Gene for controlling arabidopsis trichome development and coded protein and application thereof
A kind of epidermal hair, Arabidopsis technology, applied in the field of plant genetic engineering
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] Example 1: Construction and screening of Arabidopsis thaliana activation tag mutant library
[0031] 1) Arabidopsis seeds were cold-treated at 4°C for 3 days to germinate neatly. Sow in humus soil containing 1 / 3 vermiculite for cultivation. The culture room is kept at a temperature of 22-24°C, a relative humidity of 80%, the light source is a fluorescent lamp, and the light intensity is 85 μmol.s -1 .m -2 , the light time is 16h;
[0032] 2) About 4-5 weeks, Arabidopsis begins to flower, which can be used for transformation;
[0033] 3) Pick a single colony of Agrobacterium containing the pDSK15-11 plasmid in YEP liquid medium (composed of yeast extract 10g / L, peptone 10g / L, sodium chloride 5g / L, pH7.0Gen 100mg / L, Carb 50mg / L, Rif 50mg / L), 28 ℃, shaking culture under 200rpm overnight; Transition to fresh YEP liquid medium containing antibiotics in a ratio of 1:50 and expand to the logarithmic growth phase (bacterial liquid OD600 is about 1.5); centrifuge at 5000×g...
Embodiment 2
[0038] Example 2: TAIL-PCR amplification of T-DNA flanking sequences and identification of T-DNA insertion sites
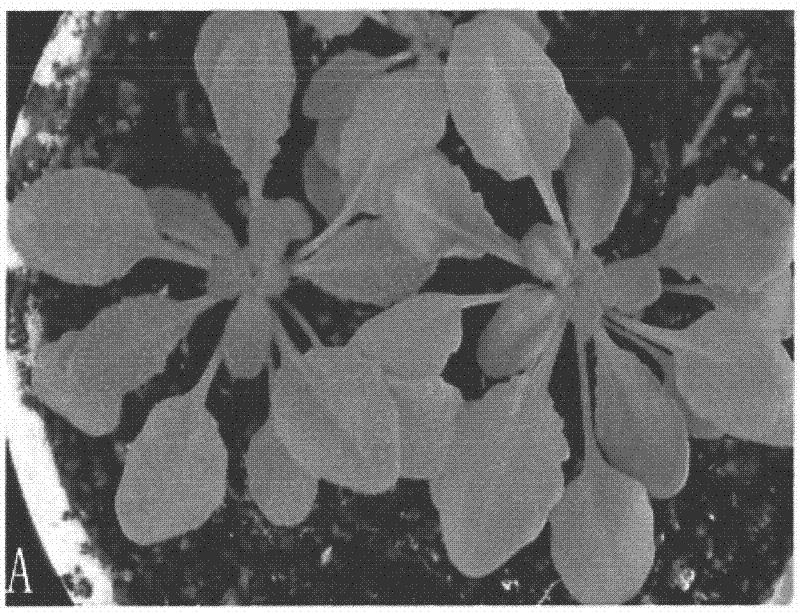
[0039] In the present invention, the amplification of the T-DNA flanking sequence adopts the method of TAIL-PCR (thermally asymmetric interleaved polymerase chain reaction), the PCR product is directly sequenced, and the T-DNA is found after comparing with the whole genome sequence of Arabidopsis thaliana Inserted between At4g01050 and At4g01060 of chromosome 4 of Arabidopsis thaliana, about 2000 bp away from the start codon of At4g01060, and its right border points to At4g01060. In order to further determine whether the mutant phenotype is caused by this T-DNA insertion, the present invention carried out genetic analysis on the offspring of the T2 generation of B11. Among the 31 plants of the T2 generation, 24 of them had the phenotype of no epidermis. , the 7 strains are normal, and the segregation ratio of phenotype and no phenotype is about 3.4:1, so it can al...
Embodiment 3
[0071] Example 3: RT-PCR detection of T-DNA insertion site flanking genes and identification of genes controlling Arabidopsis trichome development
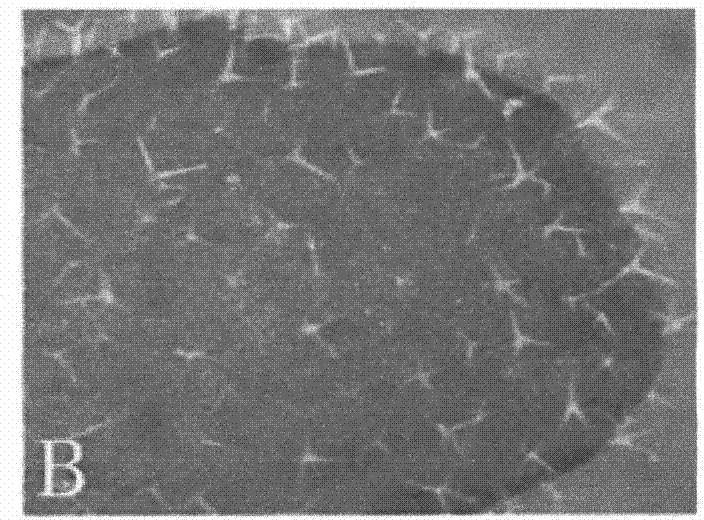
[0072] In the present invention, because the T1 generation of B11 shows the phenotype of lack of epidermis, this indicates that the mutant phenotype is a dominant mutation, which is caused by the activation of the flanking gene by the activation tag. The present invention selects 4 genes in the range of 10kb upstream and downstream on both sides of the T-DNA insertion site, including upstream At4g01040 and At4g01050 and downstream At4g01060 and At4g01070, and the expression levels of these 4 genes are carried out by RT-PCR Semi-quantitative detection, such as Figure 6 As shown, the RT-PCR results showed that among the four genes, only At4g01060 was expressed in the B11 mutant, and the expression of the other three genes was not different between bzr1-1D and the mutant B11. This result indicated that the phenotype of the mutant w...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com