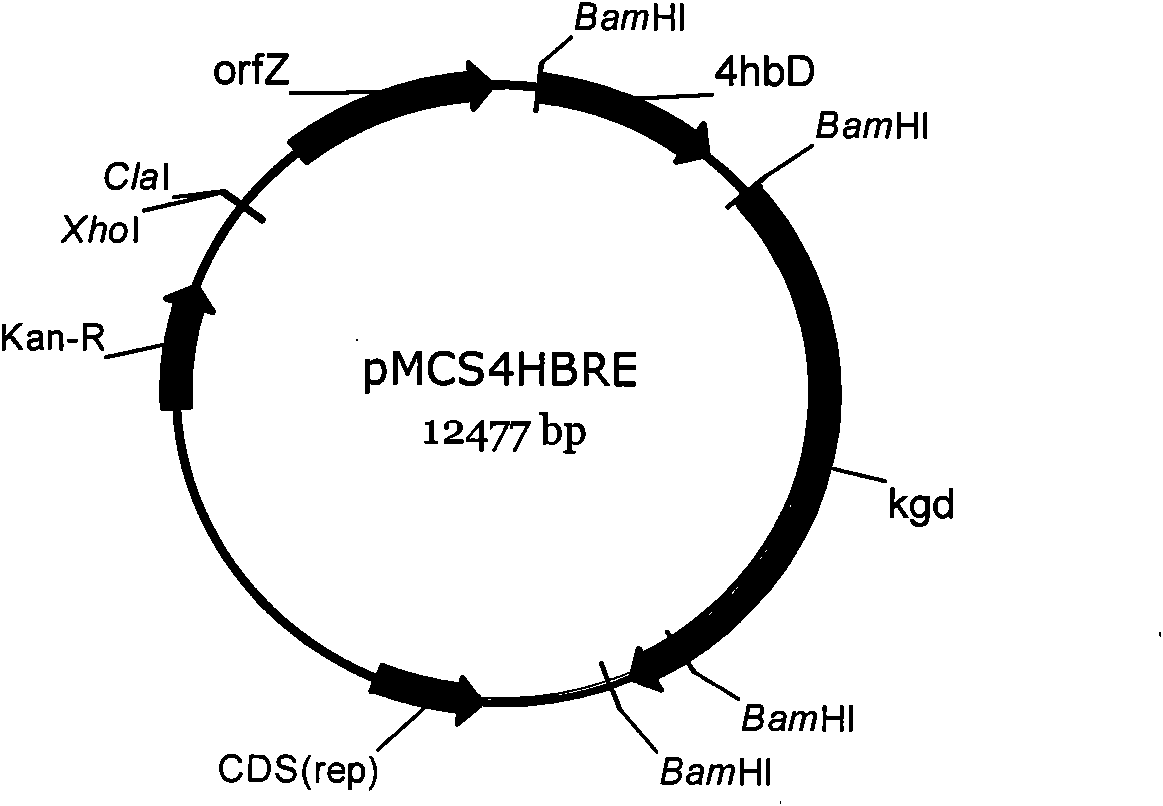
[0069] Example 3 Construction of plasmid pMCS4HBRE
[0070] 1. Double cut plasmid pCK3 with ClaI and EcoRI ( B, Gottschalk G. Molecular analysis of the anaerobic succinate degradation pathway in Clostridium kluyveri. J Bacteriol, 1996, 178: 871-880), a 1.8 kb fragment was recovered from the gel, containing the orfZ gene and its promoter sequence.
[0071] 2. The plasmid vector pBBR1MCS-2 (NCBI GenBank No. U23751) was double cut with ClaI and EcoRI to obtain a 5.1 kb DNA fragment as a vector.
[0072] 3. Use T4 DNA ligase to ligate the fragments recovered in step 1 and step 2; after the ligation reaction is completed, the plasmid pMCSorfZ is obtained. Introduced into E.coli JM109 (purchased from China General Microorganism Culture Collection Management Center) by electroporation, spread on LB-Km solid medium, and cultured at 37°C for 16h;
[0073] 4. Pick a single clone from LB-Km solid medium into LB-Km liquid medium, culture for 16h (37°C shaker, 200rpm), extract the plasm...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com