Flow cytometer apparatus for three dimensional diffraction imaging and related methods
A flow cytometer and cytometer technology, which is applied in the field of flow cytometer systems that can measure diffraction image signals and three-dimensional structural parameters, and can solve problems such as low signal-to-noise ratio, inability to apply image flow cytometers, and high particle flow rates. question
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
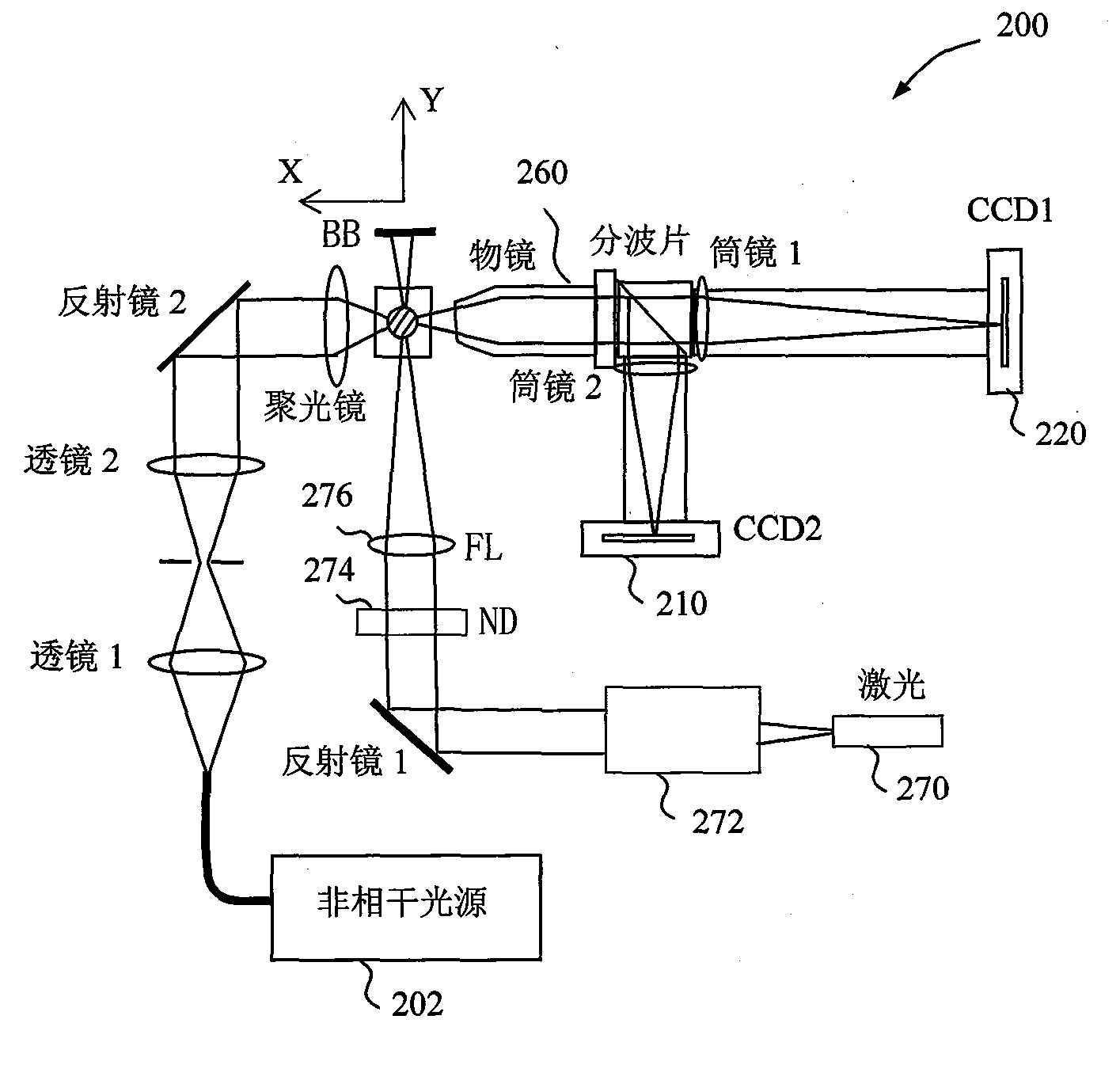
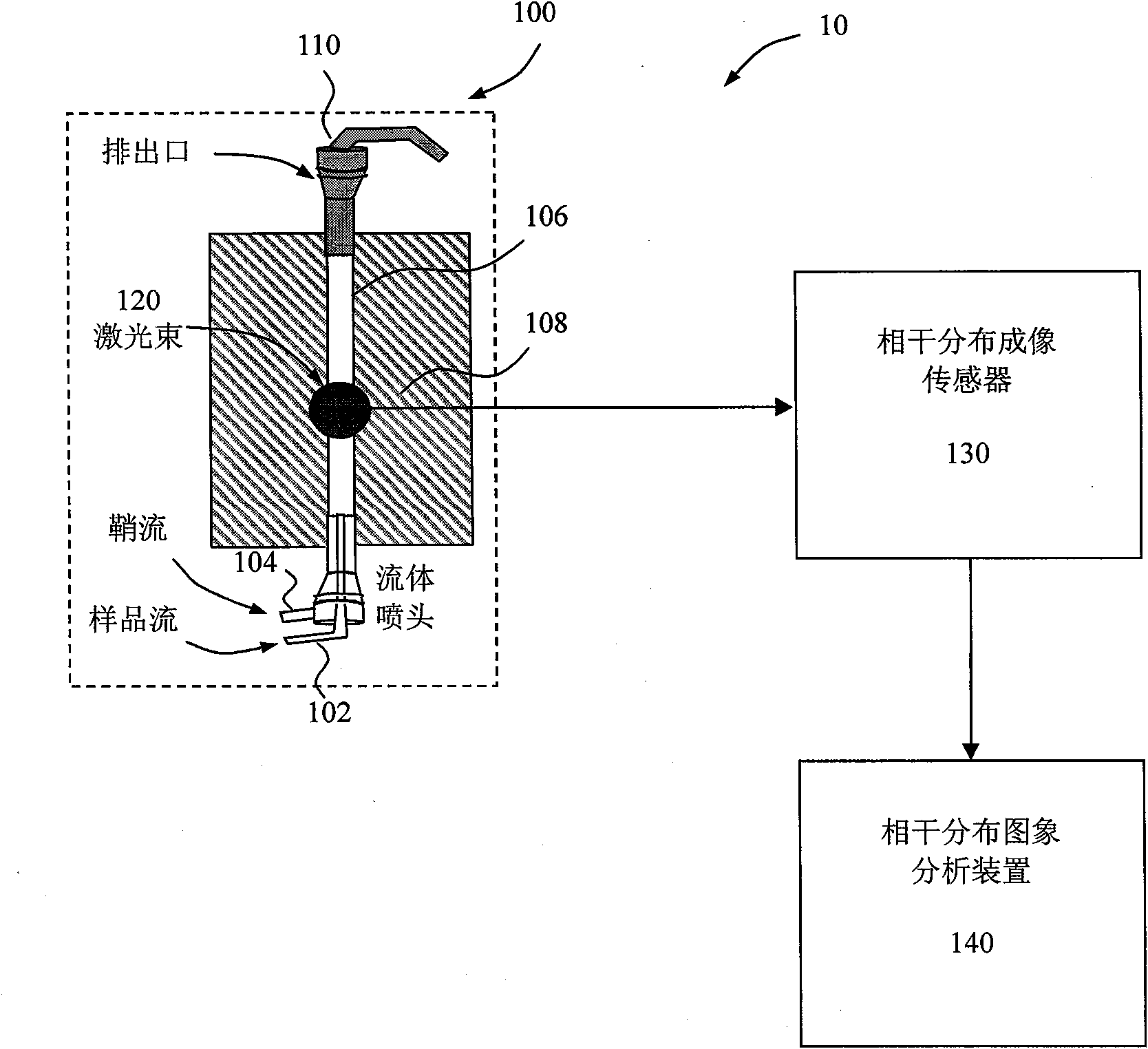
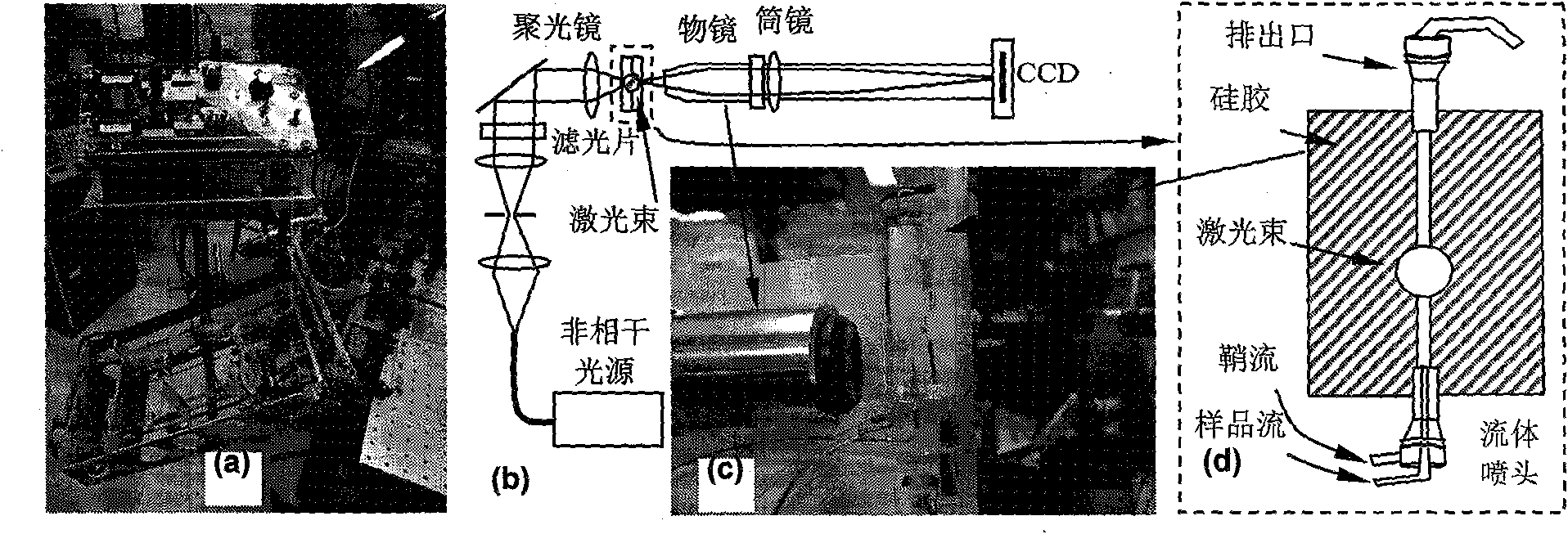
[0078] In order to extract more structural information from the elastically scattered light signal generated by particles excited by coherent scattered light, we fabricated a prototype microfluidic device-based flow cytometer to verify the use of a standard charge-coupled device A camera (Alta 2000, Apogee) measures the concept of diffraction images. The prototype is as Figure 6 a to Figure 6 As shown in d, its performance can reach the indicators listed in Table 1.
[0079] Table 1: Expected indicators of a dual-image microfluidic device-based flow cytometer
[0080] Flow rate adjustment range
0.01 to 0.50 m / s
Sample flow diameter adjustment range
20 to 150 microns
Half-angle width value of diffraction image measurement field of view*
32 degrees
Diffraction image measurement center angle value of field of view
5 degrees, 45 degrees to 135 degrees, 180 degrees
Lateral Resolution of Incoherent Image Measurement Field of V...
example 2
[0086] Figure 9 It is a schematic diagram of scattered light generated when a monochromatic coherent light beam is incident on a particle with a non-uniform internal optical refractive index n(r, λ), where r is the position coordinate vector, and λ is the incident and scattered light wavelengths (both are the same). The spatial coherence between scattered light fields results in a characteristic scattered light distribution, which can be measured as a diffraction (spatial domain) or speckle (spatial or temporal domain) image. Utilizing accurate wave models based on solutions of Maxwell's equations or wave equations can train pattern recognition software and potentially extract the light-refractive index distribution and associated 3D structural information inside scattered particles or cells from distributions representing elastically scattered light or from diffraction image data. The refractive index distribution function n(r, λ) inside the cell is related to its structure ...
example 3
[0090] We randomly selected 40 NALM-6 cultured cells at different growth cycle stages to establish a database that can be used as a training cell classification. Fluorescent microscopic image data of these cells were obtained after staining using a confocal microscope (model LSM 510, Zeiss). The reconstructed three-dimensional structure of cells can be used in two ways. One is to input into the differential time-domain parallel computing software to simulate and calculate the angular distribution of scattered light of cells excited by coherent light beams. The second is to analyze and define a variety of structural feature categories of cells, which are used to develop image pattern recognition software with cell classification functions. The light scattering process of a single biological cell can be considered as a problem of a plane electromagnetic wave incident on a dielectric particle placed in the host medium. To account for the change in polarization of scattered ligh...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| refractive index | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com