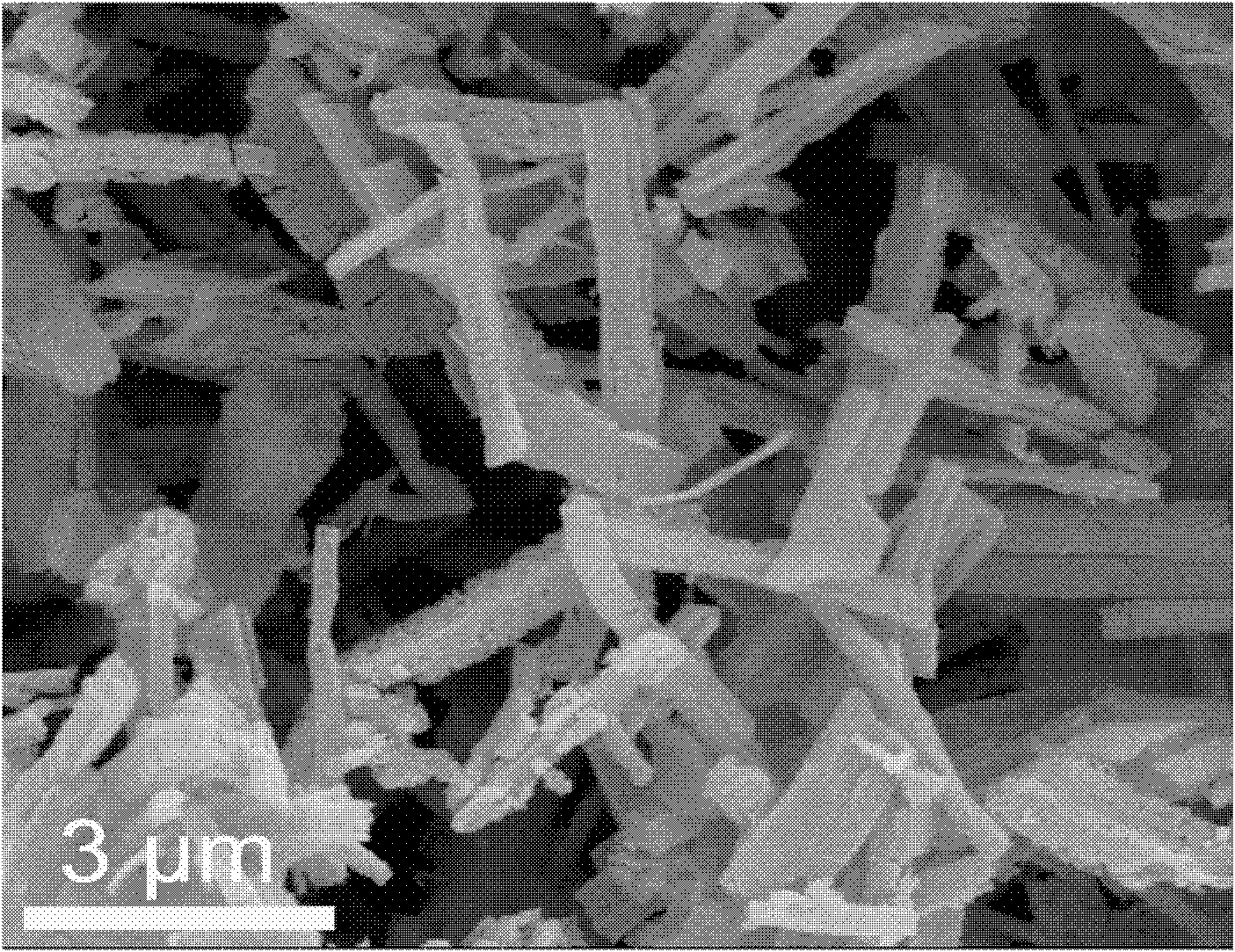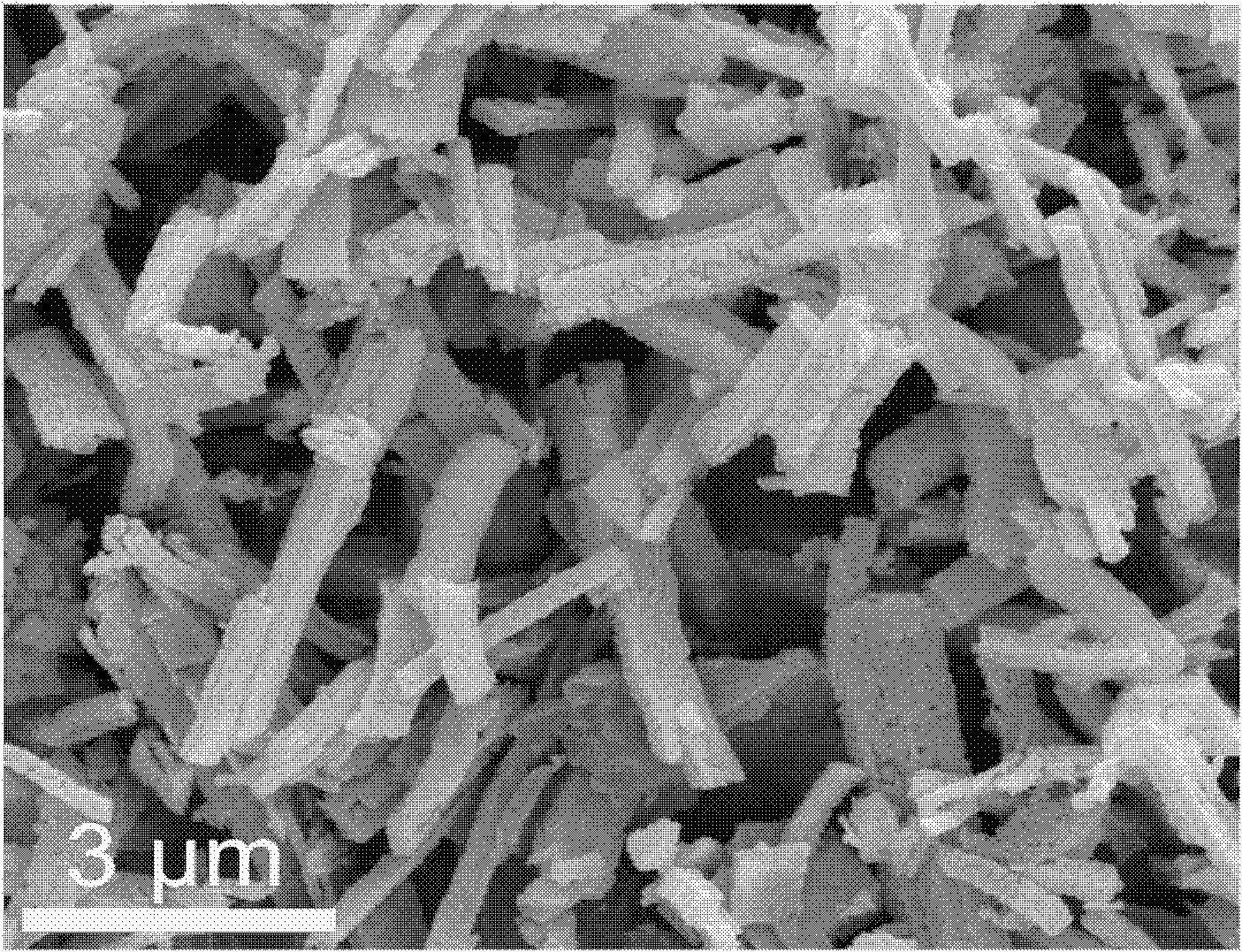A kind of porous structure lithium manganate electrode material and preparation method and application
A porous structure and electrode material technology, applied in battery electrodes, structural parts, circuits, etc., to achieve the effects of suppressing capacity decay, high rate performance and cycle performance, and easy implementation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0036] Example 1 : Preparation of Porous LiMnO Nanorods
[0037] Add 7.5 mL of 0.8 M oxalate to a mixed solution consisting of 4 g of cetyltrimethylammonium bromide, 150 mL of cyclohexane, and 5 mL of n-pentanol, and stir at room temperature for 30 min to form a transparent microemulsion . Then 2.5 mL of 0.2 M manganese nitrate solution was added to the microemulsion and stirred for 12 hours. The reaction product was centrifuged, separated and washed to obtain a white powder. The white powder was decomposed at 450 °C to obtain a black product, and the black powder and lithium hydroxide were thoroughly mixed at a molar ratio of 1:1.02 and then calcined in air at 500 °C to obtain the target product.
[0038] figure 1 is a scanning electron microscope image of the porous nanorod, which shows that the porous nanorod has a diameter of about 300-500 nm and a length of about 2-5 μm.
Embodiment 2
[0039] Example 2 : Preparation of Porous LiMnO Nanorods
[0040] The preparation of lithium manganate porous nanorods is basically the same as in Example 1. The difference is that the black powder and lithium hydroxide are fully mixed according to the molar ratio of 1:1.02, and then calcined in air at 600 °C to obtain the target product.
[0041] figure 2 It is a scanning electron microscope image of the porous nanorod, which shows that its shape and size are similar to those of the material prepared according to the method described in Example 1.
Embodiment 3
[0042] Example 3 : Preparation of Porous LiMnO Nanorods
[0043] The preparation of lithium manganate porous nanorods is basically the same as in Example 1. The difference is that the black powder and lithium hydroxide are fully mixed according to the molar ratio of 1:1.02, and then calcined in air at 700 °C to obtain the target product.
[0044] image 3 is the scanning electron microscope image of the porous nanorod, Figure 4 It is a transmission electron microscope image of the porous nanorod, which shows that the shape and size of the lithium manganate sample prepared according to the method described in Example 3 are similar to those prepared according to the method described in Example 1, and the lithium manganate sample It is composed of tiny nanoparticles.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com