Preparation of glycosyl microsphere catalyst and process for hydrolyzing cellulose
A technology of sugar-based carbon microspheres and catalytic hydrolysis, which is applied in the production, application, and sugar production of sugar, and can solve the problems of liquid mineral acid environmental pollution, equipment corrosion yield, and high cost of enzyme preparations. Short, energy-saving, easy-to-handle effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
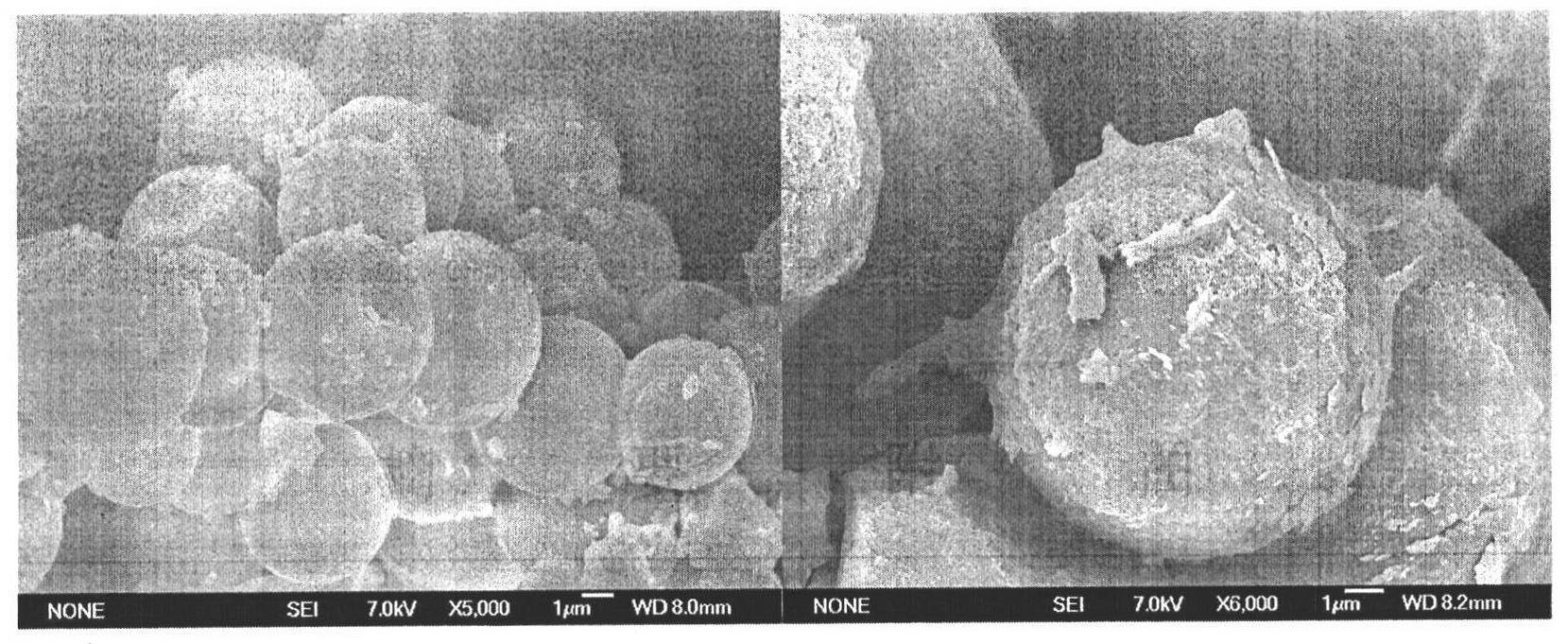
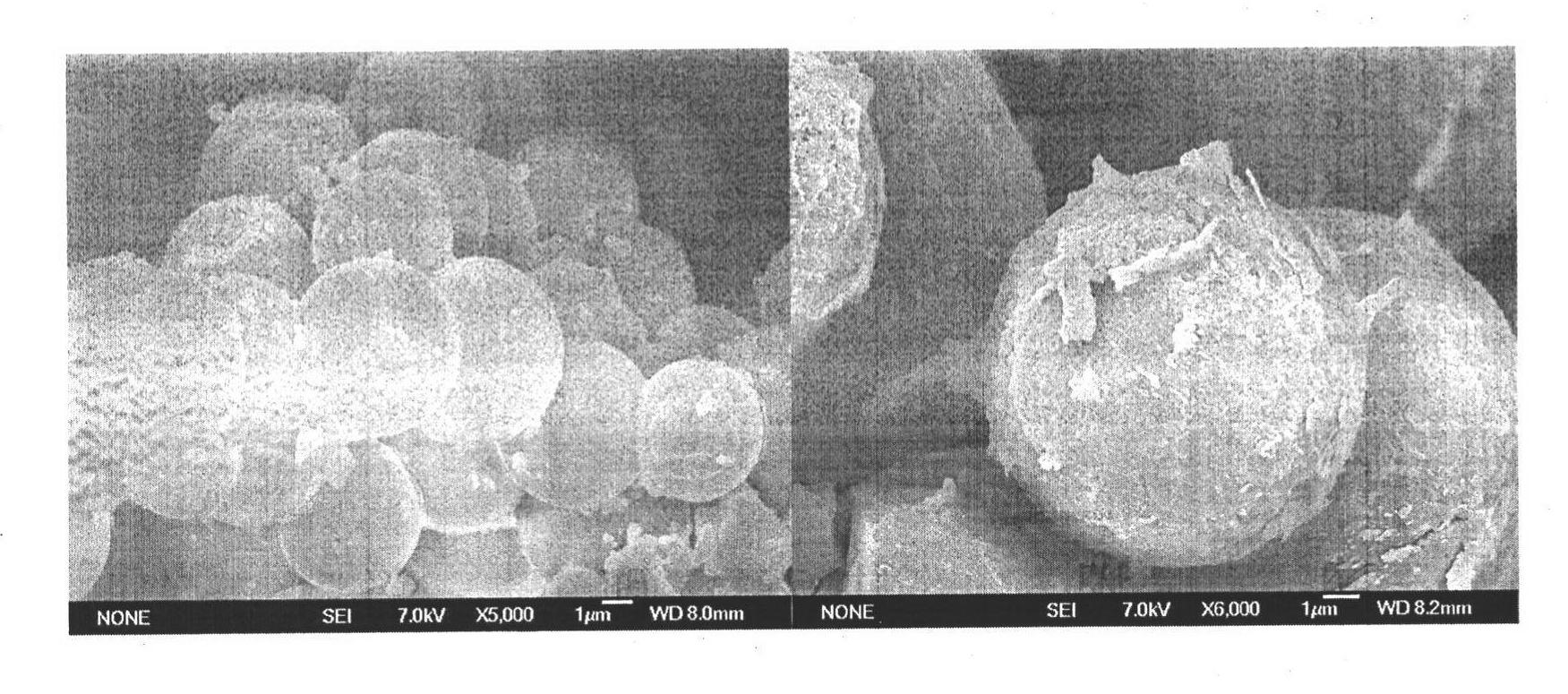
[0025] Embodiment 1, preparation and characterization of the invented catalyst:
[0026] The preparation process of the carbon microsphere solid acid catalyst is summarized as follows: 20 g of glucose, 20 g of salicylic acid sulfonate solution (20%) and 50 ml of distilled water were successively added under magnetic stirring, and the stirring was continued for 30 min. Then the mixed solution was transferred into a 100ml stainless steel autoclave lined with polytetrafluoroethylene, sealed and heated to a constant temperature of 180°C for 4 hours, and stirred at a speed of 1000 rpm. After the reaction, the reactor was cooled to room temperature. The resulting black powder was alternately washed several times with distilled water and ethanol (ten times in total, 6 times with water and 4 times with alcohol), and dried at a constant temperature of 80°C for 12 hours to remove all moisture. Afterwards, the dried black powder was ground, soaked in concentrated sulfuric acid for 12 ho...
Embodiment 2
[0027] Embodiment 2, preparation and characterization of the invented catalyst:
[0028] The preparation process of the carbon microsphere solid acid catalyst is summarized as follows: 20 g of sucrose, 20 g of salicylic acid sulfonate solution (20%) and 50 ml of distilled water were successively added under magnetic stirring, and the stirring was continued for 30 min. Then the mixed solution was transferred into a 100ml stainless steel autoclave lined with polytetrafluoroethylene, sealed and heated to 200°C at a constant temperature for 2h, and stirred at a speed of 1000 rpm. After the reaction, the reactor was cooled to room temperature. The resulting black powder was alternately washed several times with distilled water and ethanol (ten times in total, 6 times with water and 4 times with alcohol), and dried at a constant temperature of 80°C for 12 hours to remove all moisture. Afterwards, the black powder after drying was ground, added concentrated sulfuric acid to soak for...
Embodiment 3
[0029] Embodiment 3, the new catalytic process of cellulose hydrolysis:
[0030]Add 0.05g of cellulose and 1g of 1-butyl 3-methylimidazolium chloride salt ionic liquid into the 10ml reactor, dissolve the cellulose at 80°C, then add 0.01g of water and 0.05g of the catalyst synthesized in the present invention, Heat to 150 DEG C in a sealed state, react for 10 minutes, and then rapidly cool in an ice-water bath; take out the reaction solution and dilute it, and measure the yield of reducing sugar by 3,5-dinitrosalicylic acid method (DNS) to be 70%.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com