Novel process for producing high-purify magnesium oxide from salt lake brine
A salt lake brine and magnesium oxide technology, applied in the fields of magnesium oxide, inorganic chemistry, alkali metal chloride, etc., can solve the problems of unstable composition of basic magnesium carbonate, huge equipment, waste of magnesium resources, etc., and achieve product quality and stability, Ease of mass production and high product quality
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
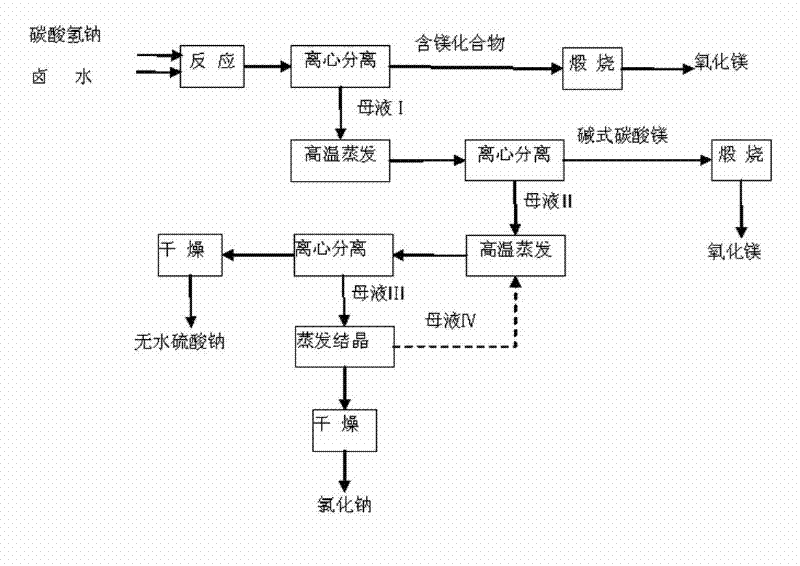
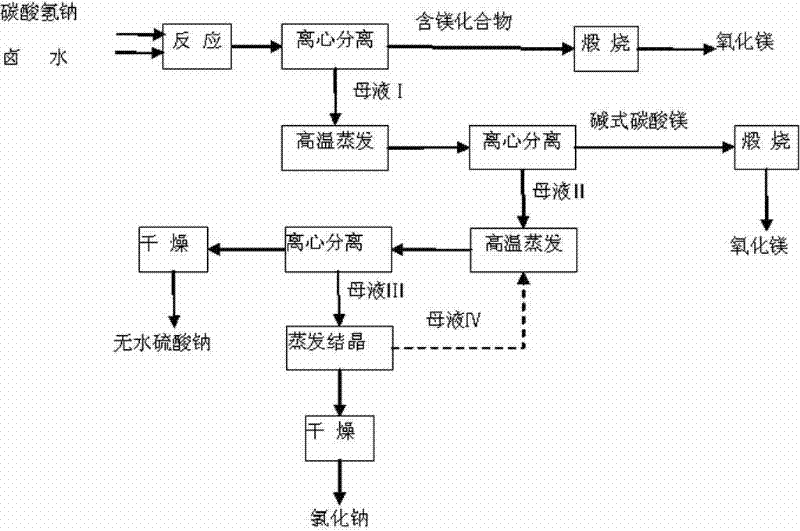
[0021] Filter the brine with diatomaceous earth and react with sodium bicarbonate, the equivalent ratio of magnesium ions to bicarbonate ions is 1:2.02 (or 1:2.03, or 1:2.04, or 1:2.05), and the brine Slowly add it into a saturated sodium bicarbonate solution at 80°C under stirring, react at this temperature for 2 hours, and keep it for 2 hours. After suction filtration, the intermediate product basic magnesium carbonate and mother liquor I are obtained. After washing with deionized water 50 times (or 20 times, or 30 times, or 40 times) the mass of magnesium, calcining at 900°C (or 850°C, or 800°C) for 4 hours (or 2 hours, or 3 hours) to obtain high-purity magnesium oxide products.
[0022] After the mother liquor Ⅰ is directly evaporated and concentrated, it is centrifuged to obtain basic magnesium carbonate and mother liquor Ⅱ. After the above two-step reaction, the conversion rate of magnesium can reach 98%. According to Na + / / SO 4 2- , Cl - —H 2 O ternary phase dia...
Embodiment 2
[0024] Take Mg 2+ 1L of brine with a content of 40g / L and 228g of NaHCO 3 Under the condition of heat preservation at 65°C, the brine was slowly added to the saturated solution of sodium bicarbonate, under stirring at a speed of 30 rpm, the reaction was carried out for 2 hours, and after 2 hours of heat preservation and aging, the solid-liquid separation was carried out. The intermediate product basic magnesium carbonate 500g and mother liquor I were obtained. After washing basic magnesium carbonate with 3.5L of deionized water, the filter cake was calcined at 900°C for 4 hours to obtain 57.7g of magnesium oxide with a mass of 99.13%.
[0025] After directly evaporating and concentrating 1.65L of mother liquor I, centrifuged to obtain 70g of basic magnesium carbonate and 0.67L of mother liquor II. After basic magnesium carbonate was washed, it was calcined at 900°C for 4 hours to obtain 7.8g of magnesium oxide, according to Na + / / SO 4 2- , Cl - —H 2 O ternary phase dia...
Embodiment 3
[0027] Take Mg 2+ 1L of brine with a content of 38g / L and 210g of NaHCO 3 Under the condition of a temperature of 70°C, the brine was slowly added to the saturated solution of sodium bicarbonate, and the reaction was carried out for 2.5 hours under stirring at a speed of 35 rpm. 480 g of intermediate product basic magnesium carbonate and mother liquor I were obtained. After washing basic magnesium carbonate with 3.0L of deionized water, the filter cake was calcined at 850°C for 3 hours to obtain 55.7g of magnesium oxide with a mass of 99.05%.
[0028] After directly evaporating and concentrating 1.55L of mother liquor I, centrifuged to obtain 68g of basic magnesium carbonate and 0.62L of mother liquor II. After basic magnesium carbonate was washed, it was calcined at 900°C for 4 hours to obtain 7.2g of magnesium oxide, according to Na + / / SO 4 2- , Cl - —H 2 O ternary phase diagram After evaporating and concentrating the mother liquor II, centrifuge to obtain 120.8 g of...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com