Method for detecting two dimensional nanostructured material film surface detect
A two-dimensional nanostructure, material thin film technology, applied in the direction of material analysis using measurement of secondary emissions, optical testing flaws/defects, etc., can solve the problems of long cycle, complex operating procedures, limited probe scanning range, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
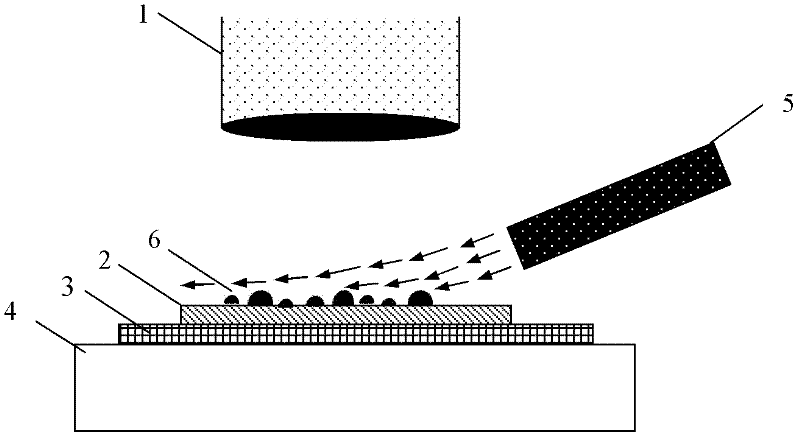
[0041] 1) Select highly oriented graphite (HOPG) with a smooth surface, and use adhesive tape to cleave the surface of the highly oriented graphite to obtain a fresh cleaved surface.
[0042] 2) Fix the highly oriented graphite on a glass slide, put it into an oven, and dry it under the protection of argon at 120°C for 1 hour. After cooling to room temperature, take out the sample and quickly seal it in a desiccator.
[0043] 3) Use a constant temperature tank to heat deionized water to 65°C and maintain a constant temperature; fix the water vapor nozzle on the side of the stage, and adjust the angle between the nozzle and the stage to a suitable value so that the airflow does not cause the sample to move. At the same time, the mixed gas of water vapor can fully contact the surface of the sample.
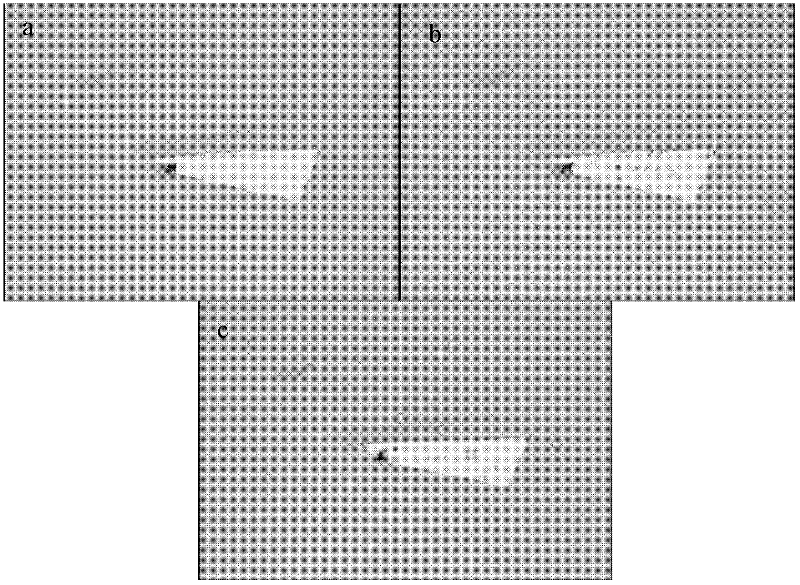
[0044] 4) Fix the highly oriented graphite in the desiccator above the stage. The focusing optical microscope makes the surface of the sample image clearly, and the CCD video is tu...
Embodiment 2
[0049] 1) Graphite flakes with tens of layers of atomic layer thickness are selected as two-dimensional film materials. The preparation of graphite flakes can be obtained by cleaving graphite films with adhesive tape, and then transferred to SiO 2 Surface (below it is Si, usually expressed as SiO 2 / Si).
[0050] 2) SiO that will support graphite flakes 2 / Si slices were fixed on glass slides with adhesive tape, and then dried under nitrogen protection at 140°C for 1 hour. After cooling to room temperature, the samples were taken out and quickly sealed in a desiccator.
[0051] 3) Heating the deionized water to 70°C and maintaining a constant temperature, adjusting the position of the water vapor nozzle on the stage and the angle of the nozzle on the stage plane.
[0052] 4) Fix the graphite flake sample in the desiccator above the stage; focus the optical microscope to image the sample surface clearly, and turn on the CCD video.
[0053] 5) Nitrogen gas is passed into the ...
Embodiment 3
[0057] 1) Single-layer and double-layer graphene are used as two-dimensional materials to be detected. This thin film material can be obtained by cleaving HOPG once or multiple times, and then transferred to SiO 2 Surface (below it is Si, usually expressed as SiO 2 / Si).
[0058] 2) SiO attached to graphene 2 / Si slices were fixed on glass slides, then dried under the protection of argon at 130°C for 1 h, cooled to room temperature and stored in a desiccator for detection.
[0059] 3) Heat the deionized water to 60°C and keep the temperature constant, fix the steam nozzle at a suitable position on the stage, and adjust the direction of the nozzle and the angle of the stage plane.
[0060] 4) Fix the cooled graphene on the stage, focus the optical microscope to image the sample surface clearly, and turn on the CCD video recording.
[0061] 5) Open the argon throttle valve, spray the mixed gas of water vapor and argon along the graphene surface, and control the flow rate of t...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com