Lipase nano-sized polymer biocatalyst particle and preparation method thereof
A nano-polymer and bio-catalysis technology, applied in the field of lipase nano-polymer bio-catalysis particles and their preparation, can solve the problems of restricted application, high cost of modifiers, long time-consuming intermediate separation steps, etc., and is convenient for industrial production and scale-up. , The effect of reducing production costs and avoiding losses
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0026] Embodiment 1, One-pot method prepares lipase nano-polymer biocatalytic particles
[0027] The raw materials are in parts by weight: 10 parts of lipase, 200 parts of enzyme modifier (glycidyl methacrylate), 250 parts of vinyl monomer (acrylamide), and the initiator system is 15 parts of ammonium persulfate and 12 parts of N, A mixture of N,N',N'-tetramethylethylenediamine.
[0028] The above lipase was dissolved in 5000 parts by mass of pH 4, 50 mM acetic acid buffer, an enzyme modifier (50% v / v dimethylformamide solution) was added, and the reaction was carried out at 30° C. for 2 hours. After adding 250 parts of acrylamide to dissolve and adding the above-mentioned initiator system, the reaction was continued at 30°C for 12 hours under stirring conditions, and then the reaction solution was placed in a dialysis bag with a molecular weight cut-off of 10KDa. Dialyze in the liquid for 24 hours, collect the liquid after dialysis and freeze-dry to obtain the target product...
Embodiment 2
[0045] Example 2, One-pot method to change monomer feeding time to prepare lipase nano-polymer biocatalytic particles
[0046] Raw materials are in parts by weight: 10 parts of lipase, 200 parts of enzyme modifier (glycidyl methacrylate), 250 parts of vinyl monomer (acrylamide), 15 parts of ammonium persulfate and 12 parts of N , a mixture of N,N',N'-tetramethylethylenediamine.
[0047] Add the above lipase, enzyme modifier (50% v / v dimethylformamide solution) and 250 parts of acrylamide into 50 mM acetic acid buffer solution with pH 4, and react at 30°C for 2 hours. Then add the above-mentioned initiator system to initiate free radical polymerization, continue to react for 12 hours under stirring conditions, then place the reaction solution in a dialysis bag with a molecular weight cut-off of 10KDa, and dialyze in pH 7, 50mM phosphate buffer for 24 hours, collect After dialysis, the liquid is freeze-dried to obtain the target product lipase nano-polymer biocatalytic particle...
Embodiment 3
[0049] Embodiment 3, One-pot method changes the dosage of modifier
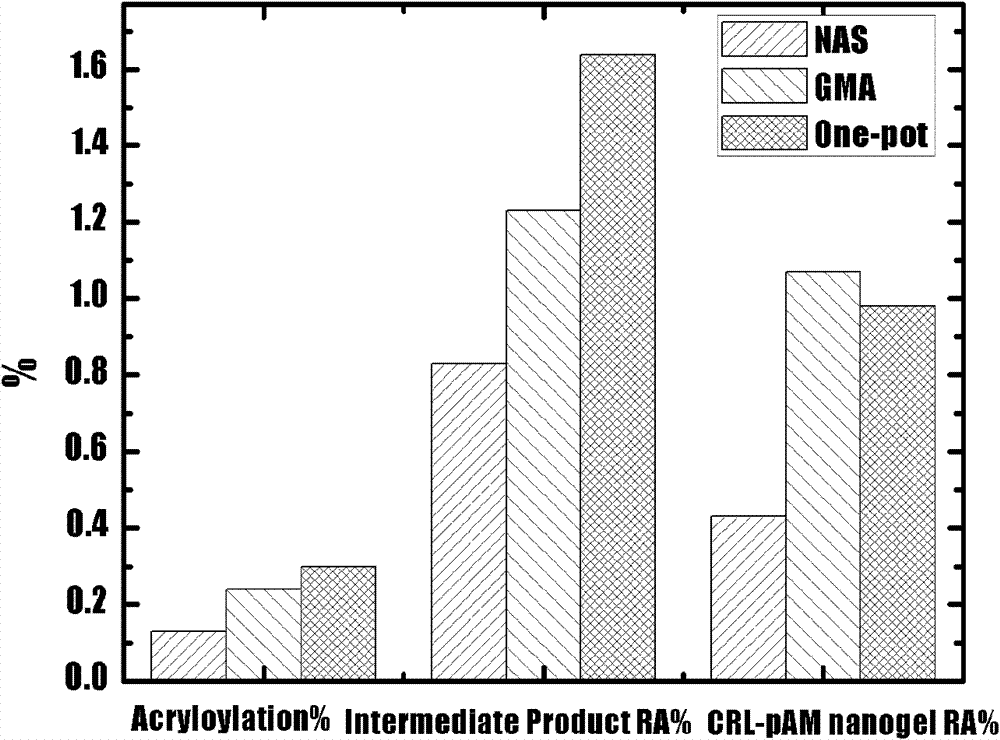
[0050] Change the dosage of the modifier in Example 1 to 2-200 parts of glycidyl methacrylate respectively, and the rest of the formula and steps are the same as in Example 1. At this time, the obtained product uses p-nitrophenol palmitate as a substrate to measure the total yield of biocatalytic activity of nano-polymer biocatalytic particles and the yield of polymerization reaction as follows: Figure 5 shown.
[0051] Wherein, the overall polymerization yield (Nanogel yield%) is equivalent, and the total yield of biocatalytic activity is reflected in the remaining relative enzyme activity of the product (CRL-pAM nanogel RA%). At low dosage of modifier, the yield of lipase nanogel is low due to the insignificant enzyme activity activation phenomenon. When the dosage of modifier exceeds 50 parts, the enzyme activity activation phenomenon begins to appear, and the enzyme activity yield begins to increase. I...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com