Preparation method for stannum, indium and stibium series lead-free solder tinning copper strip used for solar battery
A solar cell, tin, indium and antimony system technology, applied in circuits, electrical components, final product manufacturing, etc., can solve the problems of high waste liquid treatment cost, serious environmental pollution, and few applications, and achieve extended fatigue life and interface bonding. Good, lower melting enthalpy effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
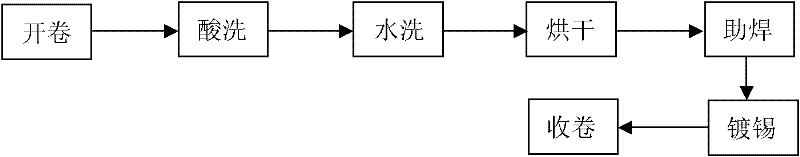
[0025] Pure tin, indium, and antimony are weighed in a mass ratio of 99:0.5:0.5, and the antimony and tin are heated and melted in a melting furnace at a ratio of 1:10 to form a tin-antimony master alloy. The remaining tin and indium are heated and melted to form a tin-antimony master alloy. Then heat and melt the two intermediate alloys, stir and water-cool at the same time to obtain Sn-0.5%In-0.7%Sb lead-free solder. Then it is dip-plated on the copper strip to form a tin-plated copper strip under the conditions of the traditional hot-dip plating production process, such as figure 1 Shown: pickling is to clean the copper strip in hydrochloric acid with a concentration of 10%, and water washing is to clean it in pure water, both of which are to remove the oxide layer and impurities on the surface of the copper strip. After drying, pass the copper strip through a container containing flux, and then through a tin melting furnace. The temperature of the tin melting furnace shou...
Embodiment 2
[0027] Sn, indium and antimony with a purity of 99.99% are weighed in a mass ratio of 96:1.5:2.5, antimony and tin are heated and melted in a smelting furnace at a ratio of 1:10 to form a tin-antimony master alloy, and then water-cooled and solidified. The remaining tin and indium are heated and melted in a smelting furnace to form a tin-antimony master alloy. Then heat and melt the two intermediate alloys in a melting furnace to obtain Sn-1.5%In-2.5%Sb lead-free solder. It is then dip-plated on copper strips to form tinned copper strips under conventional hot-dip plating production process conditions. Its microstructure is as image 3 As shown, the matrix in the alloy structure is β-Sn phase. Due to the high content of In and Sb, a large number of granular and rod-shaped intermetallic compounds InSb are distributed on the matrix. The particles are InSb phase, the alloy has a lower melting point (186°C), which is close to the traditional Sn-Pb solder for tin plating, and has...
Embodiment 3
[0029] Pure tin, indium and antimony are weighed in a mass ratio of 83:9:8, antimony and tin are heated and melted in a melting furnace at a ratio of 1:10 to form a tin-antimony master alloy. The remaining tin and indium are heated and melted in a smelting furnace to form a tin-antimony master alloy, which is then cooled and solidified. Then heat and melt the two intermediate alloys in a melting furnace to obtain Sn-9%In-8%Sb lead-free solder. It is then dip-plated on copper strips to form tinned copper strips under conventional hot-dip plating production process conditions. Its microstructure is as Figure 4 As shown, the matrix in the alloy structure is β-Sn phase, and granular and rod-shaped intermetallic compounds InSb are distributed on the matrix. The particles are InSb phase, with a melting point of about 191°C, high hardness and tensile strength, and good ductility, which meets the basic requirements of solar cells for the current-carrying capacity of the busbar, and...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com