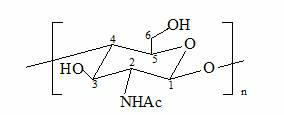
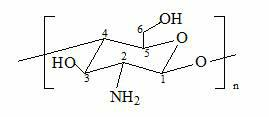
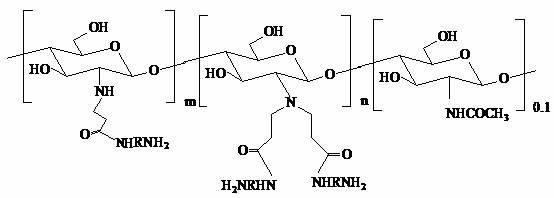
Branching polyamino chitosan derivative and preparation method thereof
A branched polyamine-based shell and chitosan-forming technology is applied in the field of derivatives of natural polymer compounds and their preparation, and can solve the problems of anti-swelling, poor solubility, and limiting the wide application of chitosan. , to achieve the effect of increasing the amino content
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0038] (a) Dissolve 0.02mol chitosan in an organic acid solution (containing 0.02mol acetic acid) at (W / V) 1:30, stir until completely dissolved, dissolve 0.04mol ethyl acrylate in 10ml methanol, and then add 0.006mol triethanolamine, stirred and reacted at 40°C for 5 days, added sodium bicarbonate to adjust the pH to 7-8, removed most of the water by vacuum low-temperature rotary evaporation, precipitated solids with absolute ethanol, suction filtered, washed several times, vacuum Dry to obtain N-carbonyl ethyl chitosan ethyl ester.
[0039] (b) Take 0.01mol of N-carbonylethyl chitosan ethyl ester and 0.01mol of ethylenediamine in a flask, add 40ml of methanol, stir and react at 45°C for 3 days, filter with suction, wash several times, and dry in vacuum to obtain 1st generation branched polyamine-based chitosan.
[0040] (c) Repeat the above reaction to generate more than two generations of hyperbranched chitosan.
Embodiment 2
[0042] (a) Dissolve 0.02mol chitosan in an organic acid solution (containing 0.02mol formic acid) at (W / V) 1:80, stir until completely dissolved, dissolve 0.1mol methyl acrylate in 25ml ethanol, and then add 0.005mol triethylamine, stirred and reacted at 60°C for 2 days, then added sodium bicarbonate to adjust the pH to 7-8, removed most of the water by vacuum low-temperature rotary evaporation, precipitated solid with ethanol, suction filtered, washed several times, vacuum Dry to obtain N-carbonyl ethyl chitosan methyl ester.
[0043] (b) Take 0.01 mol of N-carbonylethyl chitosan methyl ester and 0.03 mol of butanediamine in a flask, then add 50ml of ethanol, stir and react at 60°C for 1.5 days, filter with suction, wash several times,
[0044] Vacuum-dried to obtain the first-generation branched polyamine-based chitosan.
[0045] (c) Repeat the above reaction to generate more than two generations of hyperbranched chitosan.
Embodiment 3
[0047](a) Dissolve 0.02mol chitosan in (W / V) 1:100 in organic acid solution (containing 0.022mol malic acid), stir until completely dissolved, dissolve 0.012mol ethyl acrylate in 20ml ethanol, and then Add 0.01mol triethylamine, stir and react at 70°C for 2 days, then add sodium bicarbonate to adjust the pH to 7-8, remove most of the water by vacuum and low-temperature rotary evaporation, precipitate the solid with acetone, filter it with suction, and wash it several times. Vacuum drying to obtain N-carbonyl ethyl chitosan ethyl ester.
[0048] (b) Take 0.01mol of N-carbonylethyl chitosan ethyl ester and 0.04mol of diethylenetriamine in a flask, then add 70ml of methanol, stir and react at 40°C for 1.5 days, filter with suction, wash several times, and dry in vacuum. The 1st generation branched polyamine-based chitosan was obtained.
[0049] (c) Repeat the above reaction to generate more than two generations of hyperbranched chitosan.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com