Method for evaluating antimicrobial susceptibility of drugs
A sensitive and pharmaceutical technology, applied in fluorescence/phosphorescence, material excitation analysis, etc., can solve problems such as low sensitivity and reproducibility, expensive experiment cost, complicated operation steps, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0090] Synthesis of compound PPP shown in embodiment 1, formula I and compound OPV shown in formula II
[0091] Add 5.4mL of toluene and 3.6mL of 2M aqueous potassium carbonate solution into a 25mL two-necked flask, and after bubbling nitrogen gas for 30min, add 269mg of 2,5-dibromo-1,4-bis(4-bromobutoxy)benzenediol, 165mg 1,4-Neopentyldiboronate and 20 mg of tetrakis(triphenylphosphine)palladium were stirred and reacted at 95°C under nitrogen for 24 hours. After cooling, chloroform and water were added, and the chloroform layer was washed with water and dried with anhydrous magnesium sulfate. Concentrate by rotary evaporation, and acetone precipitates to obtain a light yellow solid; dissolve the solid in 20 mL of dichloromethane, add 1 mL of trimethylamine, stir at room temperature for 24 h, centrifuge, collect the precipitate and dry to obtain 176 mg of polymer product. Characterization of the product: M n =3.5×10 4 ; 1 H NMR (400MHz, DMSO): δ (ppm) 6.8-7.6 (m, 6H), 3.9-4...
Embodiment 2
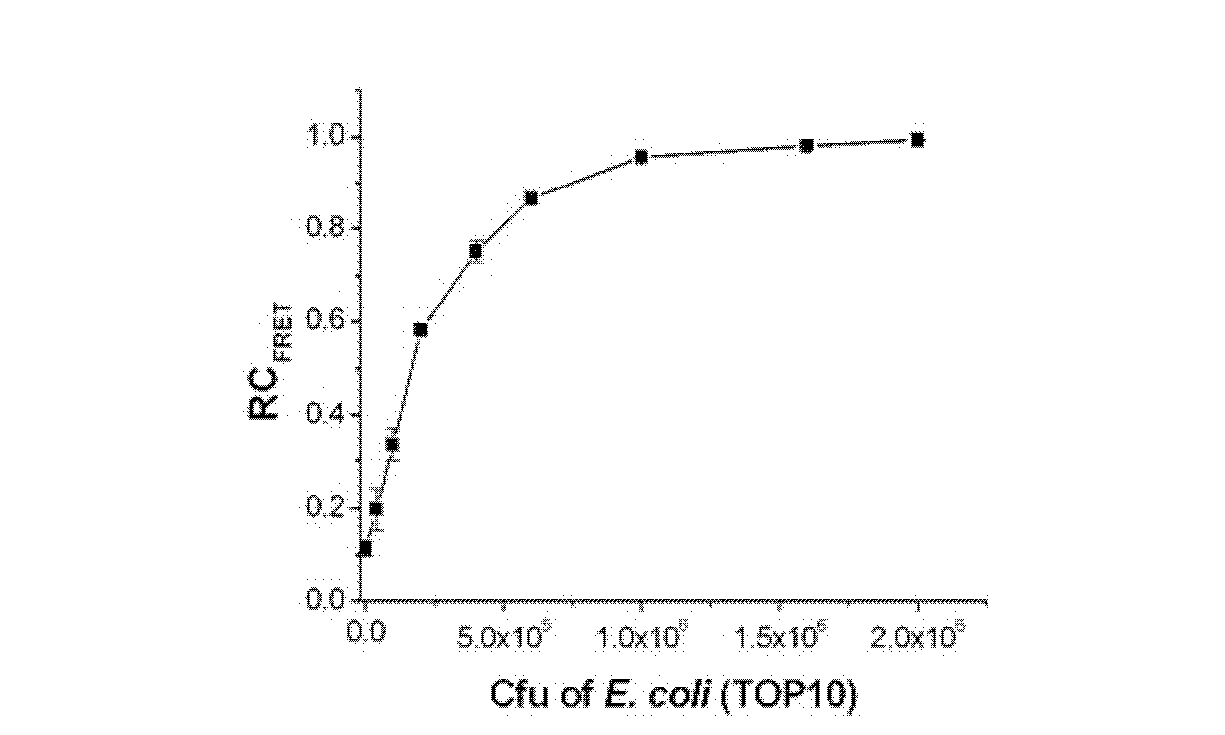
[0094] Embodiment 2, PPP and OPV are used for evaluating the antimicrobial susceptibility of ampicillin sodium to escherichia coli
[0095] One, the acquisition of pathogenic bacteria solution and the cultivation of pathogenic bacteria in the culture medium containing antibiotic ampicillin sodium:
[0096] 1) Obtaining of pathogenic bacteria solution:
[0097] Take Escherichia coli TOP10 strain (Beijing Biomed Science and Technology Development Co., Ltd., CC0101) and add it to 5 mL LB medium, and cultivate overnight at 37°C. Take a certain volume of bacterial liquid, centrifuge at 3500g for 5 minutes to remove the culture medium, wash with double distilled water for 3 times, and finally adjust the concentration of the bacterial liquid to OD in double distilled water 600 =1.0, the pathogen solution used was obtained.
[0098] 2) Pathogenic bacteria (Escherichia coli TOP10 strain (Beijing Bomed Technology Development Co., Ltd., CC0101)) were cultured in a medium containing the...
Embodiment 3
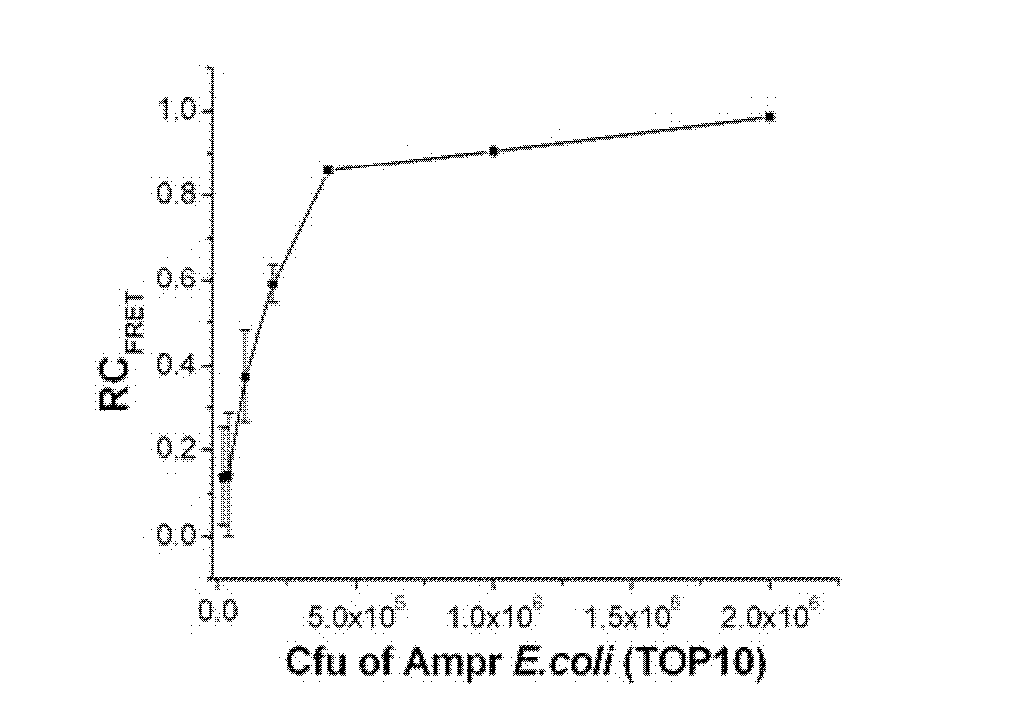
[0112] Embodiment 3, PPP and OPV are used for evaluating ampicillin sodium to ampicillin-resistant escherichia coli (Amp r E.coli) antimicrobial susceptibility
[0113] One, the acquisition of pathogenic bacteria solution and the cultivation of pathogenic bacteria in the culture medium containing antibiotic ampicillin sodium:
[0114] 1) Obtaining the pathogenic bacteria solution
[0115] Ampicillin-resistant Escherichia coli (Amp r E.coli, TOP10 transfection pcDNA3 ampicillin resistance plasmid) add 5mL containing 100μg.mL -1 Incubate overnight at 37°C in ampicillin-sodium LB medium. Take a certain volume of bacterial liquid, centrifuge at 3500g for 5 minutes to remove the culture medium, wash with double distilled water for 3 times, and finally adjust the concentration of the bacterial liquid to OD in double distilled water 600 = 1.0.
[0116] The pathogenic bacteria are cultured in a medium containing the drug to be tested, ampicillin sodium
[0117] Add sterilized ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com