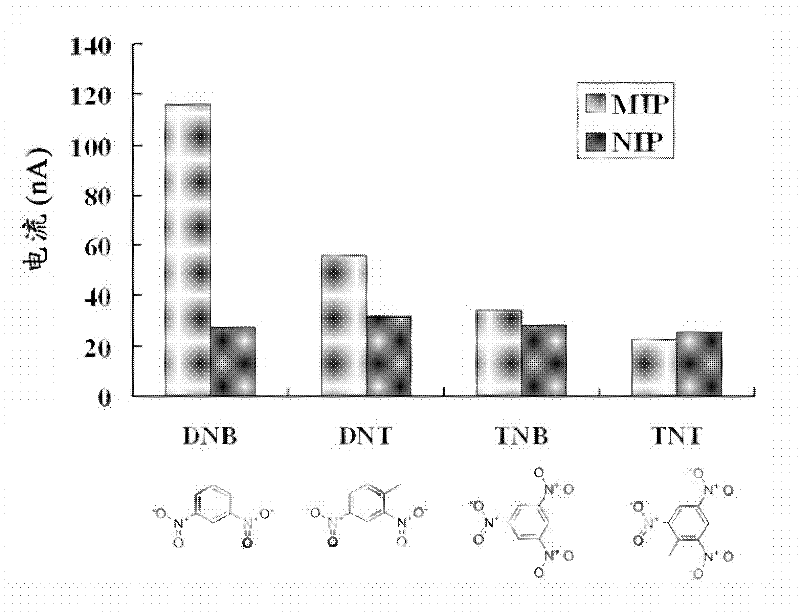
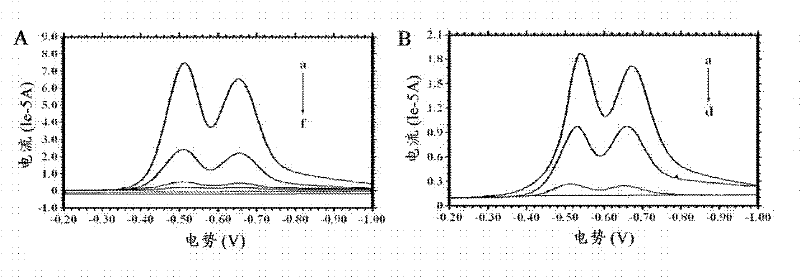
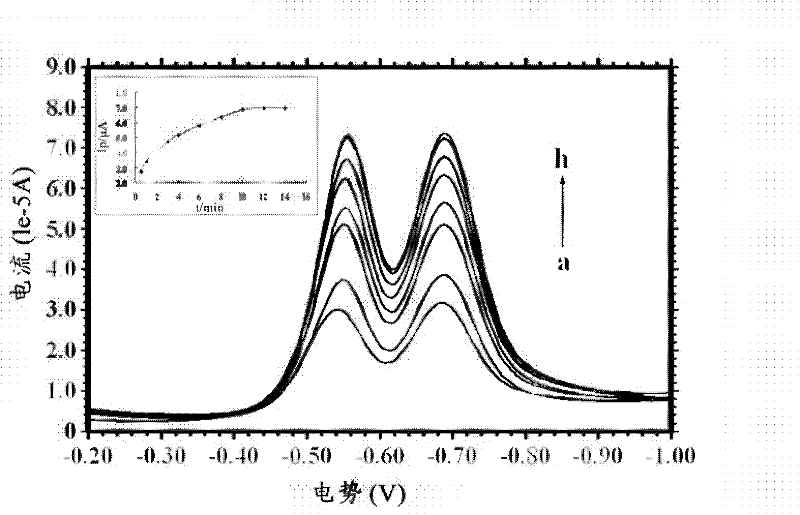
Functionalized polyaniline nanometer material, molecular imprinted polymers (MIP) composite, molecular imprinted sensor, electrochemical testing equipment and preparation method of MIP composite
A technology of nanomaterials and molecular imprinting, applied in the fields of material electrochemical variables, fiber processing, textiles and papermaking, etc., can solve problems such as poor controllability, difficult elution of internal template molecules, and uneven distribution of imprinted sites.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0068] The invention also relates to a preparation method of the molecularly imprinted polymer, which is to introduce unsaturated functional groups on the preferably doped polyaniline nanometer material.
[0069] Then, the template molecule, the polyaniline nanomaterial-functional monomer and the crosslinking agent are polymerized to form a molecularly imprinted polymer layer on the polyaniline nanomaterial.
[0070]According to one embodiment, the preparation method of the molecularly imprinted polymer of the present invention is, first, introduce (meth)acryloyl or vinyl functional groups on the doped polyaniline nanomaterials to obtain polyaniline nanomaterials-(meth)acryloyl or vinyl monomers, and then polymerize template molecules, polyaniline nanomaterials-(meth)acryloyl or vinyl monomers and cross-linking agents to form a molecularly imprinted polymer layer on the polyaniline nanomaterials. Preferably, the polymerization is carried out in the presence of an initiator.
...
Embodiment 1A
[0086] Example 1A Synthesis of doped polyaniline nanofibers E-100, E-300 and E-500
[0087] The synthesis of polyaniline nanofibers was carried out by modifying the method of Anikumar et al. (P. Anikumar, M. Jayakannan, Langmuir 22 (2006) 5952). The specific synthesis steps are shown in Scheme 1.
[0088] Schema 1:
[0089] Synthesis of dopants
[0090]
[0091] Preparation of polyaniline nanofibers
[0092]
[0093] 1) Synthesis of dopants
[0094] Heat 60mL of an aqueous solution containing sulfanilic acid (0.036mol) and sodium carbonate (0.016mol) to 60-70°C, then cool to 5°C, and add 6mL of an aqueous solution containing sodium nitrite (0.032mol). The resulting solution was poured into 40 g of ice containing 6.0 mL of concentrated hydrochloric acid, stirred at 5°C for 30 minutes, then added to a 30 mL flask containing 9 mL (0.03 mol) of aqueous solution of sodium hydroxide (0.09 mol) and cardanol, and placed on ice Stir in the cooled state for 3 hours. Neutra...
Embodiment 1B
[0102] Synthesis of Example 1B Doped Polyaniline Nanoparticles PANI-NPs
[0103] As shown in Scheme 2 below, polyaniline nanoparticles (PANI-NPs) were synthesized using dodecylbenzenesulfonic acid (DBSA) as a dopant.
[0104] Scheme 2: Preparation of polyaniline nanoparticles PANI-NPs
[0105]
[0106] Polymerization was carried out in a thermostat at 20°C. Equimolar amounts (0.13 moles) of aniline and DBSA were added to 100 mL of water and mechanically stirred in a round bottom flask for 1 hour. Then 100 mL of 1.3M ammonium persulfate was added dropwise to form a milky white aniline / DBSA solution. After 2.5 hours of polymerization, a dark green dispersion was obtained. The dispersion was dialyzed in Milli-Q water (ultrapure water) for 48 hours with a dialysis membrane (D25mm, current carrying range 8000-14000, Sigma company) with a molecular weight cutoff of 12000. After dialysis, the dispersion was centrifuged at 10000 rpm for 10 minutes. Decant the supernatant, ad...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com