Self-solidified microspheres and preparation method and application thereof
A self-curing, microsphere technology, applied in cosmetic preparations, fixed on/in organic carriers, pharmaceutical formulations, etc., can solve the problem of reducing the uniformity of microsphere particle size, difficulty in droplet shedding, slow emulsification speed, etc. problems, to achieve the effect of maintaining activity, facilitating diffusion, and the preparation method is simple and mild
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
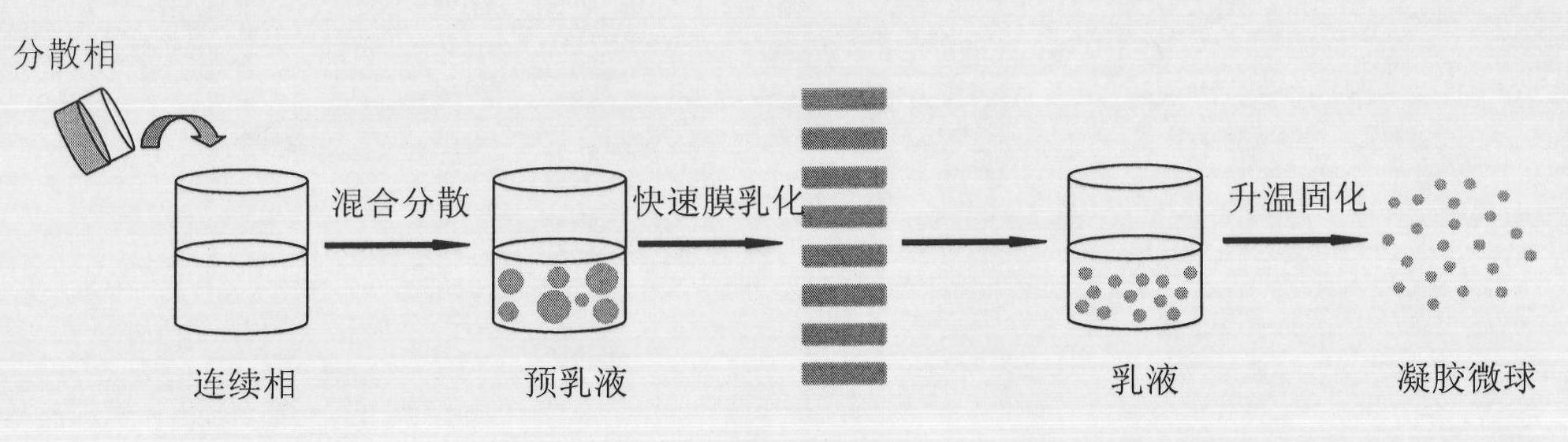
[0059] The method for preparing the above-mentioned self-curing microspheres of the present invention comprises the steps of:
[0060] (1) Provide a solution of a temperature-sensitive material added with a biologically active substance or a functional component as a dispersed phase;
[0061] The active substance or functional ingredient must be completely dissolved or uniformly dispersed in the dispersed phase in step 1, and the functional ingredient can be selected from proteins, polypeptides, enzymes, vaccines, cells, genes, hormones, antibiotics, anticancer drugs One or more of animal and plant extracts and their mixtures, the concentration of functional components in the dispersed phase is 0-10g / mL. The concentration of the functional components in step 1 may be 0 g / mL, and blank microspheres are prepared at this time.
[0062] In some embodiments of the method of the present invention, the solution of the thermosensitive material in step 1 is chitosan-glycerophosphate m...
Embodiment 1
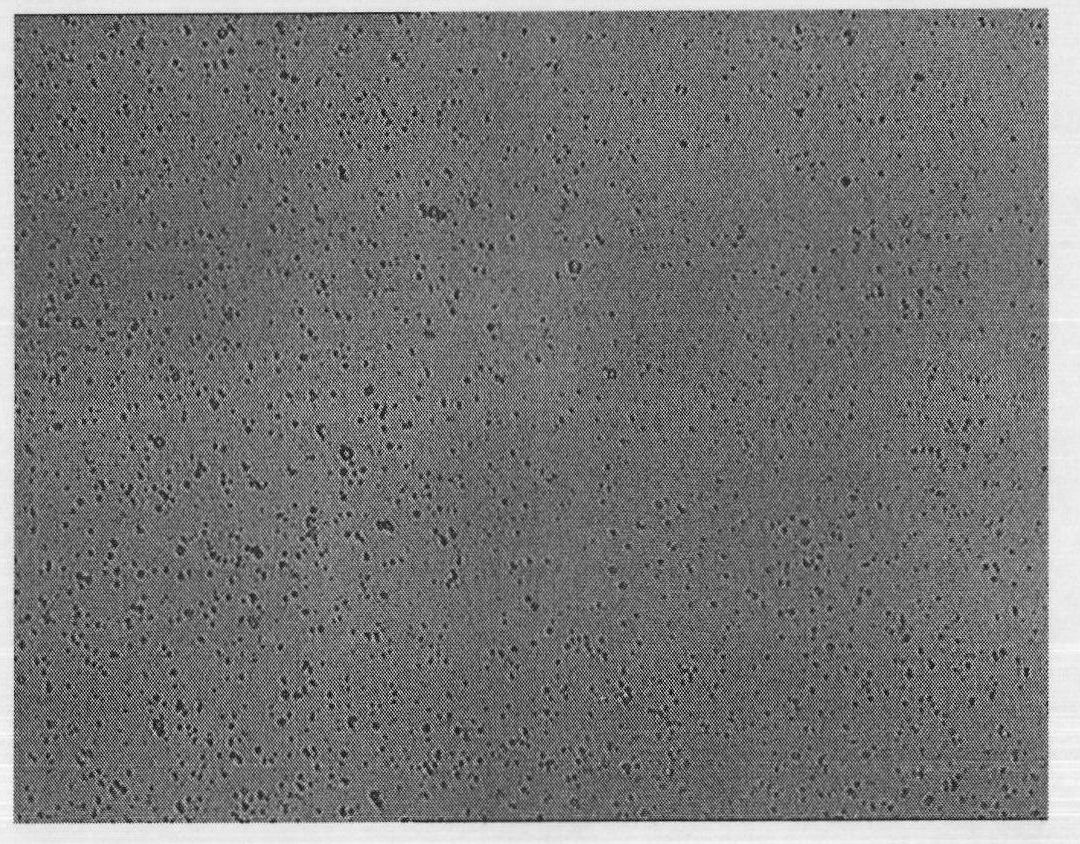
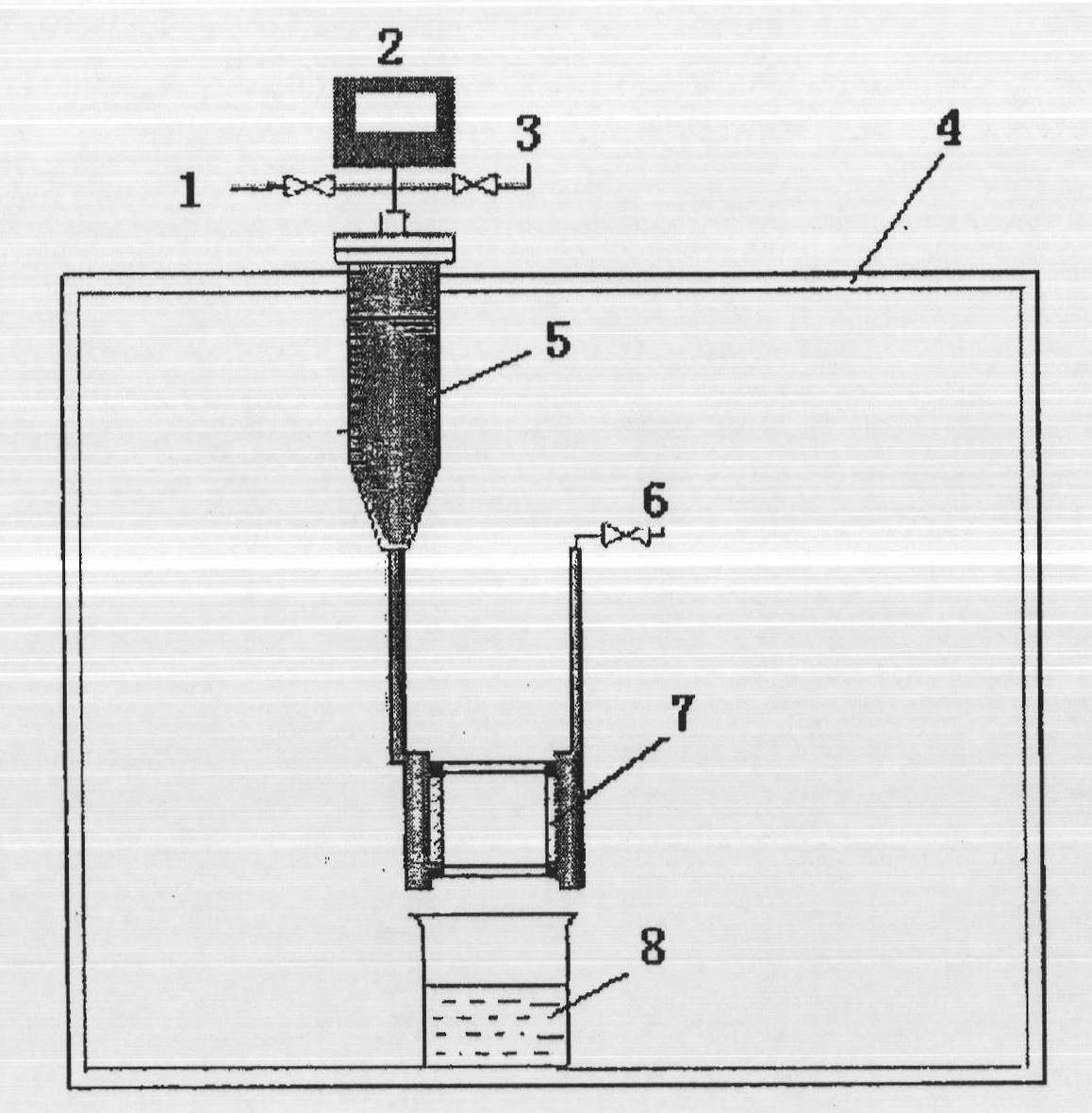
[0094] Hydrophobic modification of the membrane: soak the hydrophilic SPG membrane with a pore size of 1.4 μm in the mixed oil phase of liquid paraffin and petroleum ether (petroleum ether boiling range is 60-90°C, volume ratio 5:7) overnight to make the membrane pores Fully moist.
[0095] Dispersed phase preparation: temperature sensitive material selects chitosan-glycerophosphate system, and its preparation method is: accurately weigh a certain amount of chitosan and dissolve in 9mL acetic acid solution (0.1mol / L), make it under magnetic stirring Fully dissolve to obtain chitosan acetic acid solution; another certain amount of sodium glycerophosphate is dissolved in 1mL deionized water. After the chitosan acetic acid solution and the sodium glycerophosphate solution were incubated at 4°C for 10 minutes, the sodium glycerophosphate solution was slowly added dropwise to the chitosan acetic acid solution, and magnetically stirred (300 rpm, 10 minutes) to mix them evenly. The ...
Embodiment 2
[0099] Chitosan microspheres are prepared using the same device and method as in Example 1, wherein the difference is that the membrane aperture of the SPG membrane used is 10.2 microns, and the hydrophobic modification step of the membrane is: the hydrophilic SPG membrane is placed in pure water at normal temperature Sonicate for 30 minutes, then put into 3% (V / V) modifier KP-18C (origin: Japan) aqueous solution, then depressurize (vacuum degree: 0.5MPa) sonicate for 2h, and then heat at 120°C for 4h.
[0100] Dispersed phase: the concentration of chitosan in the dispersed phase is 0.8wt.%, the concentration of sodium glycerophosphate in the dispersed phase is 8.0wt.%, the solvent is a hydrochloric acid solution of 0.1mol / L, and its LCST is 60°C.
[0101] Continuous phase: The continuous phase is a mixture (volume ratio of 2:1) of liquid paraffin and petroleum ether (the boiling range of petroleum ether is 90-120°C), the emulsifier is polyoxyethylene hydrogenated castor oil, a...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com