High-yield strain of high temperature resistant 1,4-beta-D-xylanase, method for producing high temperature resistant 1,4-beta-D-xylanase through fermentation of high-yield strain, and high temperature resistant 1,4-beta-D-xylanase
A technology of xylanase and high-yield strains, which is applied in the field of biotechnology and engineering, can solve problems such as application limitations, and achieve good stability and broad application prospects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0059] Screening Example 1: Screening and identification of xylanase-producing strains
[0060] (1) Enrichment culture
[0061] Take 0.1g of soil sample, add it into 10mL of sterile water, shake and mix well, then pipette 1mL of bacterial suspension into 5mL of enrichment medium, and incubate in a 37°C water bath for 48h with shaking.
[0062] (2) Primary screening by transparent circle method
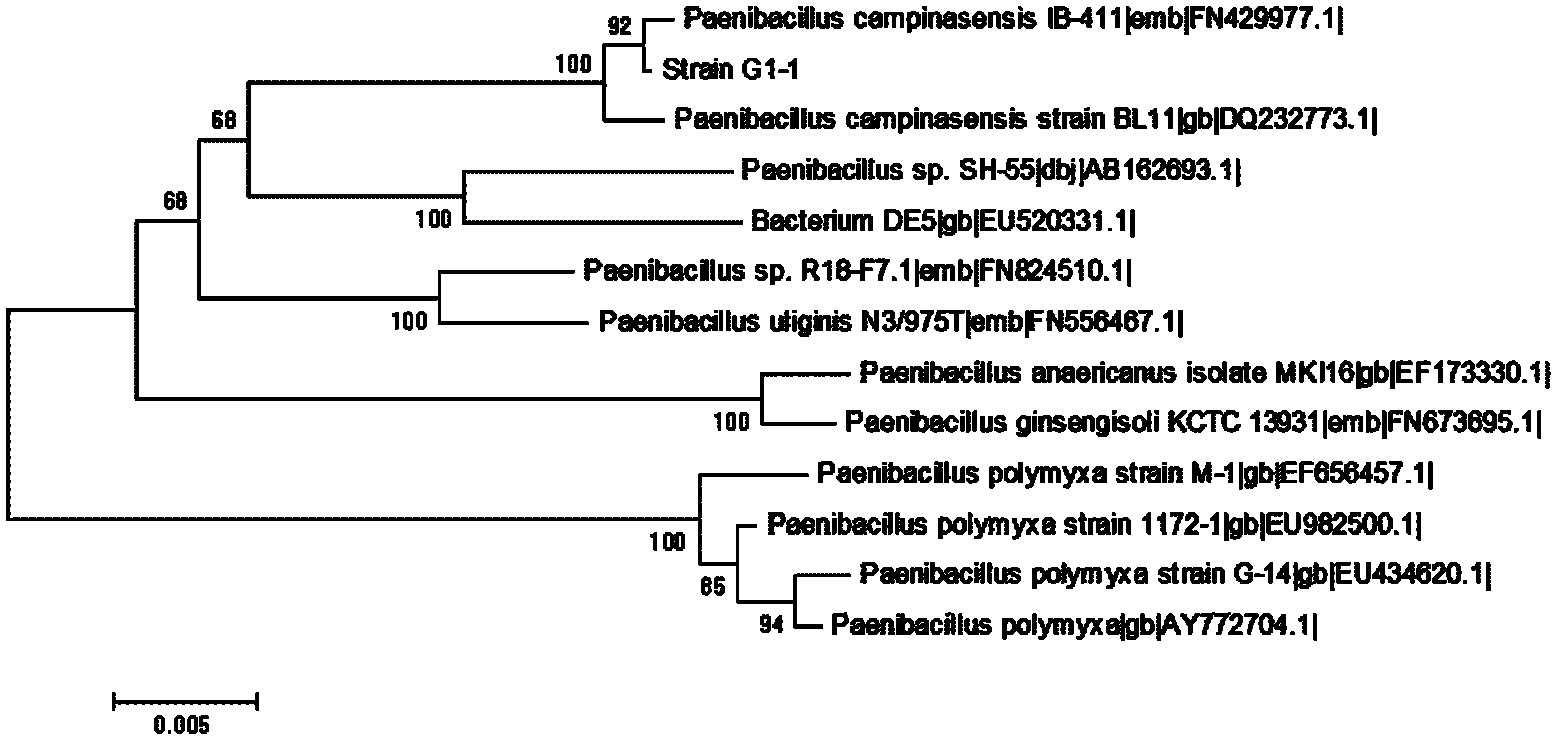
[0063] Dilute the enriched culture 10-fold step by step, and take the dilution factor as 10 -3 , 10 -5 and 10 -7 0.5 mL of the bacterial suspension was spread on the selective medium plate, cultured at 37°C for 24 hours, and single colonies with relatively large transparent circles were picked for isolation and purification ( figure 1 ), access to the slant medium to preserve the original strains.
[0064] (3) Shake flask fermentation re-screening
[0065] Inoculate the primary screened strains in 50mL seed medium, cultivate overnight at 37°C, 180rpm, take 1mL of the overnight cu...
Embodiment 2
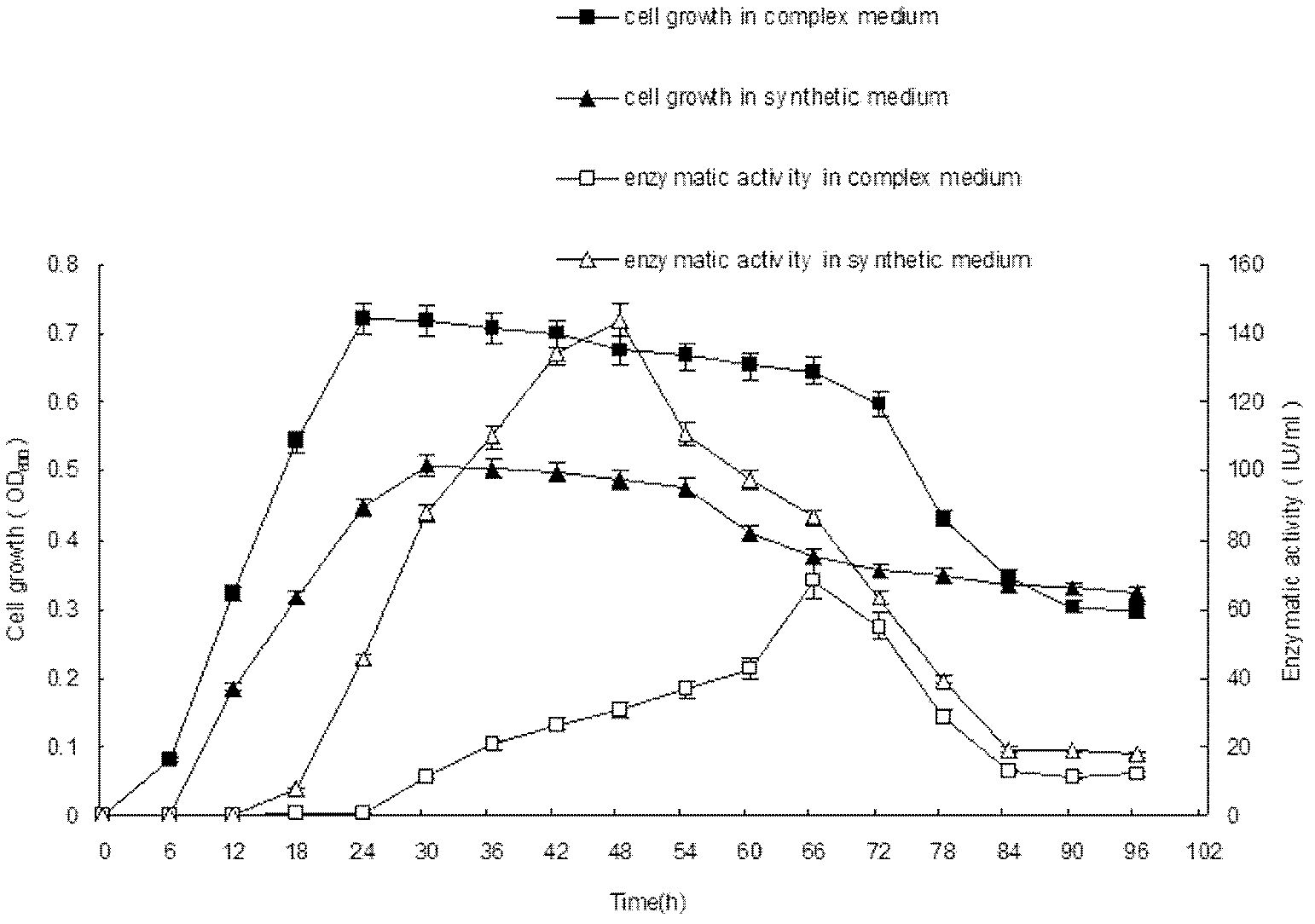
[0068] Enzyme Activity Example 2: Study on Fermentation Conditions and Enzyme Production Activity of P. campinasensis G1-1
[0069] (1) The assay method for xylanase activity is (DNS method):
[0070] Draw 0.1mL of appropriately diluted enzyme solution into a 5mL stoppered scale test tube, then add 0.1mL of 10g / L xylan substrate solution, cover the test tube tightly, react in a water bath at 50°C for 10min, and immediately add 0.6 Mix mL DNS reagent and mix to terminate the reaction, then boil in boiling water for 10 min, add water to make up to 5 mL after cooling, shake well, and calculate the sugar content of the reaction system according to the regression equation of the xylose standard curve.
[0071] The definition of xylanase activity unit in the test is: 1mL enzyme solution produces 1 μ moL of reducing sugar (calculated as xylose) per minute as an activity unit, expressed in IU:
[0072] IU=N×R / 10min×0.1mL
[0073] In the formula: N is the dilution factor of the enzym...
Embodiment 3
[0077] Enzyme separation example 3: separation and purification of high temperature resistant xylanase
[0078] (1) Centrifuge the fermentation broth at 8000rpm for 10min at 4°C, and take the supernatant;
[0079] (2) Slowly add ammonium sulfate to the fermentation supernatant to make the saturation of ammonium sulfate reach 70%, and salt out overnight at 4°C;
[0080] (3) The fermentation supernatant that was salted out overnight was centrifuged at 4° C., 8000 rpm, for 10 minutes, and the precipitate was taken, and an appropriate volume of PBS buffer solution of pH 7.0 was used to dissolve the precipitate to obtain a crude enzyme solution of high-temperature-resistant xylanase for later use;
[0081] (4) Octyl Sepharose Fast Flow hydrophobic interaction chromatography: adjust the ammonium sulfate saturation of the crude enzyme solution to 40%, and perform hydrophobic interaction chromatography, column type: Equilibrium solution: 0.02mol / L PBS buffer solution (pH7.0) contain...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Relative molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com