Genetic engineering bacterium for producing monophosphoryl lipid A as well as construction method and application thereof
A technology of genetically engineered bacteria and monophosphoric acid lipids, applied in the direction of microorganism-based methods, biochemical equipment and methods, bacteria, etc., can solve problems such as numerous steps, unfavorable large-scale production, and difficult operation, so as to reduce production costs, Facilitate the effect of large-scale industrial production
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0015] Example 1 Construction of Mutant E.coli W3110 ΔlacI
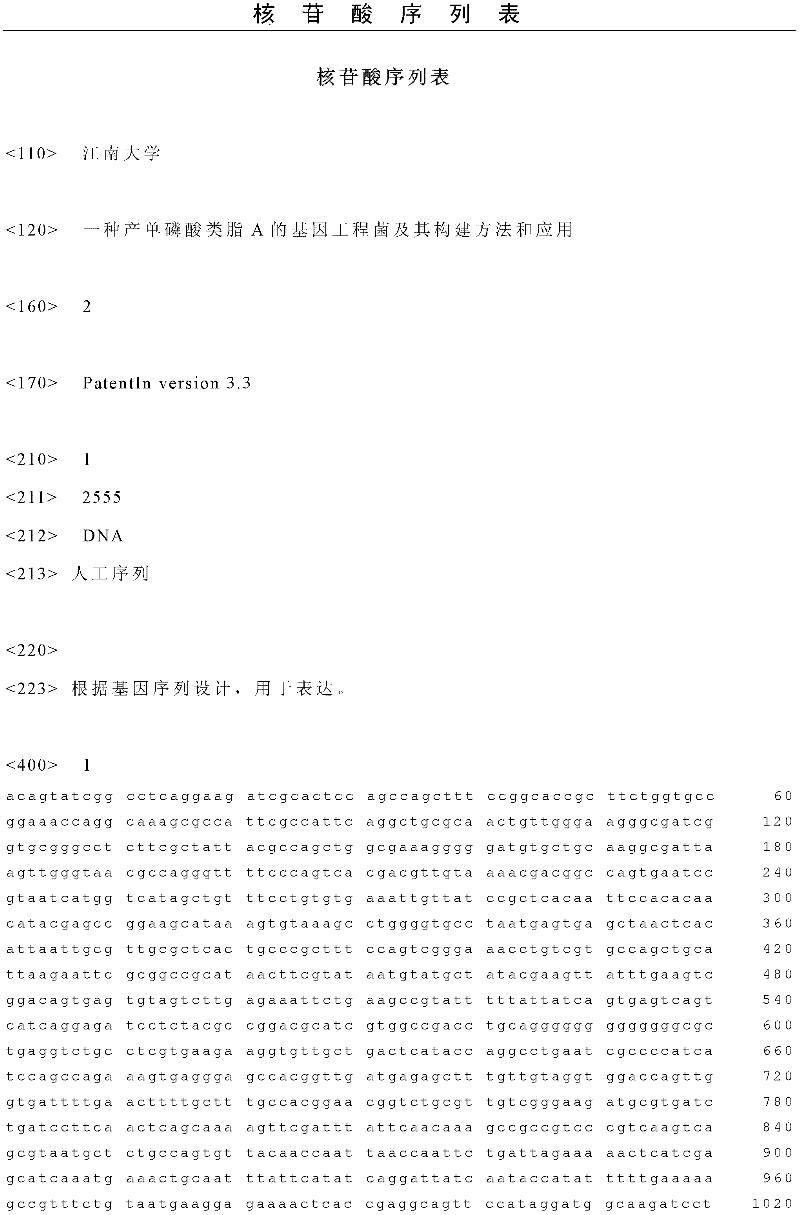
[0016] 1. Obtaining the lacI gene knockout fragment
[0017] The lacI gene knockout fragment is obtained by chemical total synthesis or PCR step-by-step amplification, and its two ends are the upstream and downstream homology arms of the lacI gene, and the middle is a kan fragment. The nucleotide sequence of the lacI gene knockout fragment is shown in SEQ ID NO.1. The lacI gene knockout fragment was cloned into pBlueScript II SK(+) to obtain the recombinant plasmid pBlueScript II SK(+)-lacI(U)-pkan-lacI(D).
[0018] 2. Preparation and electrotransformation of knockout competent cells
[0019] Inoculate with Red recombinant helper plasmid pKD46 (Datsenko K A, Wanner B L. One-Step inactivation of chromosome genes in Escherichia coli K-12 using PCR products.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2000, 97(12): 6640-6645) Escherichia coli W3110 (ATCC39936) was cultured overnight in LB liquid medium containing 100 μg / mL ampicillin at ...
Embodiment 2
[0025] Construction of embodiment 2 mutant strain HW001
[0026] 1. Obtaining the knock-in fragment FnlpxE-Fkan
[0027] According to the sequence of pWSK29-FnlpxE-Fkan (Jiuzhou Chen et al.2010), artificially synthesize or PCR amplify the knock-in fragment FnlpxE-Fkan with lacZ-a natural homology arm, its nucleotide sequence is shown in SEQ IN NO.2 shown. Among them, there are FRT sites on both sides of the kan gene.
[0028] 2. Preparation and electrotransformation of knockout competent cells
[0029] The W3110 ΔlacI strain carrying the pKD46 plasmid was used as the starting strain to prepare competent cells, and the method was the same as above. 500-1000ng of the FnlpxE-Fkan knock-in fragment was electrotransformed into competent cells, and the mutant strain W3110 ΔlacI lacZ::FnlpxE-Fkan knocked in and expressing FnlpxE-Fkan inside the chromosome lacZ gene was obtained by kan resistance screening.
[0030] 3. Removal of mutant resistance markers
[0031]By transferring ...
Embodiment 3
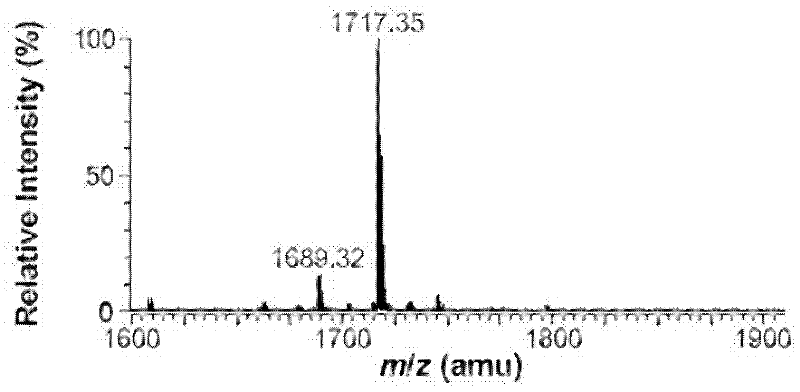
[0032] Lipid A structure analysis of embodiment 3 mutant strain HW001
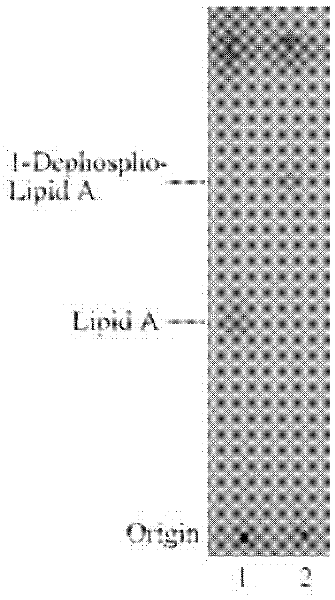
[0033] 1. Lipid A extraction and thin layer chromatography (TLC) analysis of mutant strain HW001
[0034] Lipid A was extracted by chloroform / methanol / water mixed phase extraction. The overnight cultured bacterial solution was divided into initial OD 600 =0.02 transferred to 200mL LB liquid medium, cultivated to OD at 37°C 600 = 1 hour 8000rpm centrifugal 10min collects bacterial cell, ddH 2 After washing the cells once, use the Bligh-Dyer one-phase system (chloroform / methanol / water, 1:2:0.8, v / v / v) to suspend the cells, magnetically stir for 1 h, and centrifuge at 2000 rpm for 20 min to separate the phases. Use a one-phase system Wash cell debris 2-3 times. Add 27mL of 12.5mM sodium acetate (PH4.5) solution, shake for 10min, and cleavage the sugar chains in a water bath at 100°C for 30min. After cooling to room temperature, add 30 mL of chloroform and 30 mL of methanol to form a Bligh-Dyer two-phase ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com