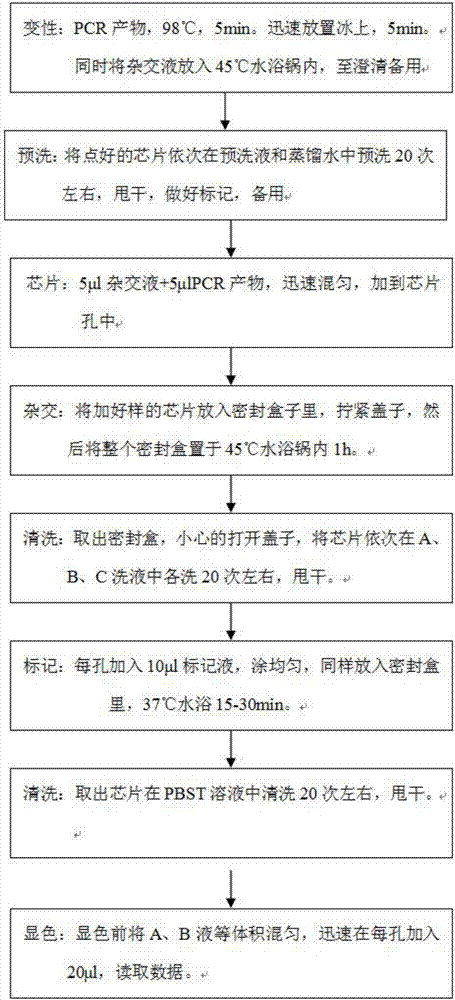
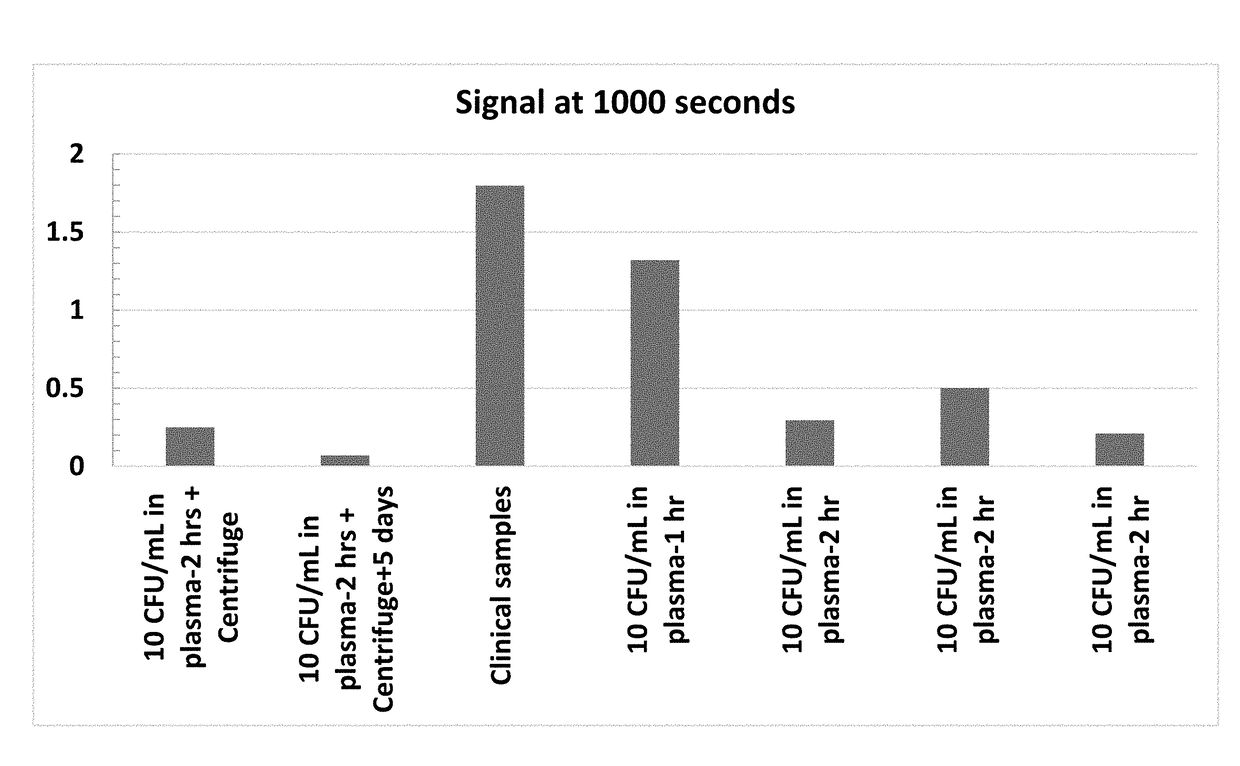
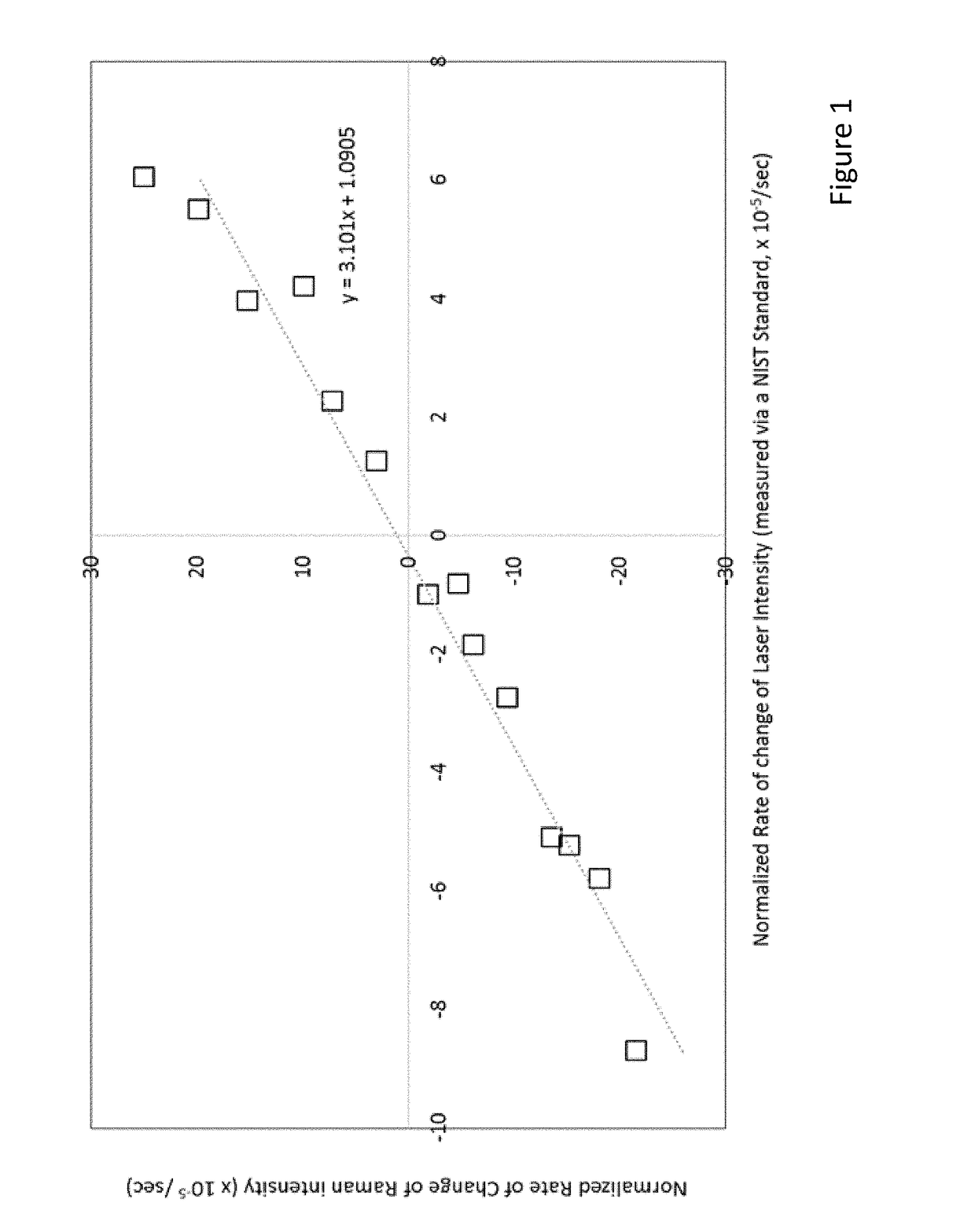
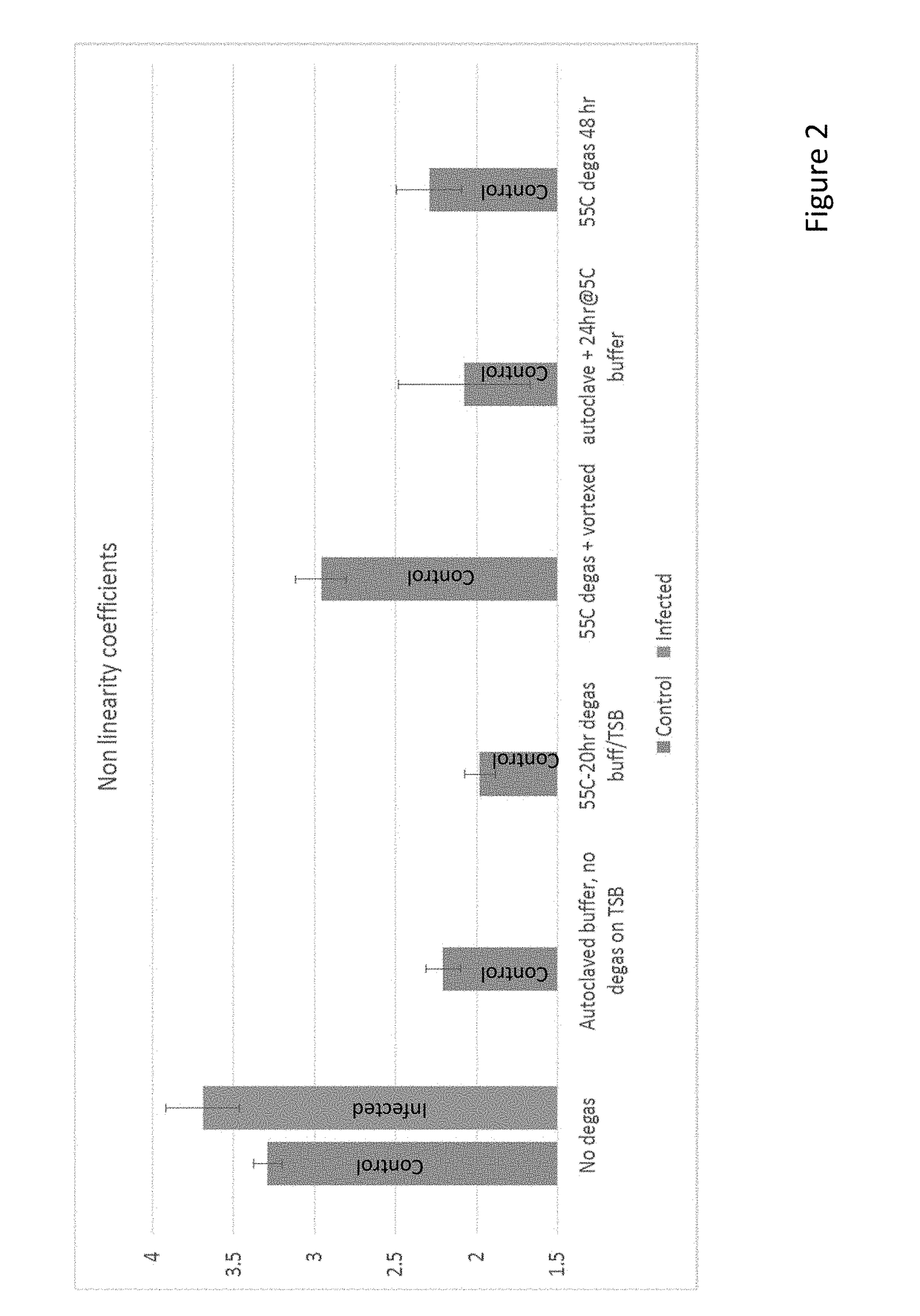
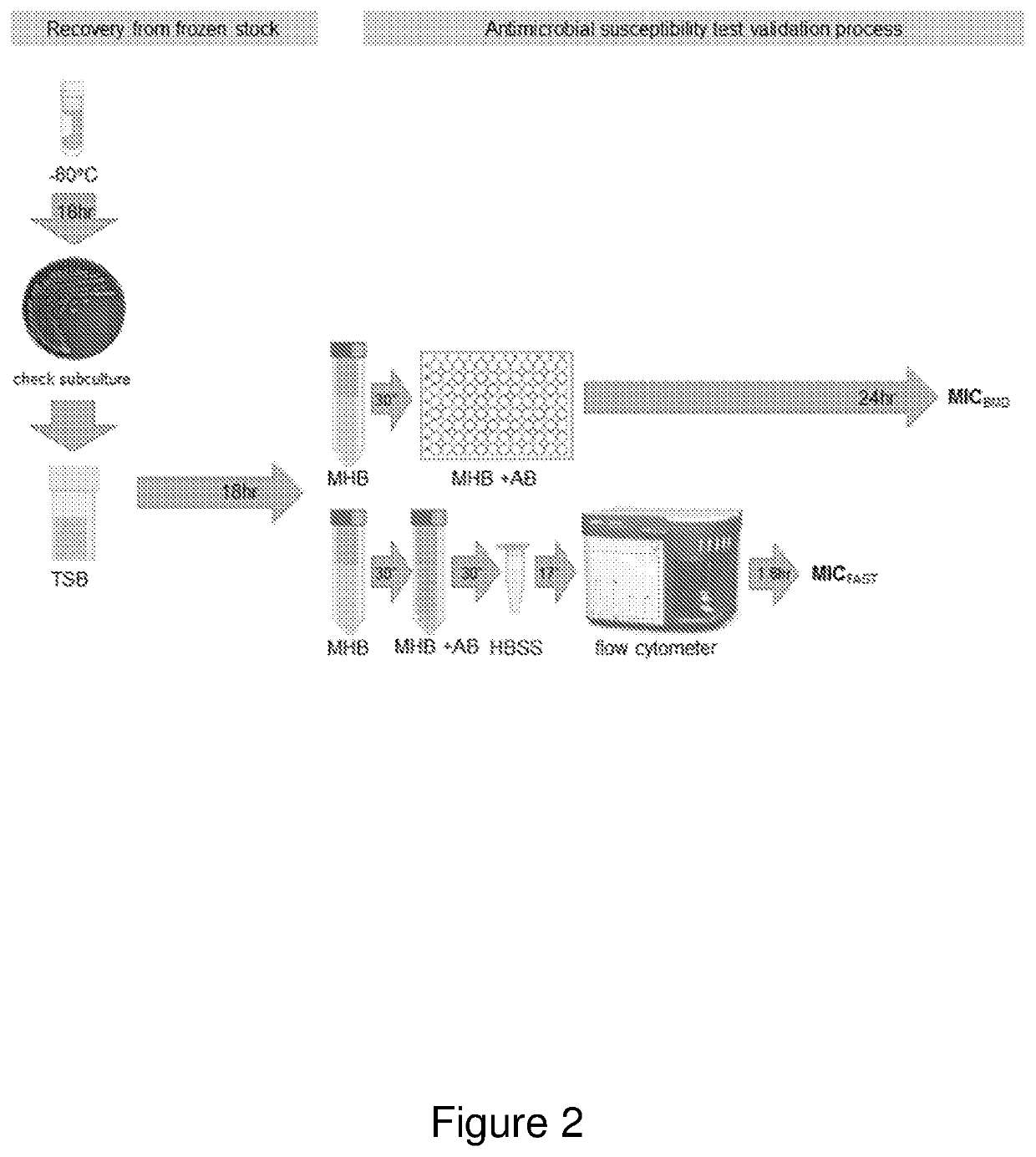
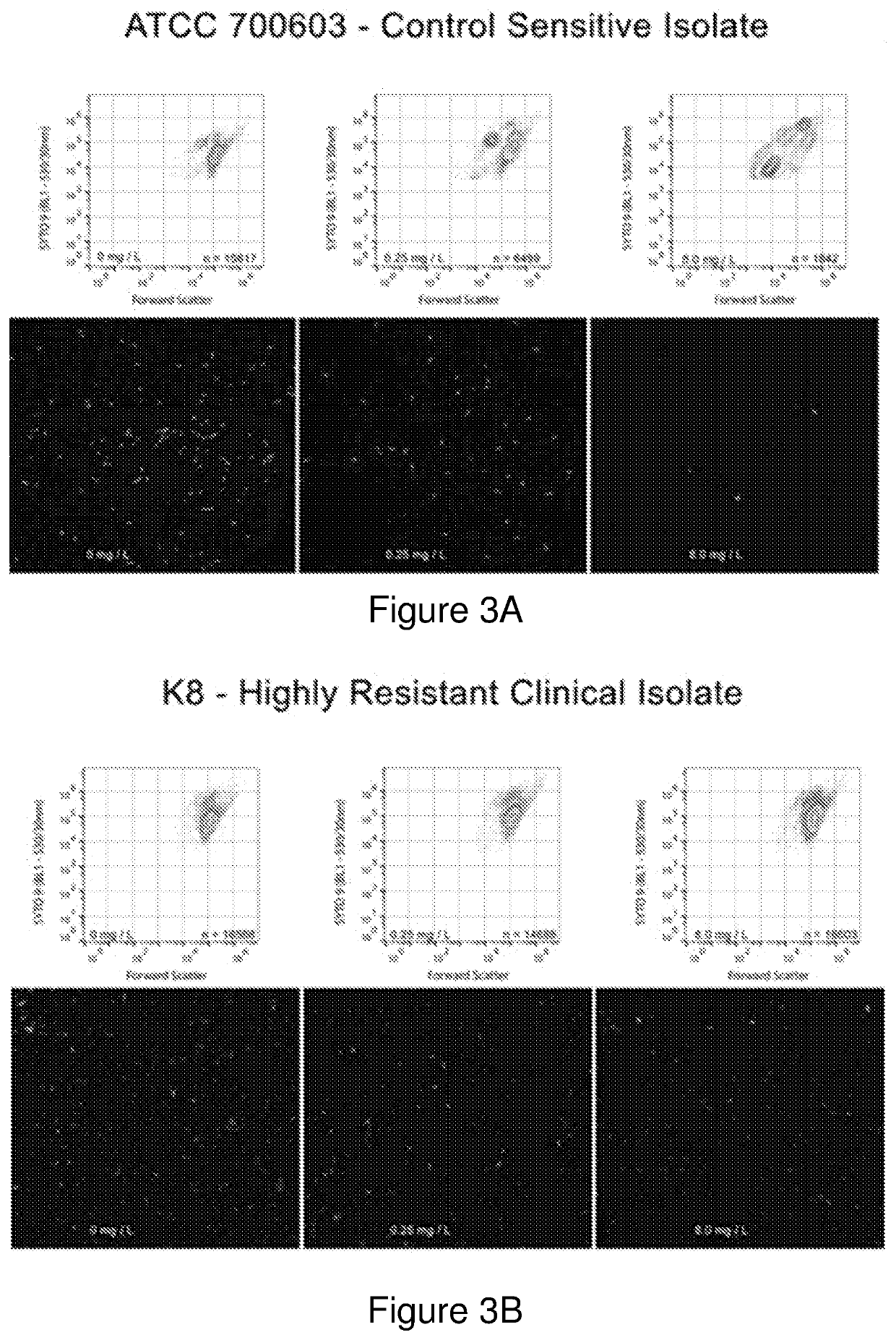
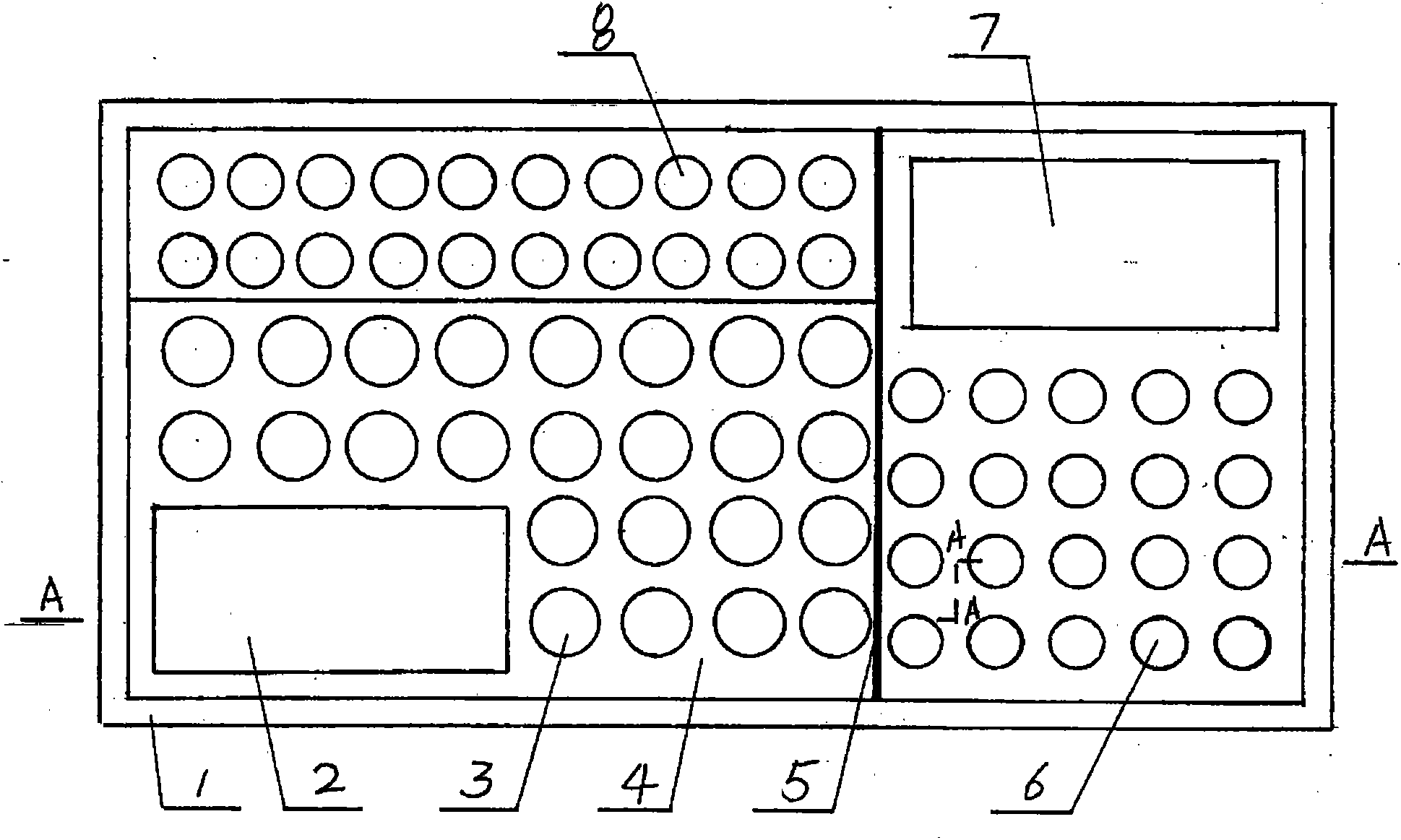
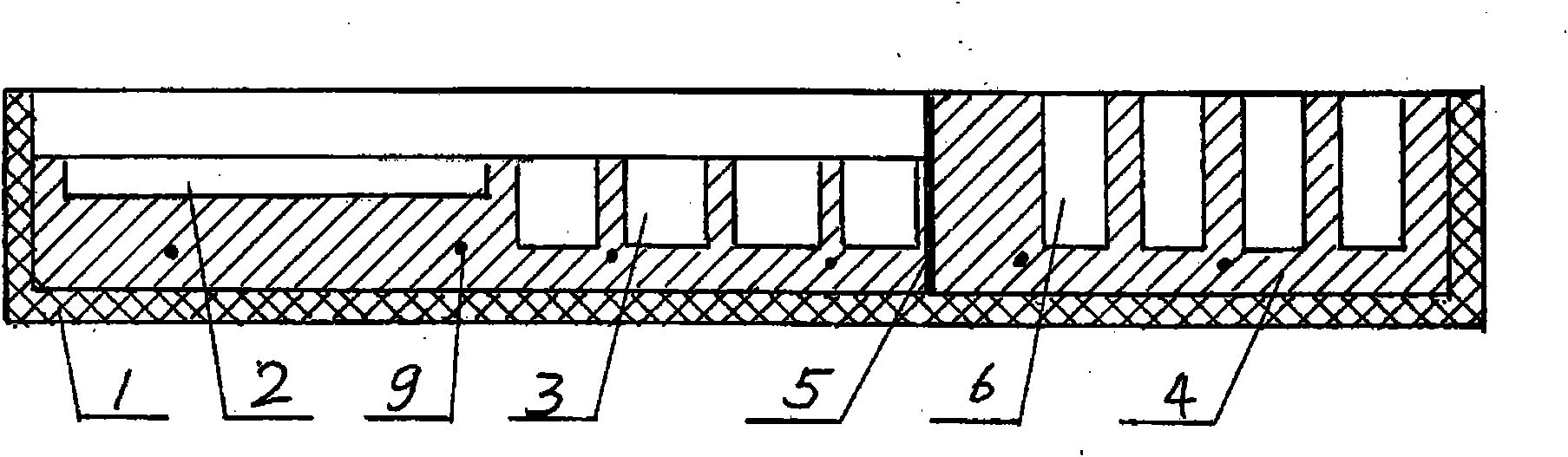
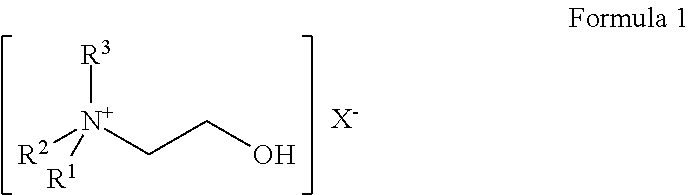Patents
Literature
87 results about "Antimicrobial susceptibility" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
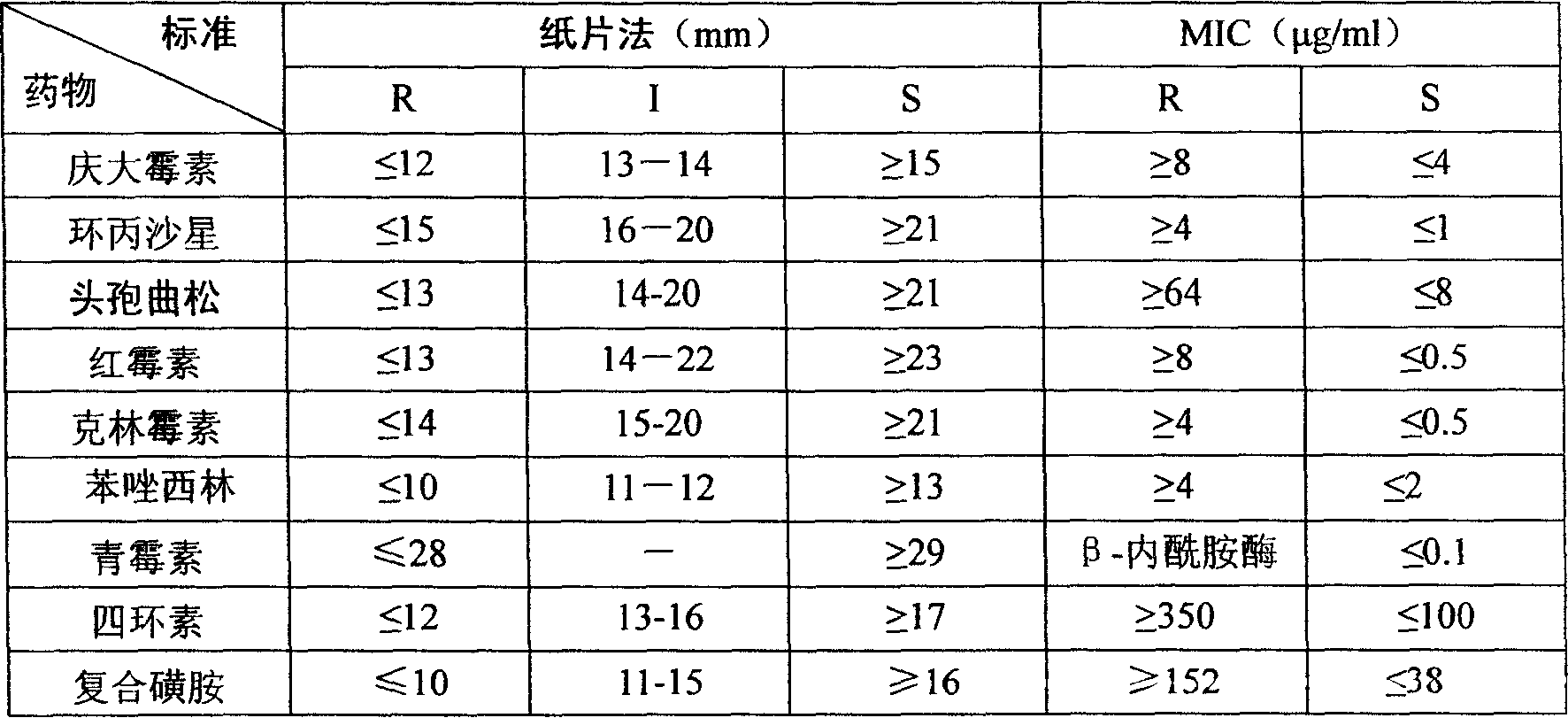
Antimicrobial Susceptibility. There are several factors to consider in choosing an appropriate antibiotic for treatment of a bacterial infection. The most basic of these is whether the causative organism is susceptible to a particular antibiotic, and how much of that antibiotic will be necessary to inhibit or kill the organism.
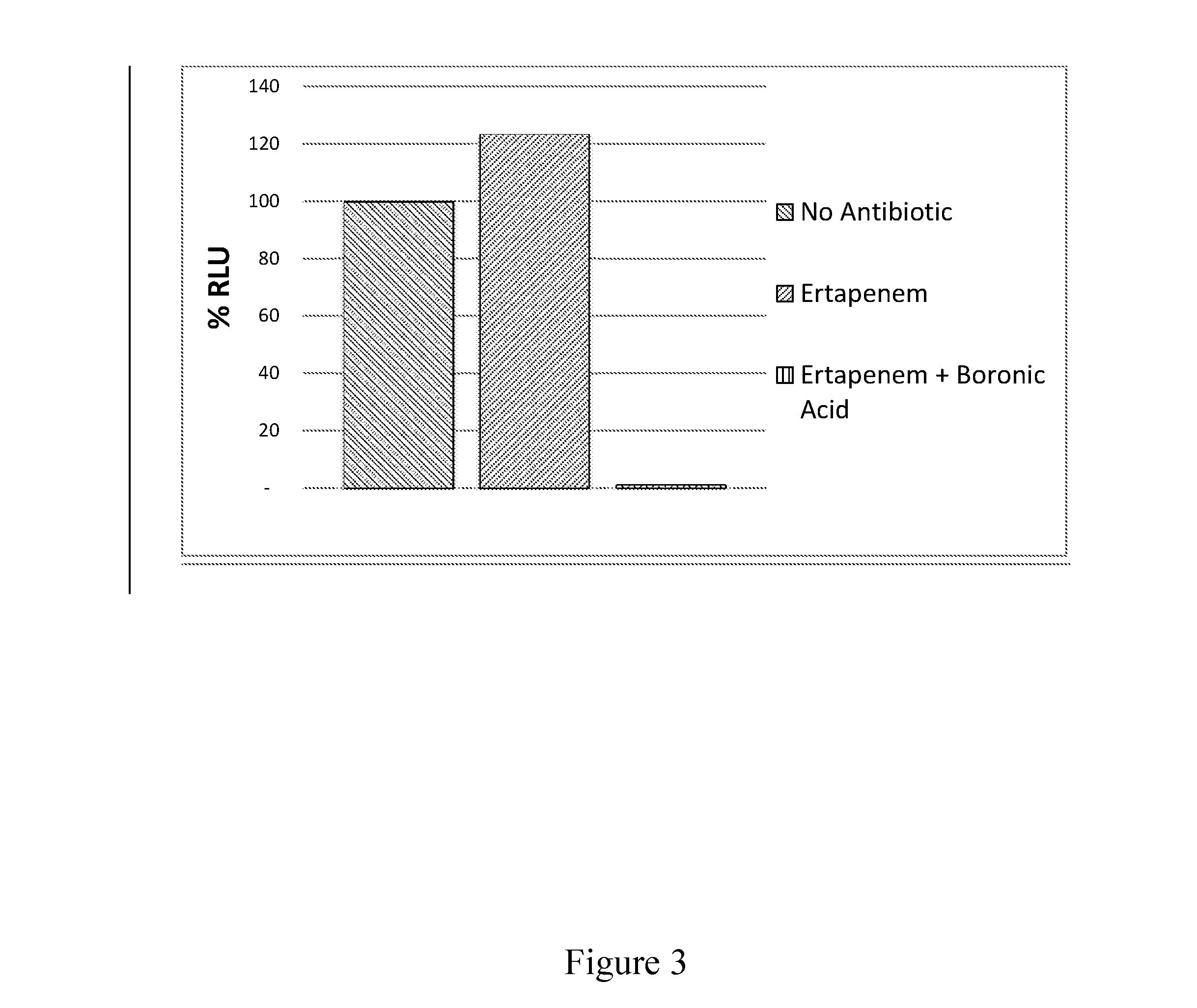
Sensitive and rapid determination of antimicrobial susceptibility
ActiveUS20050048599A1Quick checkReduce sensitivityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMicroorganismFiltration
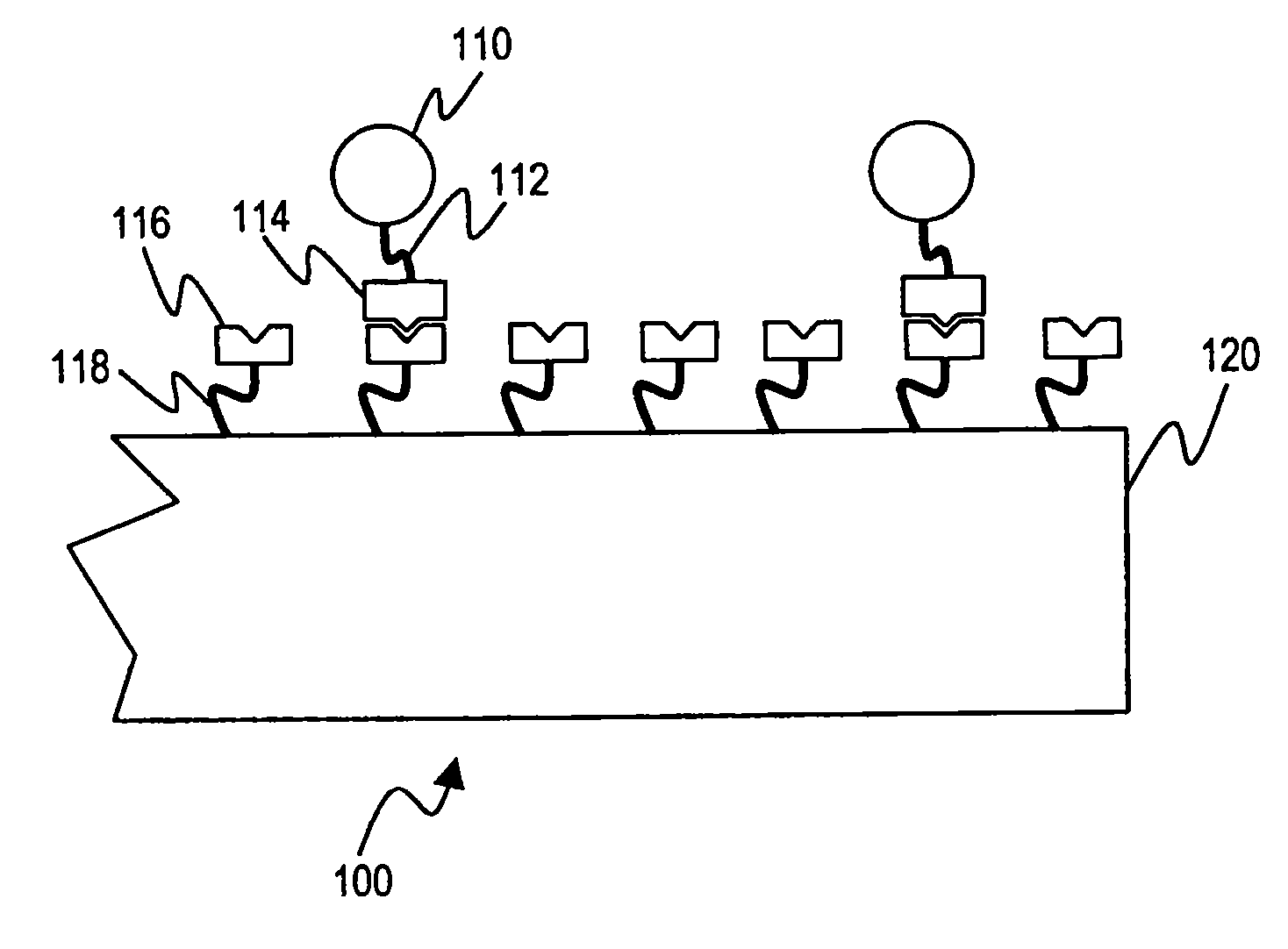
The present invention relates to moving microorganisms to a surface, where they are grown in the presence and absence of antimicrobials, and by monitoring the growth of the microorganisms over time in the two conditions, their susceptibility to the antimicrobials can be determined. The microorganisms can be moved to the surface through electrophoresis, centrifugation or filtration. When the movement involves electrophoresis, the presence of oxidizing and reducing reagents lowers the voltage at which electrophoretic force can be generated and allows a broader range of means by which the target can be detected. Monitoring can comprise optical detection, and most conveniently includes the detection of individual microorganisms. The microorganisms can be stained in order to give information about their response to antimicrobials.
Owner:ACCELERATED MEDICAL DIAGNOSTICS INC
Automated microbiological testing apparatus and method therefor
InactiveUS7115384B2Quick analysisAccurate identificationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBiotechnologyFluorescence
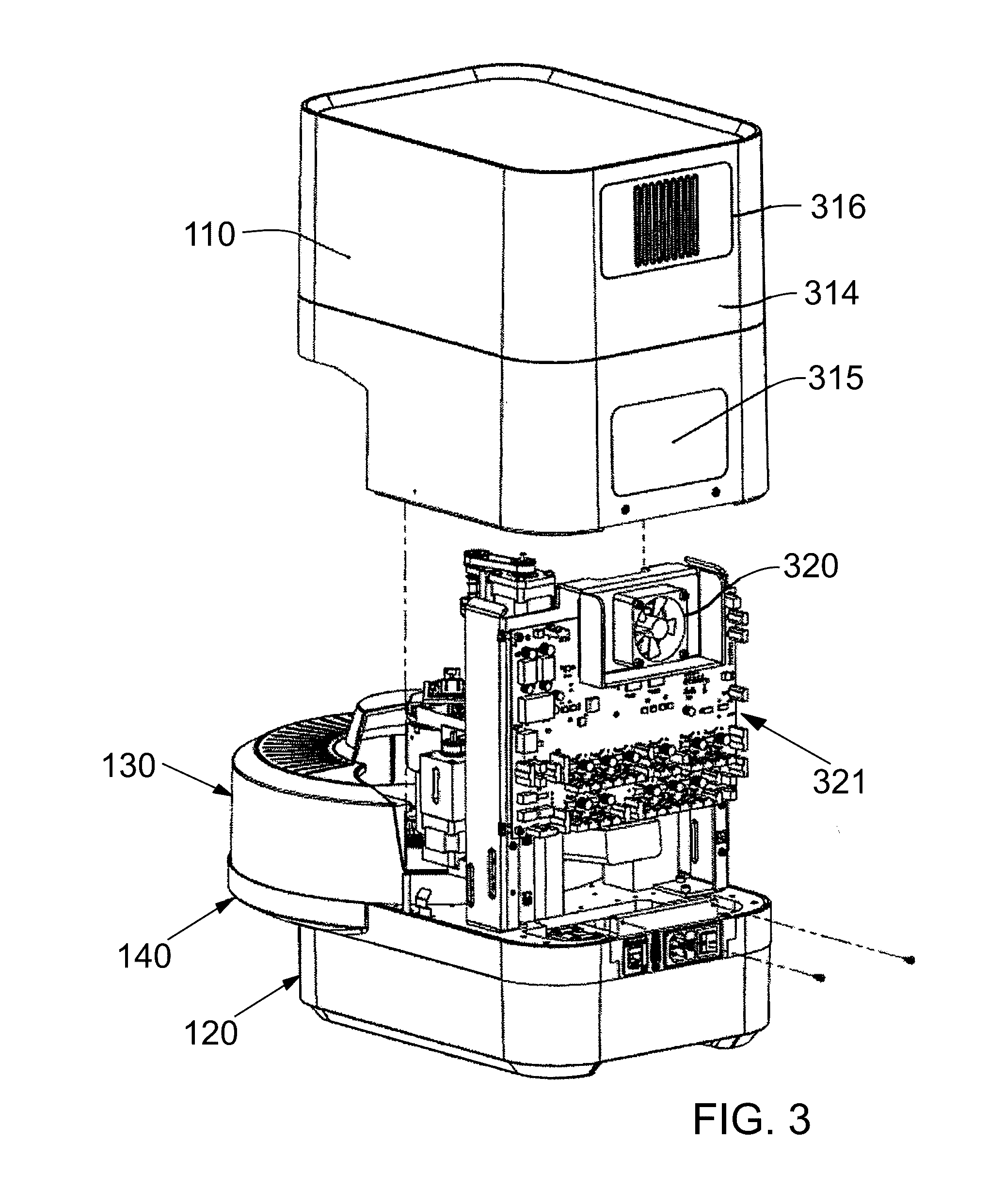
A diagnostic microbiological testing system and method for microorganism identification (ID) and antimicrobial susceptibility determinations (AST). The system includes multiple-well test panels capable of performing ID and AST testing on the same test panel. Each test panel is inoculated with reagents, broth-suspended organisms, and placed into the instrument system. The instrument system includes a rotating carousel for incubation and indexing, multiple light sources each emitting different wavelength light, precision calorimetric and fluorometric detection, barcode test panel tracking and a control processor for making determinations based on measured test data. One light source includes a plurality of LEDs arranged in a linear array. Each of the LEDs' junction currents are controllable to produce a predetermined illumination profile.
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON & CO
Sensitive and rapid determination of antimicrobial susceptibility
ActiveUS7687239B2Quick checkReduce sensitivityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsFiltrationReducing agent
The present invention relates to moving microorganisms to a surface, where they are grown in the presence and absence of antimicrobials, and by monitoring the growth of the microorganisms over time in the two conditions, their susceptibility to the antimicrobials can be determined. The microorganisms can be moved to the surface through electrophoresis, centrifugation or filtration. When the movement involves electrophoresis, the presence of oxidizing and reducing reagents lowers the voltage at which electrophoretic force can be generated and allows a broader range of means by which the target can be detected. Monitoring can comprise optical detection, and most conveniently includes the detection of individual microorganisms. The microorganisms can be stained in order to give information about their response to antimicrobials.
Owner:ACCELERATED MEDICAL DIAGNOSTICS INC
Method and apparatus for identification of bacteria
ActiveUS20120009558A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMicroorganismMicrobial Susceptibility
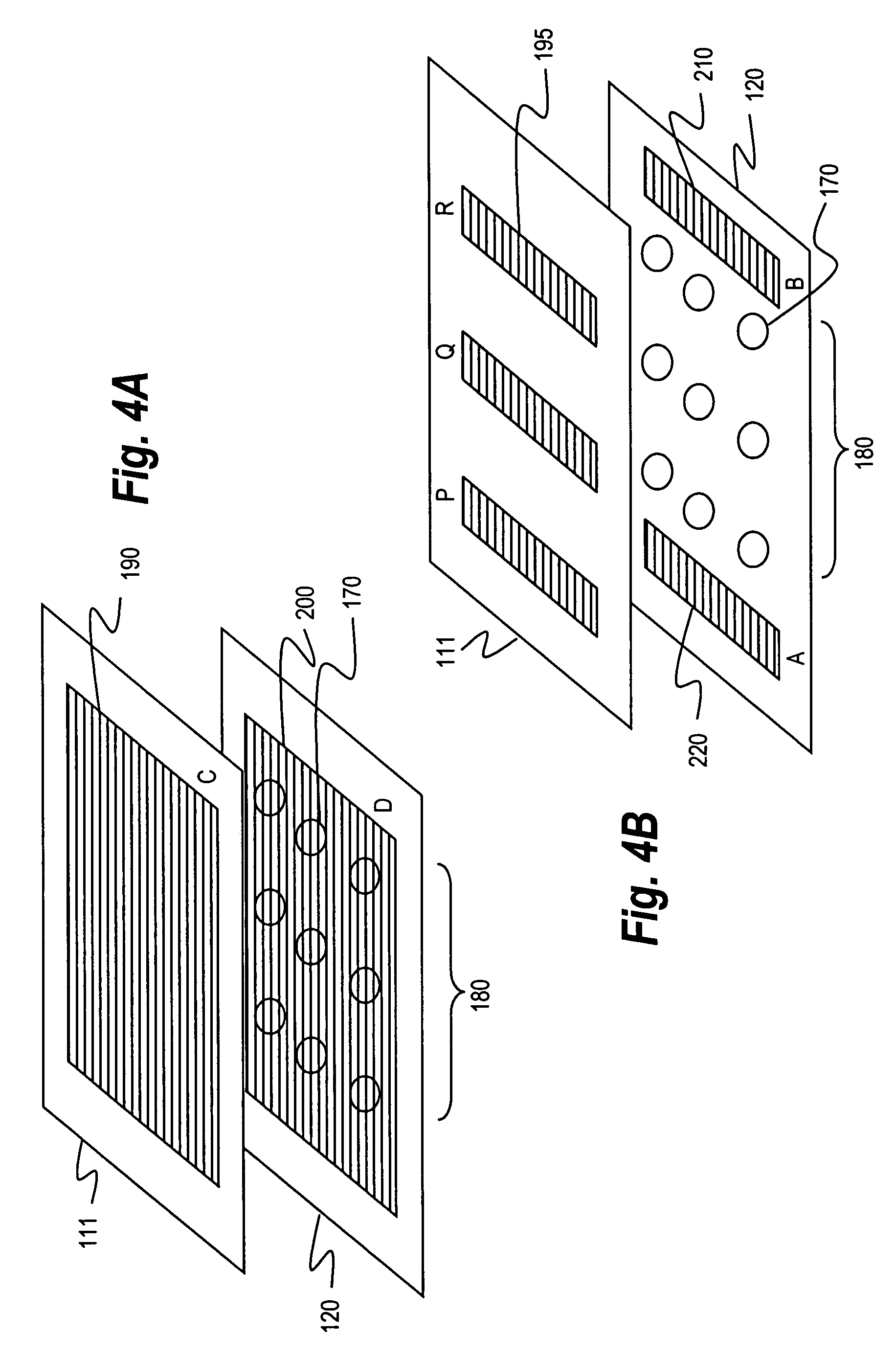
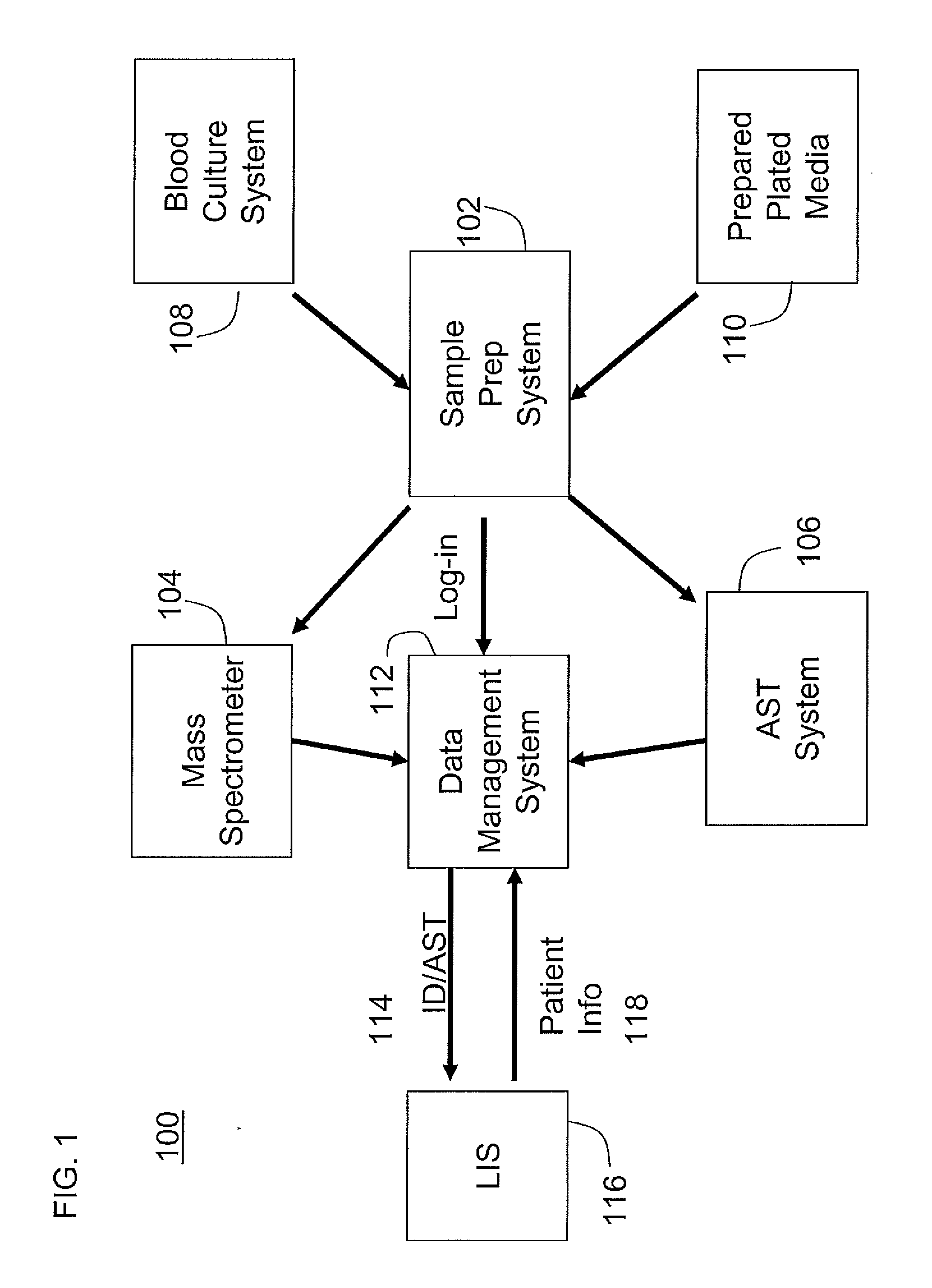
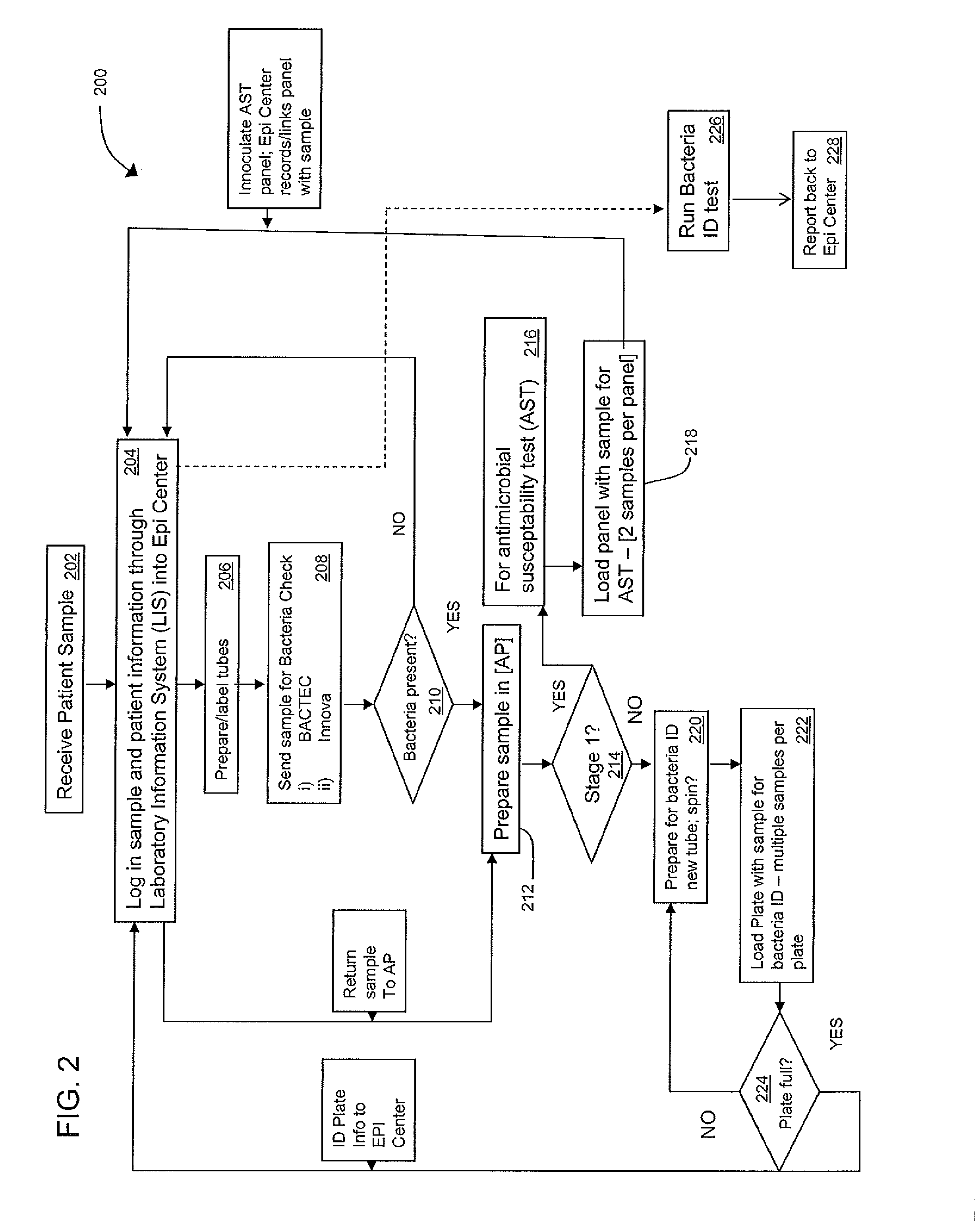
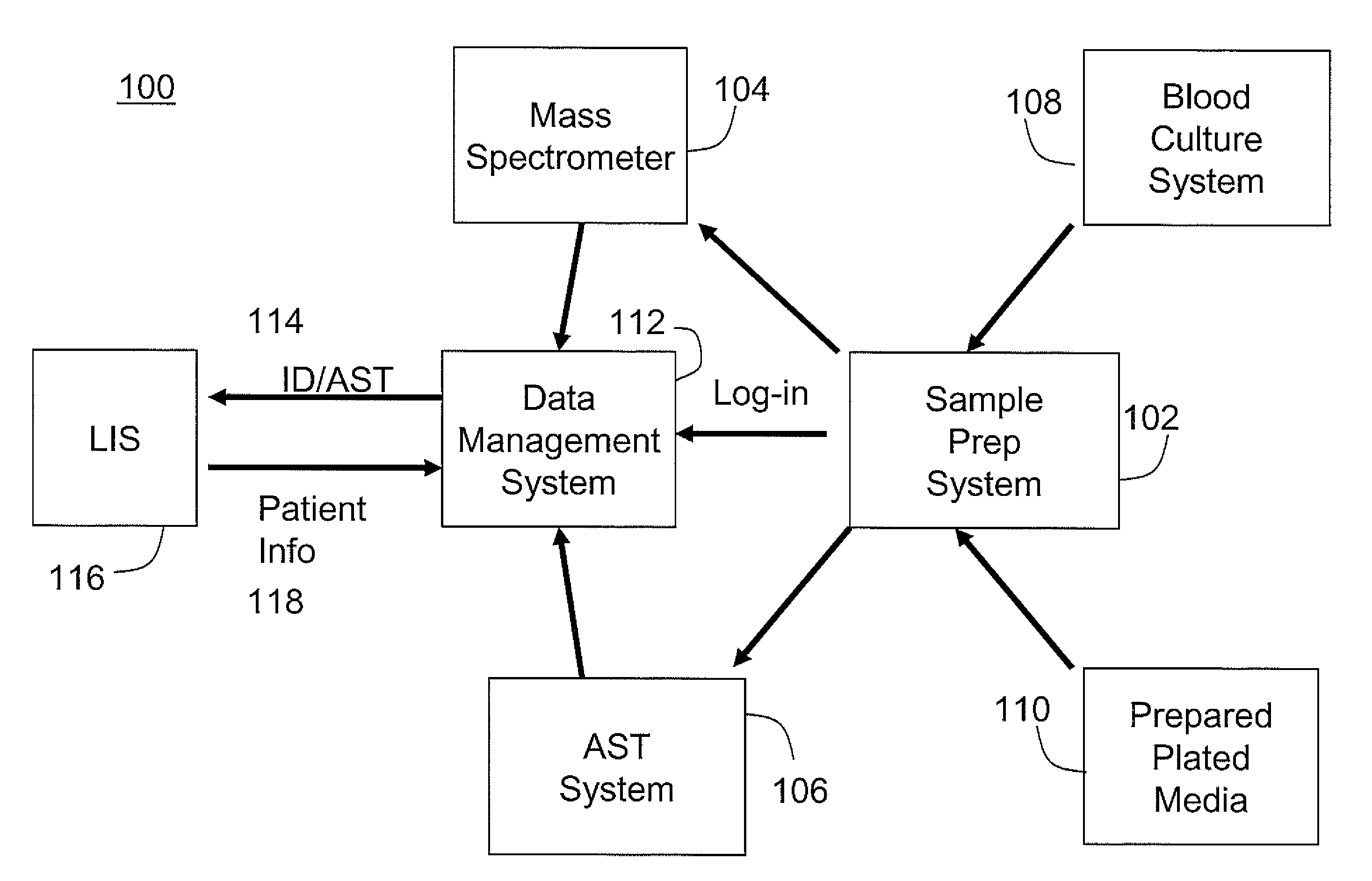
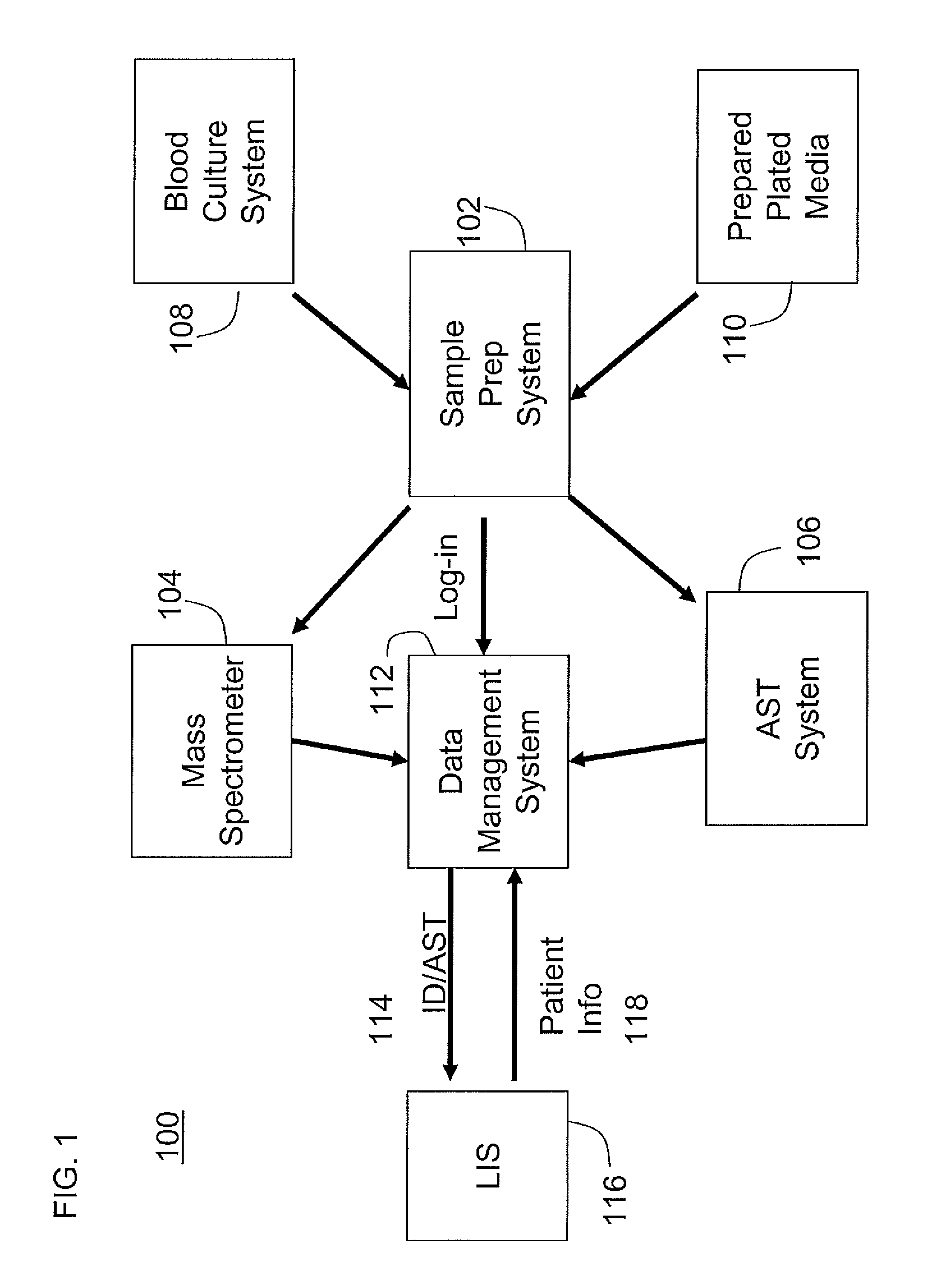
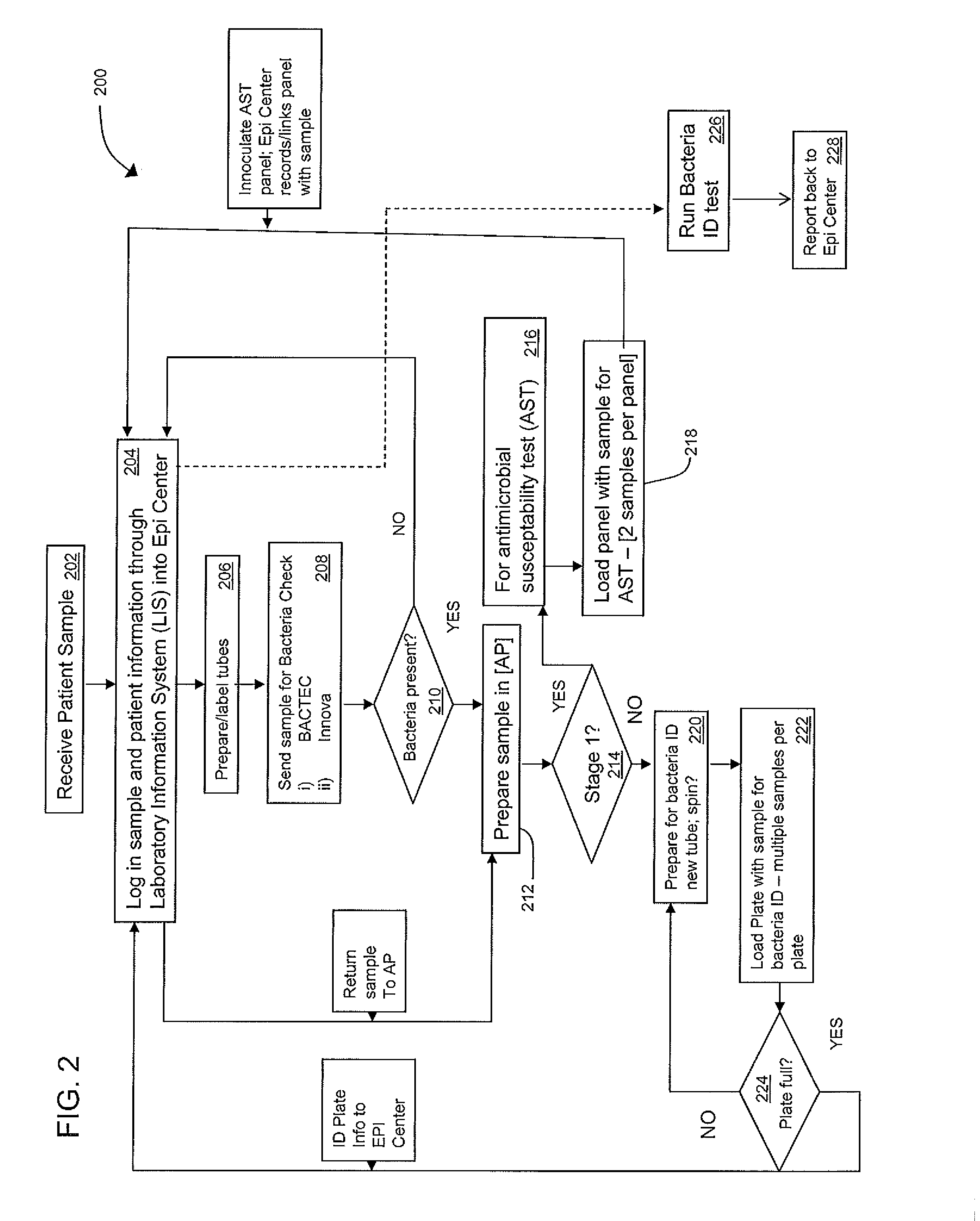
An automated system for identifying in a biological sample microorganisms and their antimicrobial susceptibility (AST). The system provided an automated platform for preparing, from a single biological sample, inoculates for both ID and AST. The system loads a plate for ID testing as samples are being prepared for AST testing. The system tracks the sample and the inoculates from the samples to link the test results to the sample and the patients from whom the sample was obtained.
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON & CO
Sensitive and rapid determination of antimicrobial susceptibility
ActiveUS20100136570A1Quick checkReduce sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementNanoinformaticsFiltrationReducing agent
The present invention relates to moving microorganisms to a surface, where they are grown in the presence and absence of antimicrobials, and by monitoring the growth of the microorganisms over time in the two conditions, their susceptibility to the antimicrobials can be determined. The microorganisms can be moved to the surface through electrophoresis, centrifugation or filtration. When the movement involves electrophoresis, the presence of oxidizing and reducing reagents lowers the voltage at which electrophoretic force can be generated and allows a broader range of means by which the target can be detected. Monitoring can comprise optical detection, and most conveniently includes the detection of individual microorganisms. The microorganisms can be stained in order to give information about their response to antimicrobials.
Owner:ACCELERATED MEDICAL DIAGNOSTICS INC
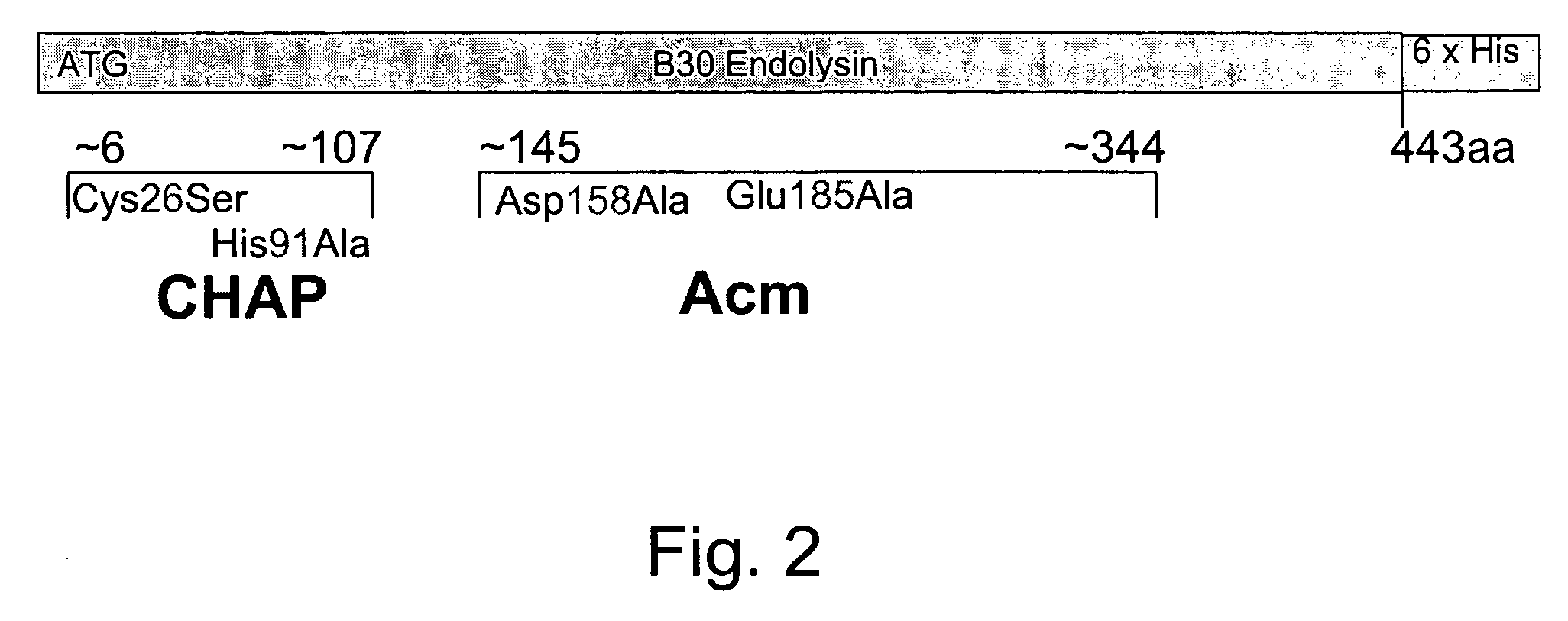
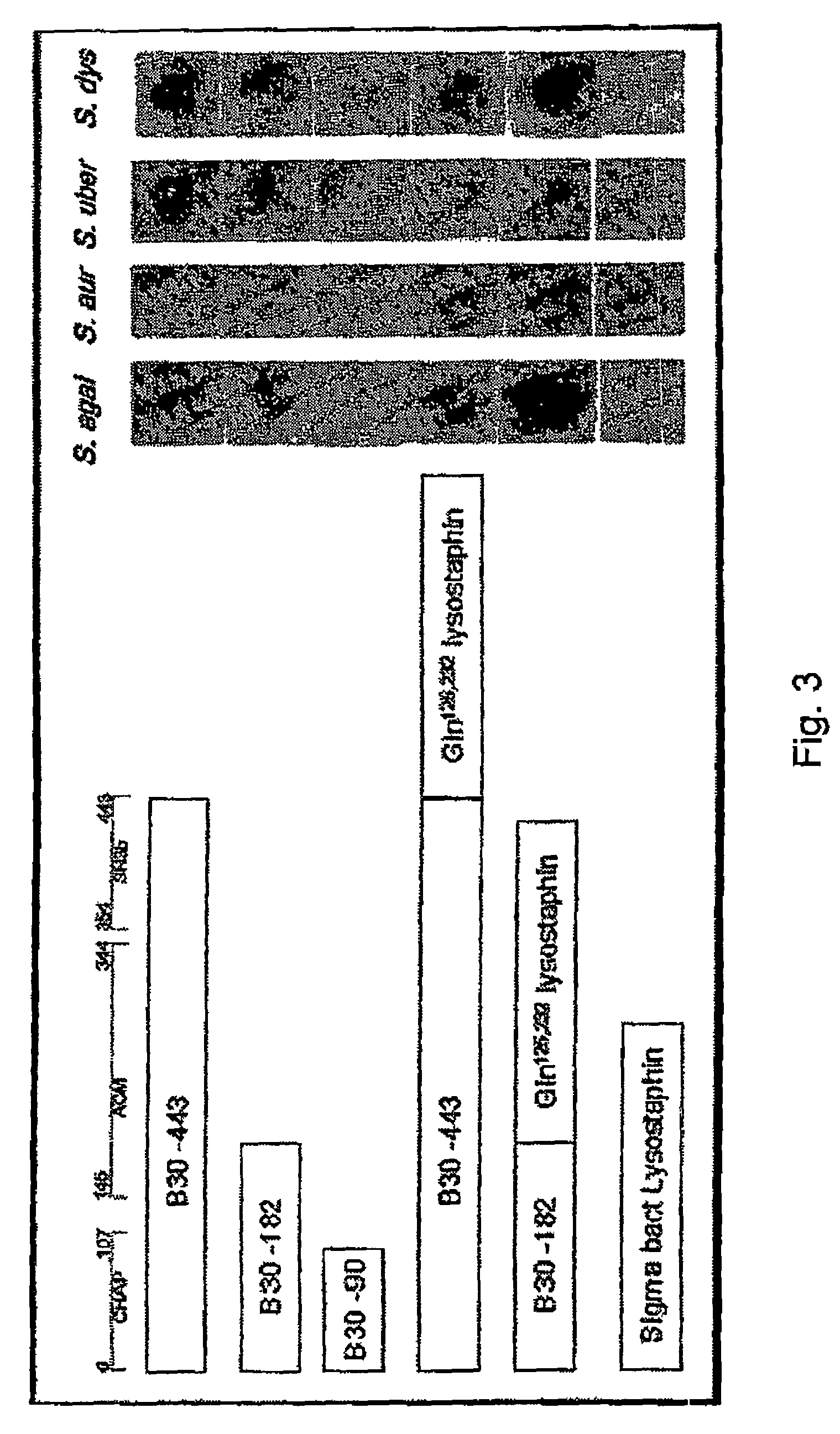
Nucleic acid encoding endolysin fusion protein
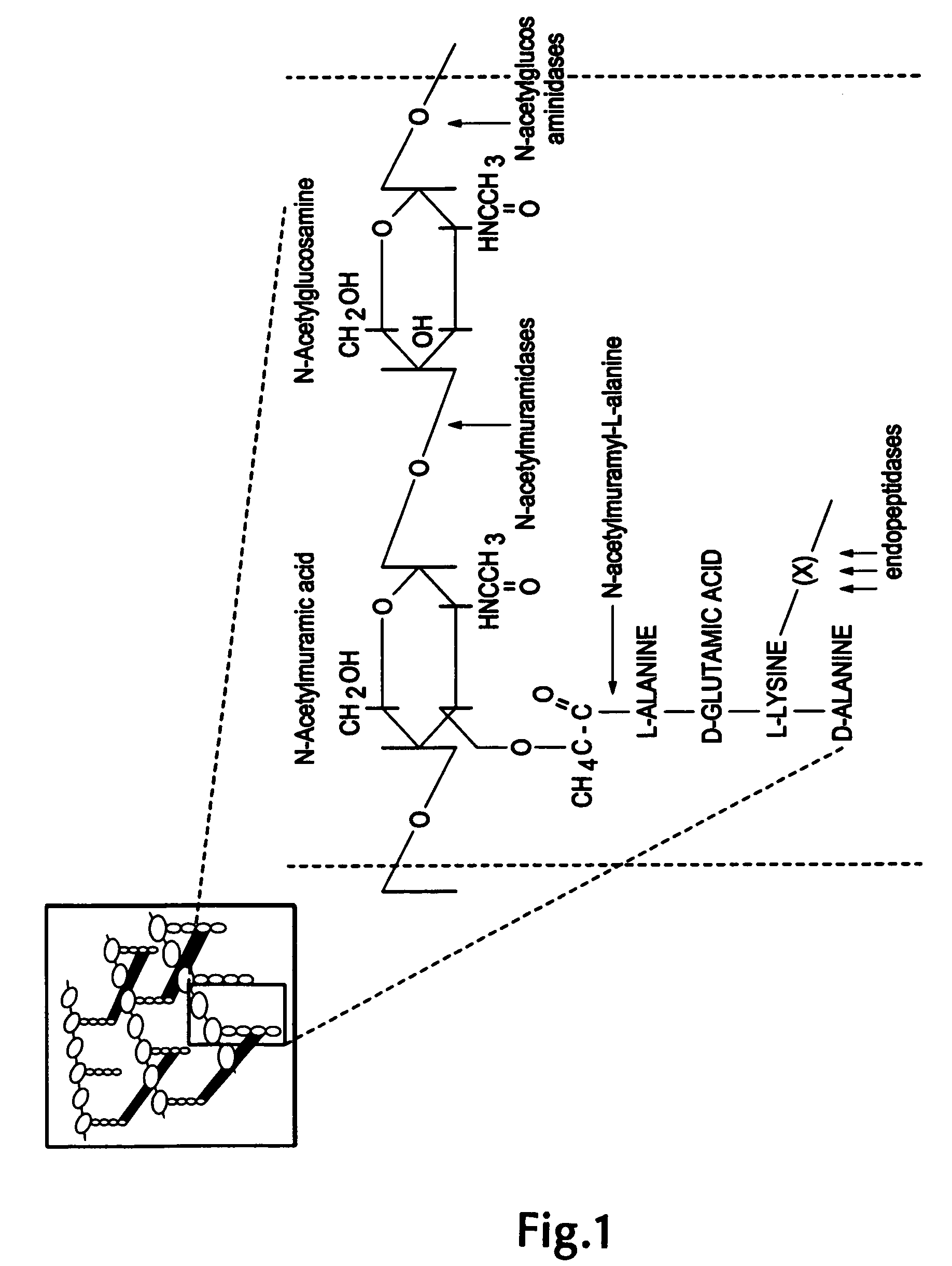
The invention concerns a recombinant nucleic acid molecule encoding an antimicrobial fusion peptidoglycan endopeptidase. The recombinant nucleic acid molecule according to the invention is formed from a nucleic acid encoding a bacterial endopeptidase (lysostaphin) from Staphylococcus simulans and a nucleic acid encoding a second endopeptidase (endolysin) module from Group B streptococcal bacteriophage B30. The encoded fusion endopeptidase has antimicrobial activity and kills both Staphylococcus bacteria and Streptococcus bacteria.
Owner:US SEC AGRI
Instrument and system for rapid microorganism identification and antimicrobial agent susceptibility testing
ActiveUS20170023599A1Rapid and accurate identificationRapid and accurate and antibiotic susceptibility testing resultMicrobiological testing/measurementBiochemistry apparatusMicroorganismMicrobial Susceptibility
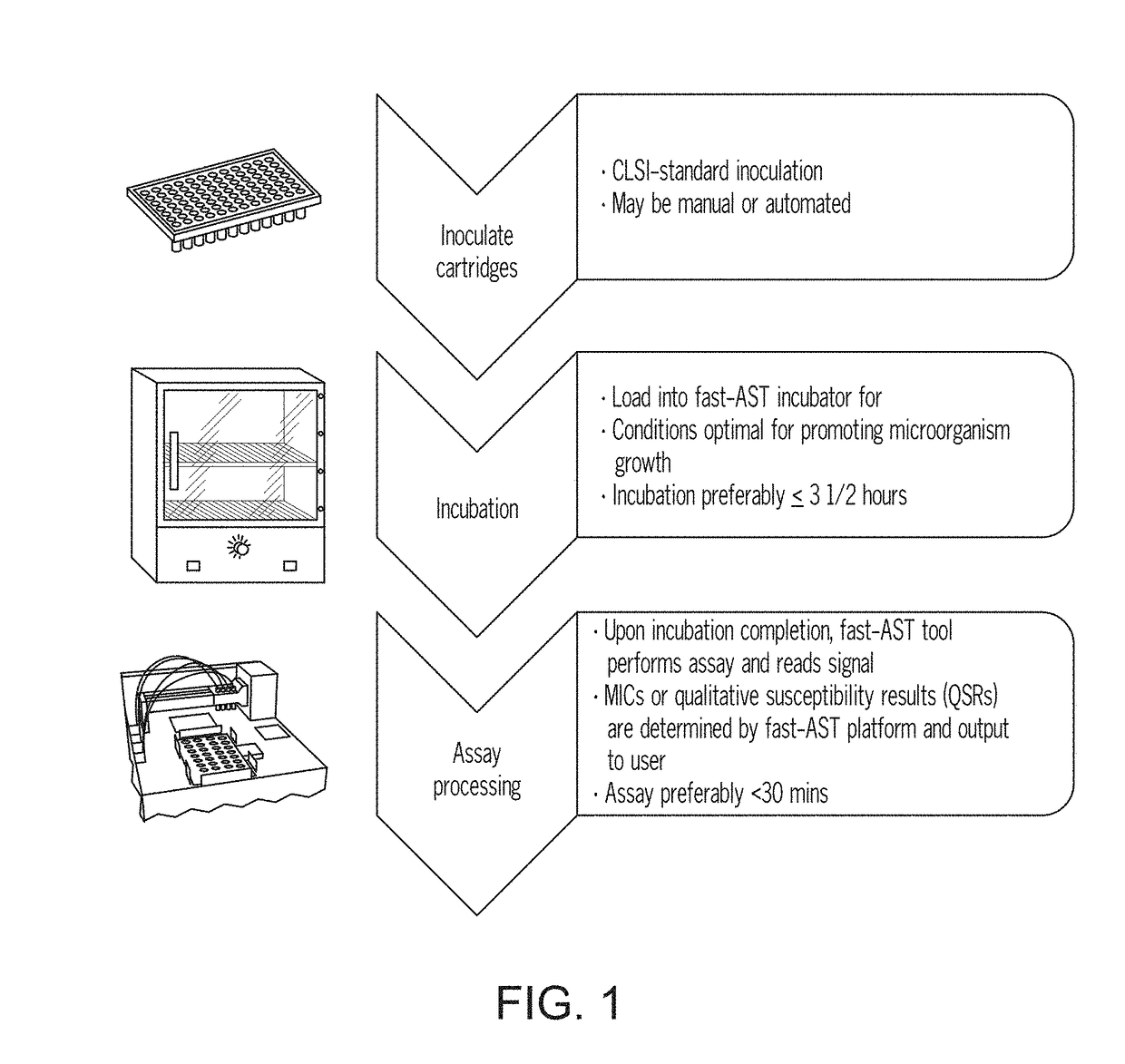
A system for automated microorganism identification and antibiotic susceptibility testing comprising a reagent cartridge, a reagent stage, a cassette, a cassette, stage, a pipettor assembly, an optical detection system, and a controller is disclosed. The system is designed to dynamically adjust motor idle torque to control heat load and employs a fast focus process for determining the true focus position of an individual microorganism. The system also may quantify the relative abundance of viable microorganisms in a sample using dynamic dilution, and facilitate growth of microorganisms in customized media for rapid, accurate antimicrobial susceptibility testing. Automated quality control test components and methods of their use are also disclosed.
Owner:ACCELERATED MEDICAL DIAGNOSTICS INC
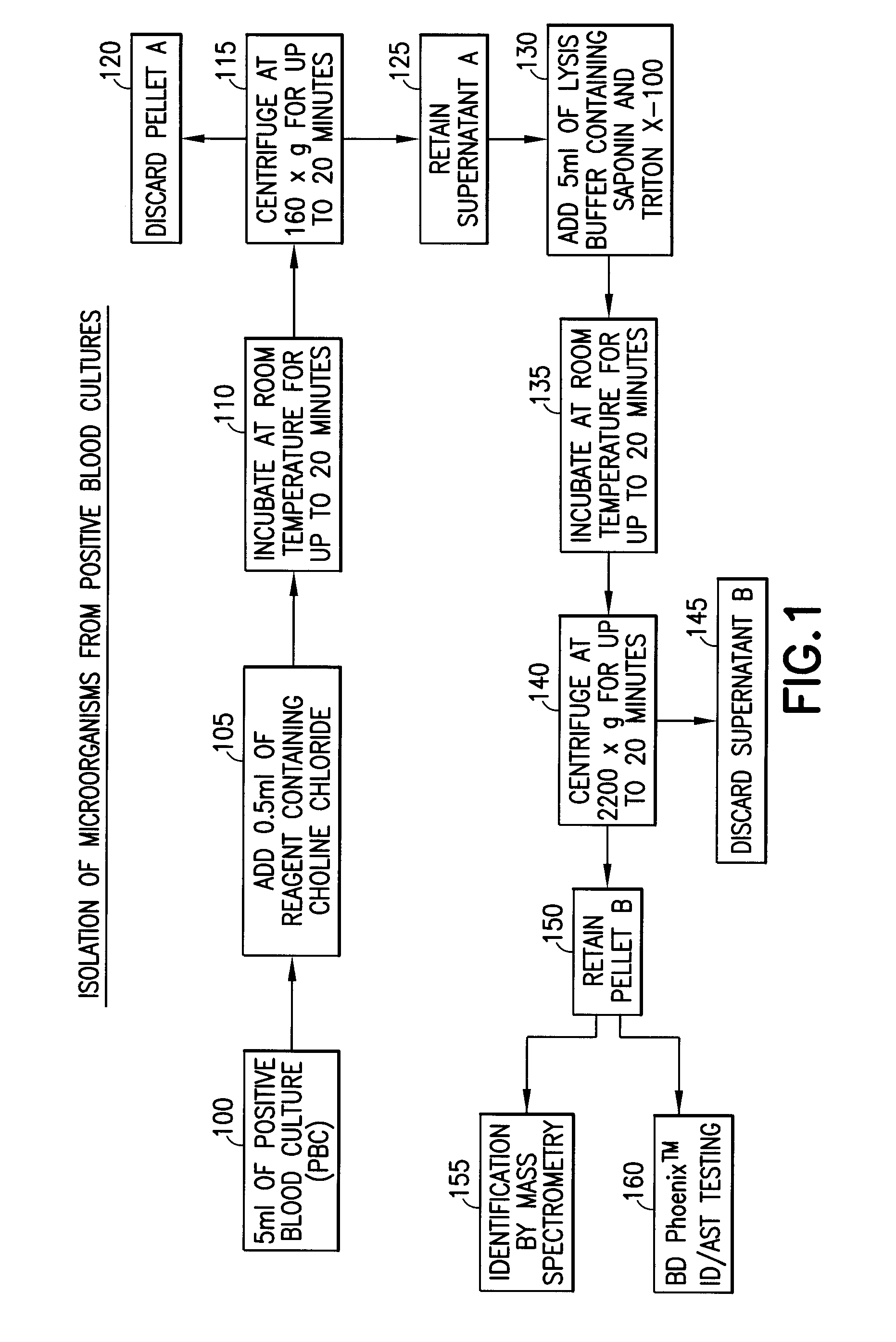
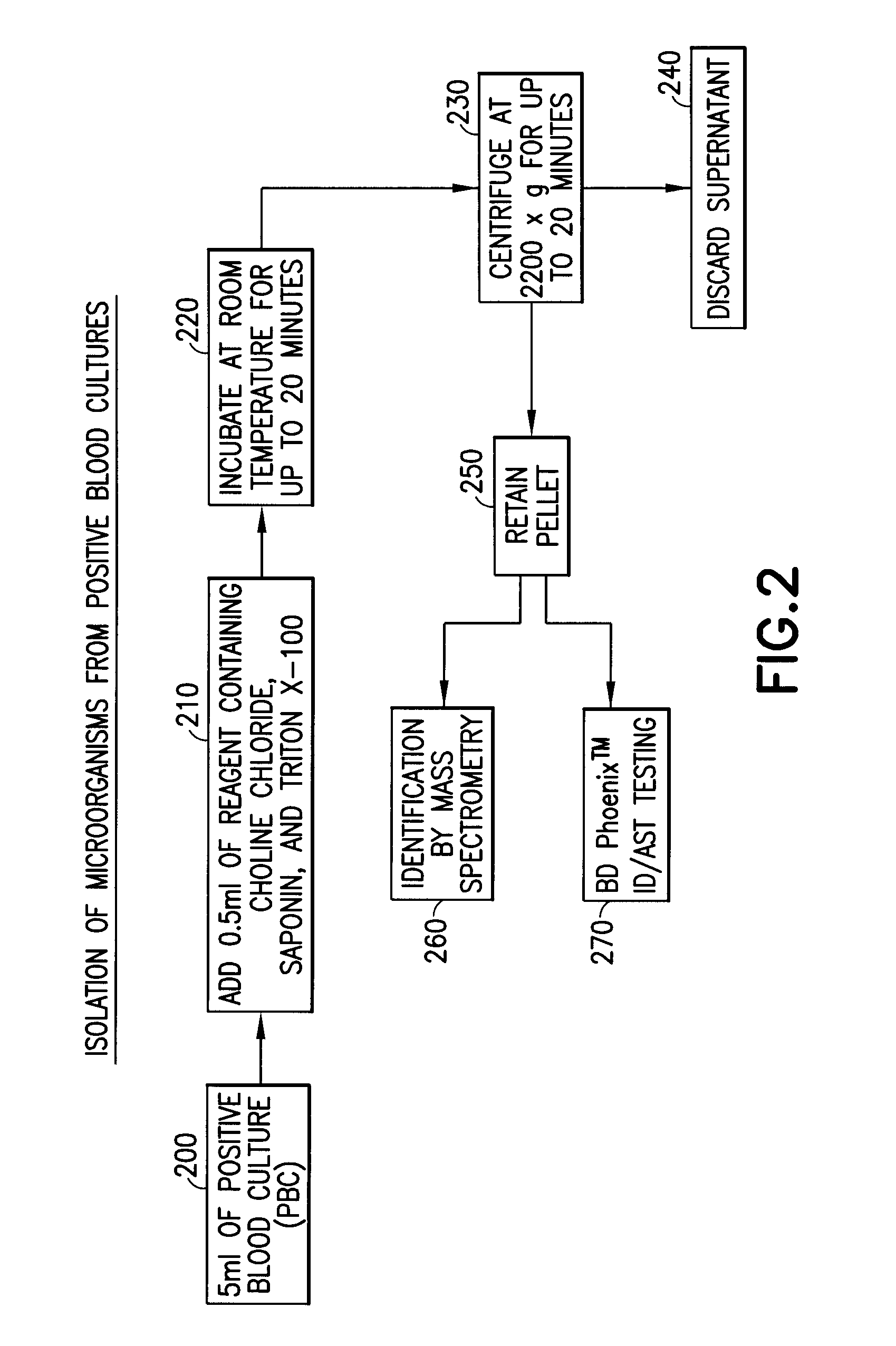
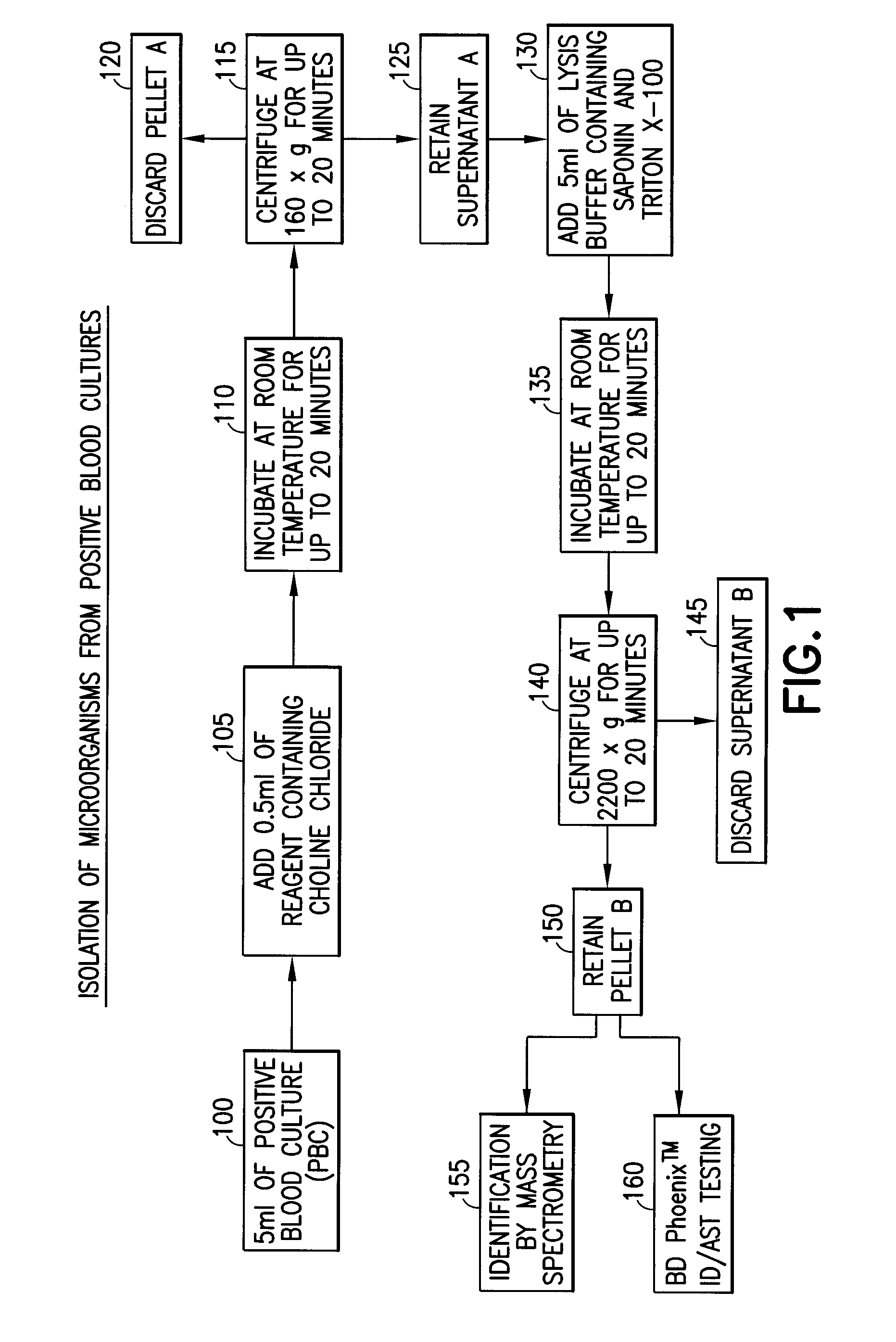
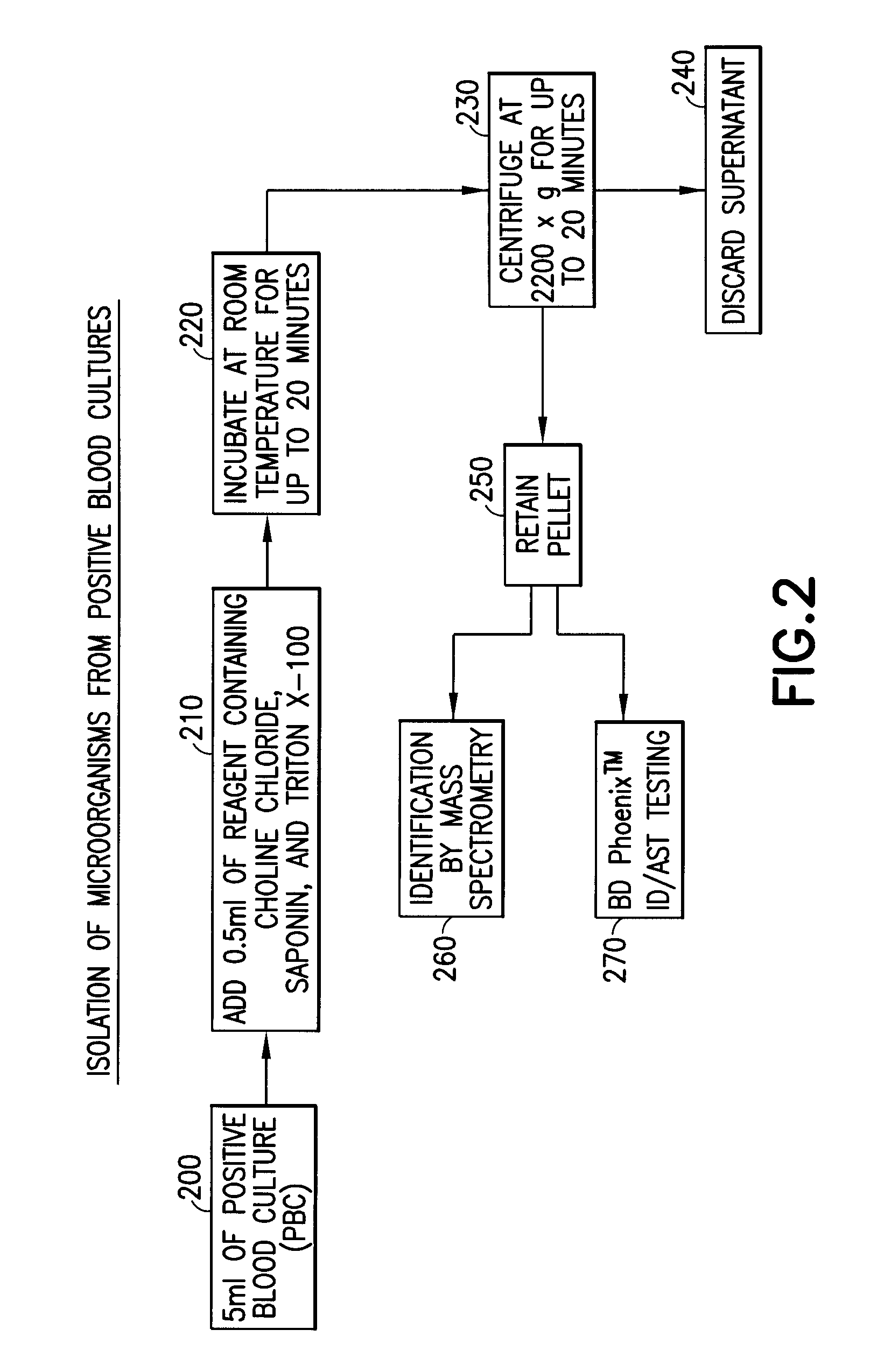
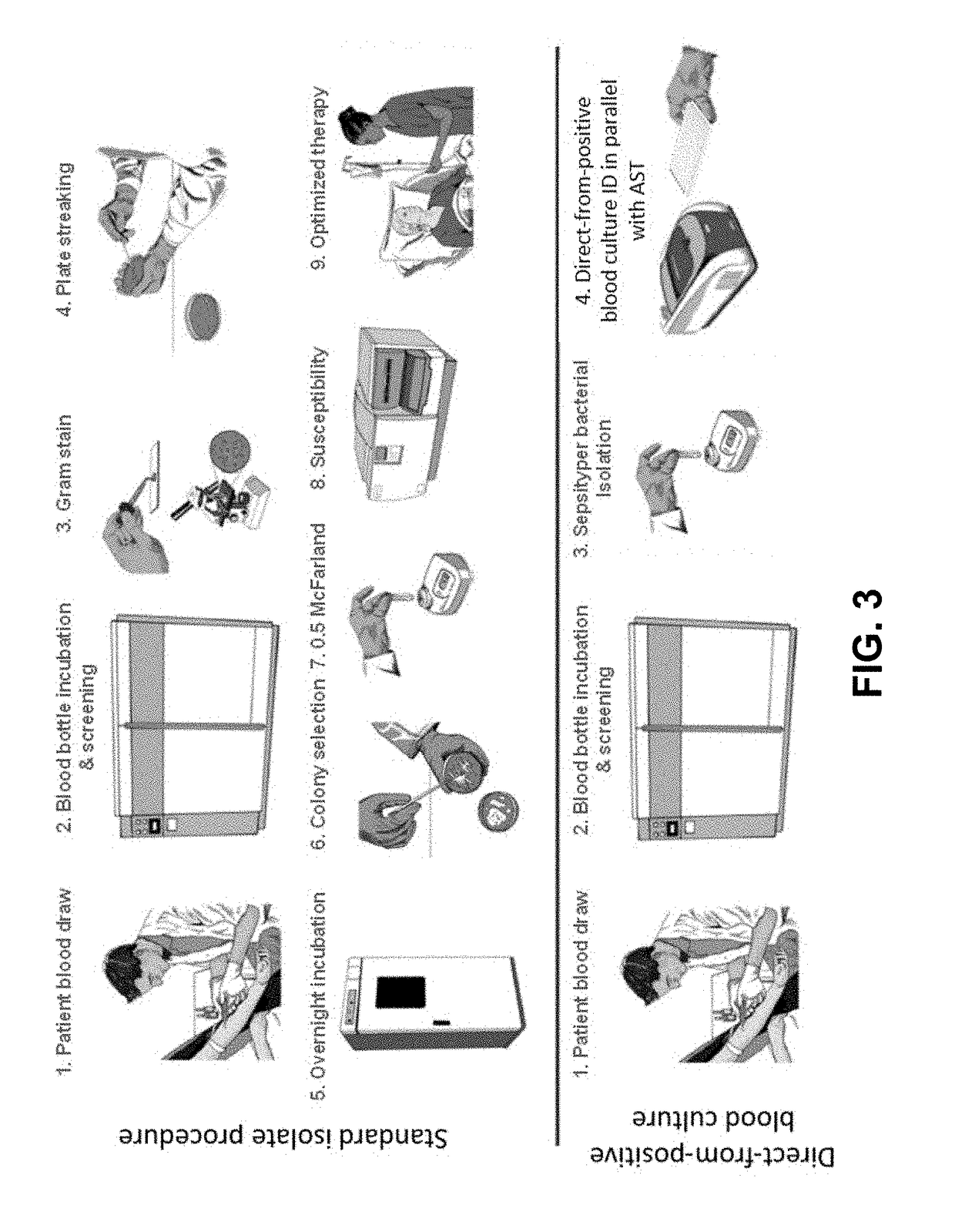
Method for direct and rapid identification of microorganisms and antimicrobial susceptibility testing from positive blood cultures
ActiveUS20130089886A1Rapid isolationBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganismMicrobial Susceptibility Test
Methods of the invention include the isolation of intact, viable microorganism(s) from positive blood culture (“PBC”) samples for use in downstream analyses such as identification and antimicrobial susceptibility testing (“AST”). The methods involve collecting a portion of the PBC sample, adding a choline-containing solution, lysing the blood cells, isolating the viable microorganism, and performing downstream analysis of the isolated, viable microorganism. The methods can be applied to a variety of gram-positive bacteria, gram-negative bacteria, and / or yeast, and particularly to strains of S. pneumoniae.
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON & CO
Method for direct and rapid identification of microorganisms and antimicrobial susceptibility testing from positive blood cultures
ActiveUS8603769B2Rapid isolationBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganismMicrobial Susceptibility Test
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON & CO
Methods for rapid antibiotic susceptibility testing
ActiveUS9834808B2Rapid determinationLess timeCompound screeningApoptosis detectionMicroorganismMicrobial Susceptibility
The present invention relates, in part, to methods and kits for rapidly determining antimicrobial susceptibility of microorganisms.
Owner:SELUX DIAGNOSTICS
Antimicrobial peptides and bacterial strains that produce them
InactiveUS20090214498A1Reduce the possibilityImprove securityAntibacterial agentsNervous disorderBacteroidesAntimicrobial peptides
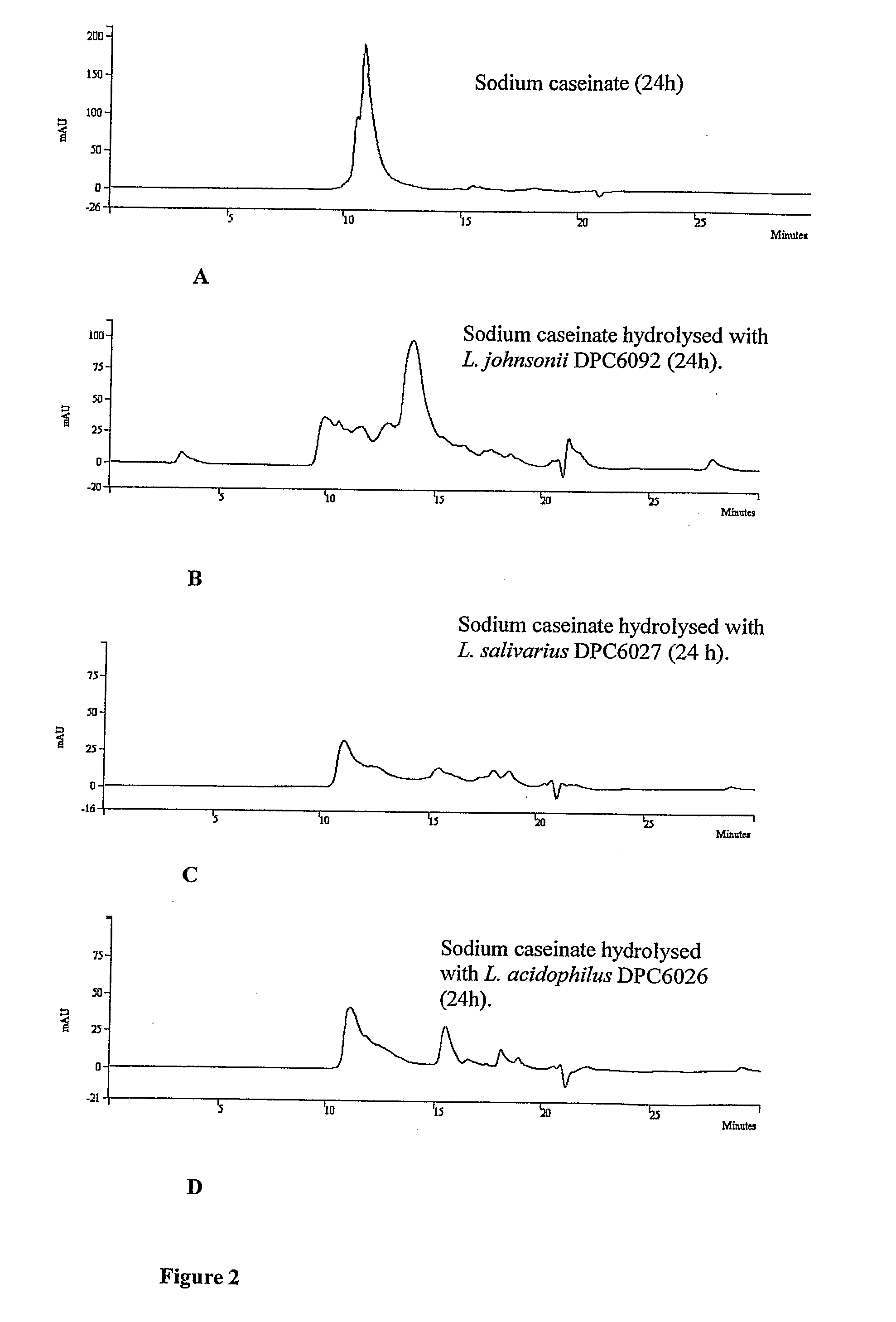
The present invention relates generally to the field of health promoting agents, in particular antimicrobial agents and provides antimicrobial peptides and bacterial strains that provide the antimicrobial peptides. In one aspect, the invention provides a biologically pure culture of Lactobacillus acidophilus, strain DPC6026, a sample of which has been deposited at the National Collection of Industrial and Marine Bacteria, Aberdeen, Scotland on 18th Nov. 2005 under the accession number NCIMB 41354, or a derivative or mutant thereof capable of producing from milk or a milk product, peptides having antimicrobial activity.
Owner:TEAGASC - NAT DAIRY PROD RES CENT
Method and apparatus for identification of bacteria
ActiveUS9180448B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMicroorganismMicrobiology
An automated system for identifying in a biological sample microorganisms and their antimicrobial susceptibility (AST). The system provided an automated platform for preparing, from a single biological sample, inoculates for both ID and AST. The system loads a plate for ID testing as samples are being prepared for AST testing. The system tracks the sample and the inoculates from the samples to link the test results to the sample and the patients from whom the sample was obtained.
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON & CO
Quantitative determination and drug allergy determination kits for helicobacter pylori viable bacteria and determination method
InactiveCN103757088ASolve the deficiency of only qualitative detection of Helicobacter pyloriSimple methodMicrobiological testing/measurementUrocaninaseDrug allergy
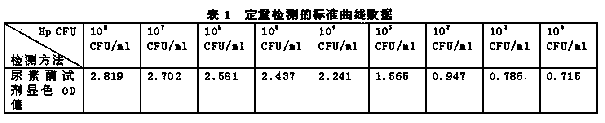
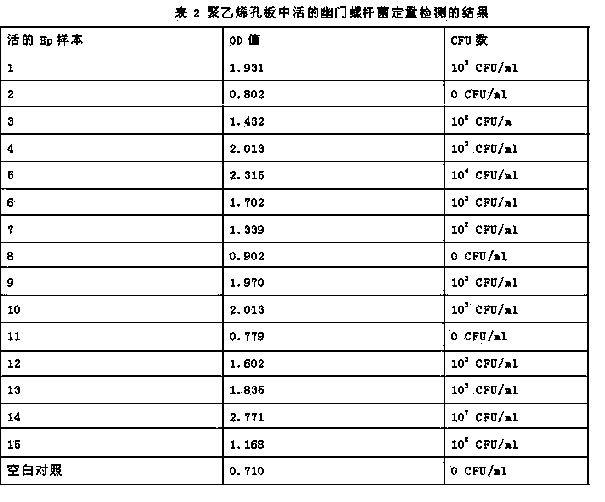
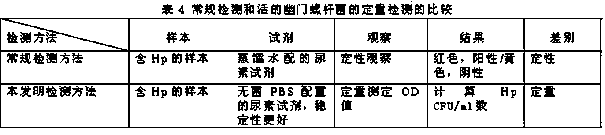
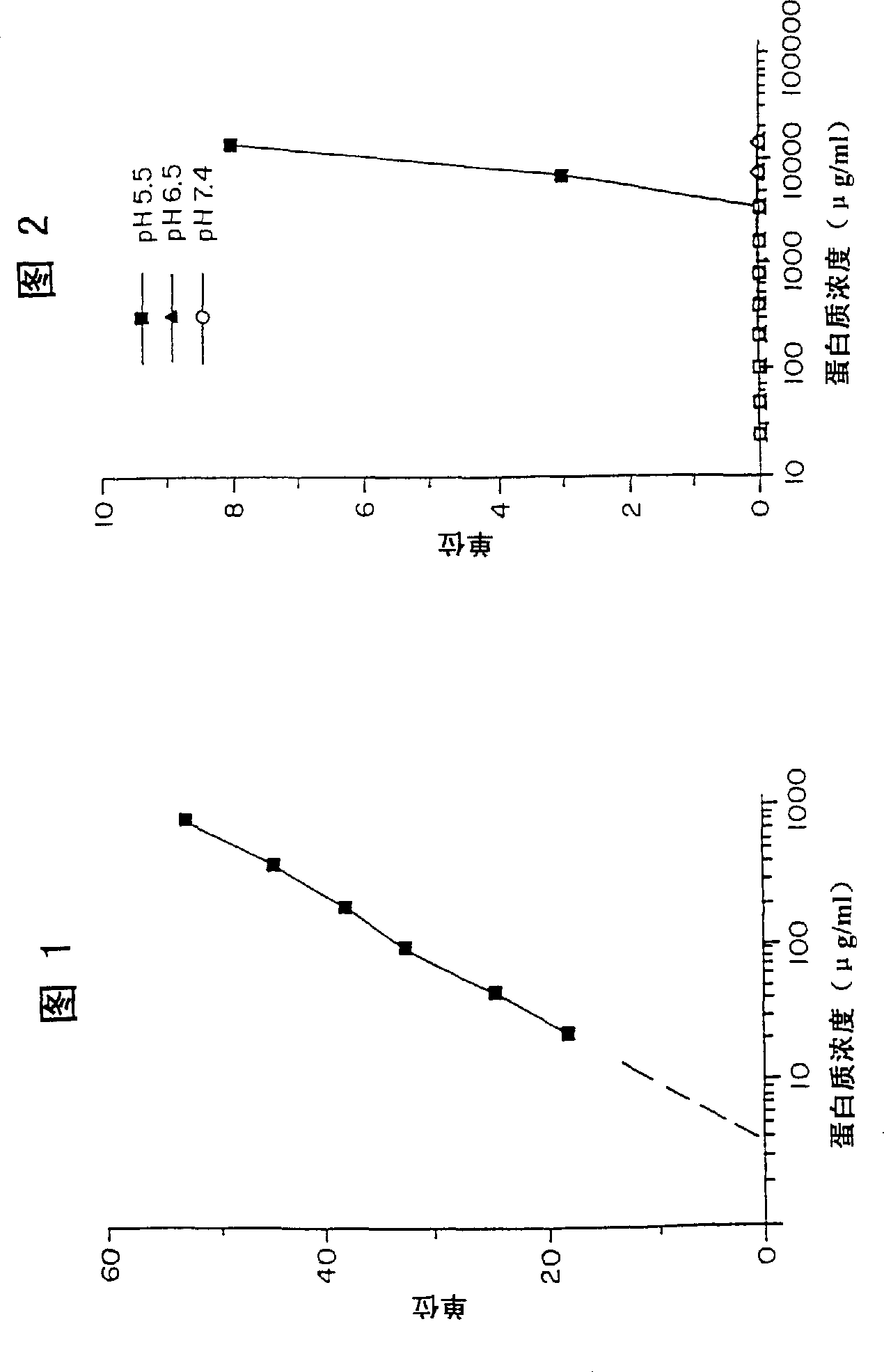
The invention discloses quantitative determination and drug allergy determination kits for helicobacter pylori viable bacteria and a determination method. The method adopts viable helicobacter pylori as a sample to be detected; the property that the viable helicobacter pylori can generate urease is used for rapidly and accurately reading the quantity of the helicobacter pylori by a helicobacter pylori colony counting standard method (CFU / ml, namely the bacterium individual quantity in each ml of bacterium liquid and a colony quantity standard curve); the detection result is accurate and sensitive and has high reliability; the counting difficulty of existing helicobacter pylori clinic microbiological identification, caused by difficult culture and complicated operation, is solved; the drug allergy determination kit and a preparation method, which are expanded by the invention, can be used for carrying out various drug allergy tests at the same time; clinicians can rapidly and conveniently screen suitable anti-helicobacter pylori medicines so that the time and the labor are saved and the cost is saved, so as to provide a beneficial technical solution for clinical scientific treatment.
Owner:SICHUAN VACCINE TECH
Method and apparatus for concurrently detecting pathogenic organisms and antimicrobial susceptibility
InactiveUS6984499B2Reduce riskCross-contamination between wells is preventedBiocideBioreactor/fermenter combinationsMicroorganismMicrobial Susceptibility
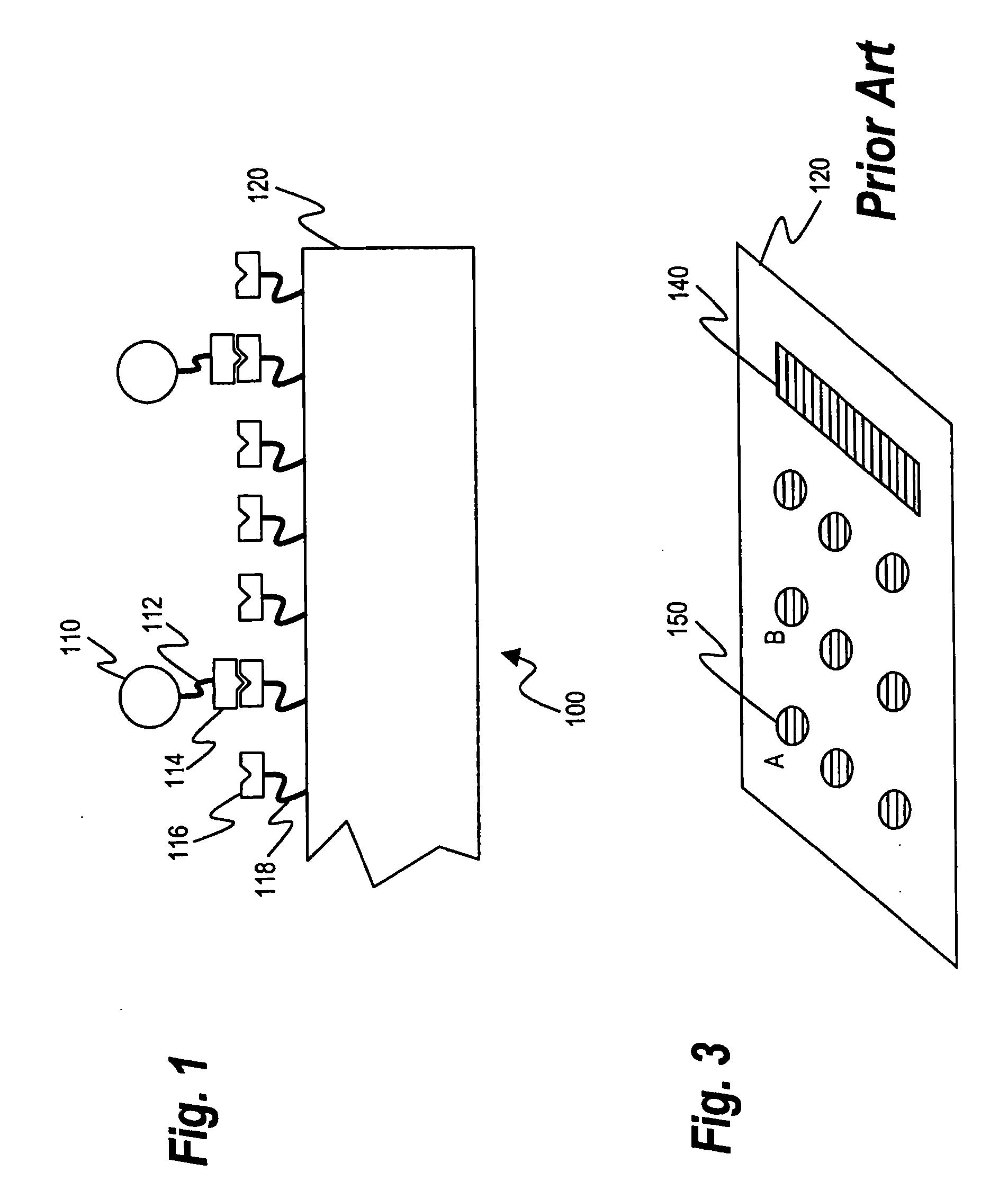
The present invention relates to a method of detecting the presence of target microorganisms in a biological sample and of simultaneously determining the susceptibility of the microorganisms to antimicrobial agents. The target microbial organisms may be urinary pathogens. The methods include the steps of providing a multicompartment assay device with at least one compartment containing a medium capable of sustaining the growth of total viable microorganisms, at least one compartment containing a medium capable of sustaining the growth of target microorganisms, and at least one compartment containing an antimicrobial susceptibility interpretation medium. A biological sample is placed in each compartment and the presence and antimicrobial susceptibility of the target microorganisms which may be present is determined by analyzing which compartments exhibit microbial growth.
Owner:IDEXX LABORATORIES
Mammalian-derived peptides for the treatment of microbial infection
The present invention provides compositions useful as antimicrobial agents which include mammalian hemoglobin, the alpha and beta chains of hemoglobin free of heme, fragments of the alpha and beta chains that result from cyanogen bromide cleavage of the alpha and beta chains, and synthetic peptides derived therefrom. The compositions exert antimicrobial activity against both bacteria and fungi that is comparable to known antimicrobial peptides from human neutrophils, cathepsin G and azurocidin. Sensitive organisms include Gram-negative bacteria such as Escherichia coli and Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Gram-positive bacteria such as Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus faecalis, and the fungus Candida albicans. Methods for preparing the compositions also are provided.
Owner:THERAGEM
Kit for quickly detecting drug resistance gene of pneumophila pathogenic bacteria
ActiveCN107475422AEasy to operateNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementMethicillin resistanceAntibiotic Y
The invention relates to a kit for quickly detecting a drug resistance gene of pneumophila pathogenic bacteria, which comprises a gene chip capable of detecting 24 main drug resistance genes of pneumophila pathogenic bacteria and a reaction system for multiple asymmetric PCR reactions. The 24 drug resistance genes are derived from aminoglycosides, quinolones, extended spectrum beta-lactamases (ESBLs), cephalosporins (AmpC), carbapenems and drug resistance genes with vancomycin resistance and methicillin resistance causing membrane permeability transition. The kit can be used for directly detecting drug resistance genes of pneumophila pathogenic bacteria in clinical samples, is simple and quick to operate, does not need culture or drug sensitive tests, gains valuable time for reasonable application of antibiotics to a great extent, and is worthy of clinical popularization and application.
Owner:GENERAL HOSPITAL OF PLA +1
Spectroscopic methods to detect and characterize microorganisms
Methods and systems for Resonant Raman spectroscopy are provided. Methods according to certain embodiments include irradiating a sample with a monochromatic light source at a first irradiation intensity and a second irradiation intensity, determining the intensity of one or more of the Resonant Raman scattering and fluorescence scattering at the first irradiation intensity and second irradiation intensity, calculating a rate of change of one or more of the intensity of Resonant Raman scattering and fluorescence in response to the change in irradiation intensity from the first irradiation intensity to the second irradiation intensity and comparing one or more of the rate of change in the intensity of Resonant Raman scattering and the rate of change in the intensity of fluorescence scattering with the rate of change in the irradiation intensity by the monochromatic light source to determine the Resonant Raman response of the sample. Methods also include determining the presence or absence of a microorganism in a sample and correcting for variations associated with measurement instrumentation (e.g., monochromatic light source) and variations associated with the sample (e.g., fluorescence from non-target compounds). Also provided are methods for determining the antimicrobial susceptibility of a microorganism to an antimicrobial agent as well as methods for characterizing a phenotype of an unknown microorganism in a sample. Systems for practicing the subject methods are also provided.
Owner:SPECTRAL PLATFORMS
Preparing method for cow mammitis staphylococcus culture fluid and its use
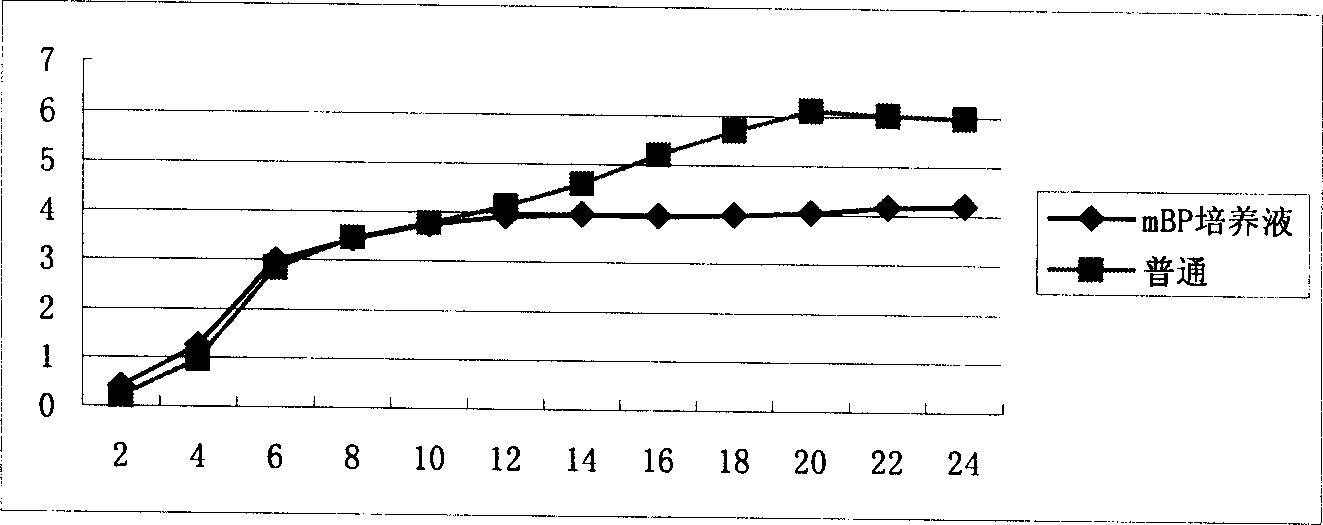
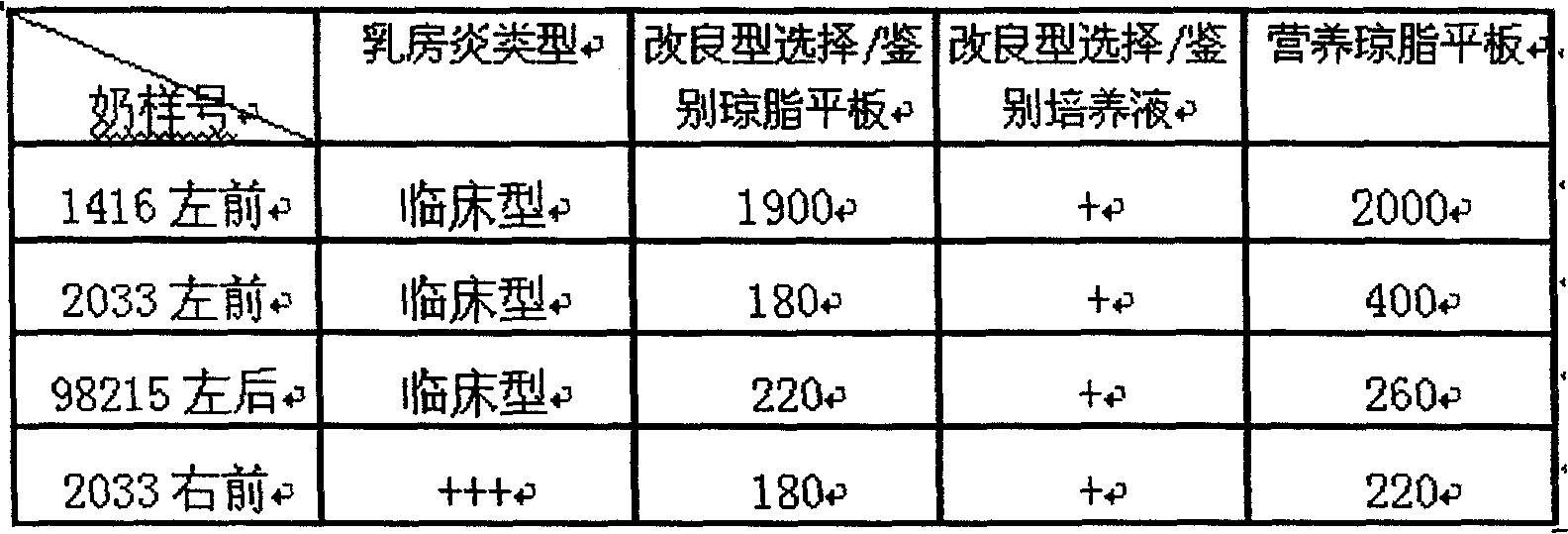
InactiveCN1858234AQuick selection/identificationRapid identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementAntibiotic sensitivityYeast
The preparation process of cow mammitis staphylococcus culture fluid and its use belongs to the field of animal epidemic disease diagnosing, preventing and treating technology. The preparation process includes dissolving peptone 10 g, yeast powder 5 g, sodium pyruvate 10 g, glycin 12 g and lithium chloride 5 g in water of 980 ml; regulating pH to 7.3 with sodium hydroxide; sterilizing at 121 deg.c; cooling to 50+ / -10 deg.c; adding bacteria-free 1% concentration potassium tellurite water solution in 10 ml and Tween-80 in 7 ml, and preservation at 4 deg. c. The culture fluid may be used in the fast identification of cow mammitis staphylococcus and antibiotic sensitivity test.
Owner:兆丰华生物科技(南京)有限公司
Method for evaluating antimicrobial susceptibility of drugs
ActiveCN102558511AEasy to handleLow costFluorescence/phosphorescenceHigh-Throughput Screening MethodsChemical compound
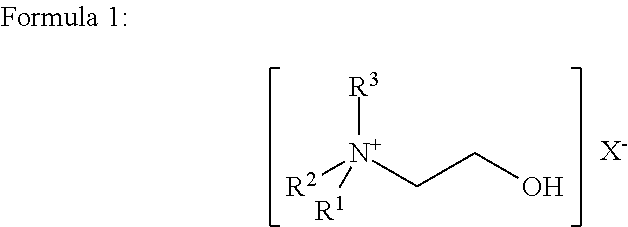
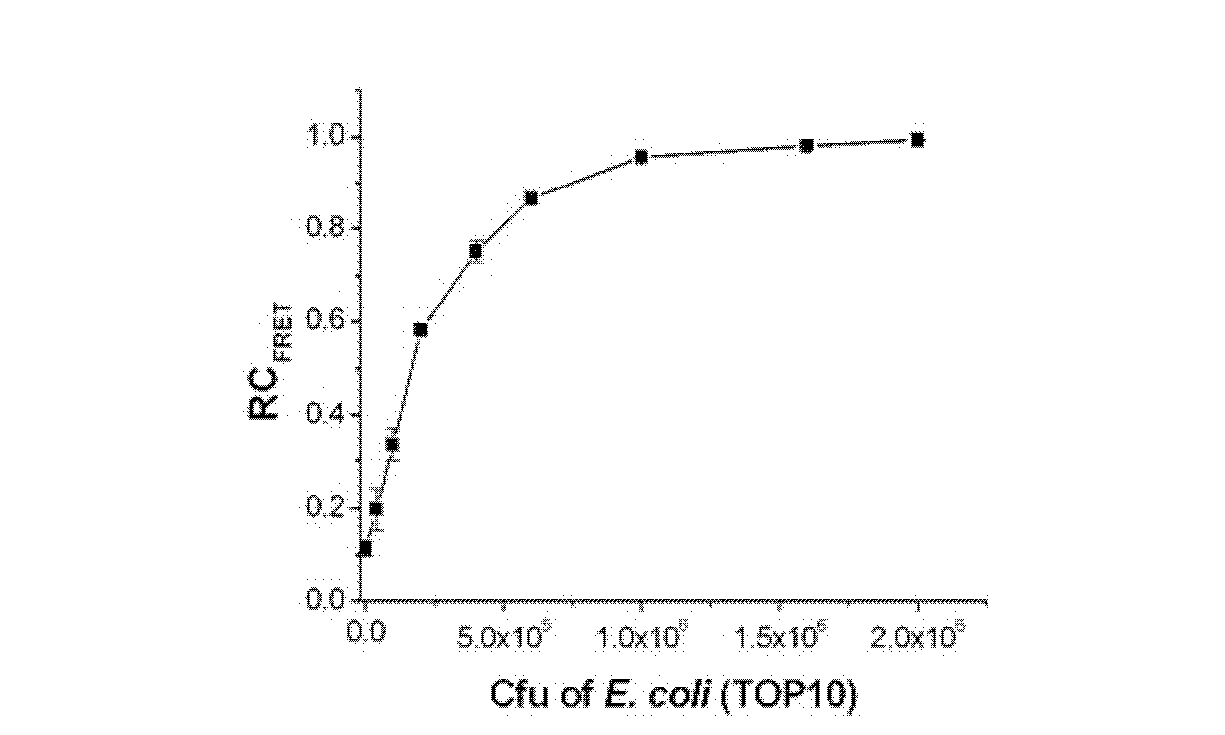
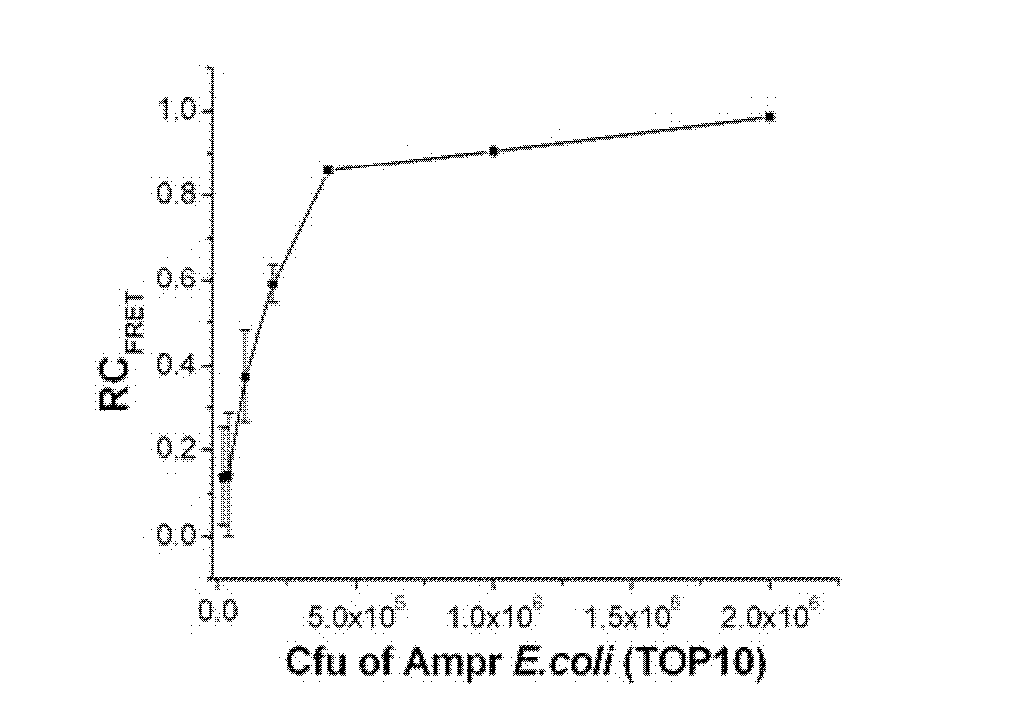
The invention discloses a method for evaluating antimicrobial susceptibility of drugs. The method utilizes compounds represented by general formulas (I) and (II) to assist to give quantitative susceptibility data of antibiotics against pathogens. The method has the advantages of being sensitive (as low as 2*104 c f u), quick (4-5hours), accurate, visible and the like. Besides, the method is applicable to high throughput screening of antibiotics. Compared with various systems with advanced technologies, the method needs not complicated instruments and equipment, sample treatment is simple, cost is low, outside non-specific effects are few, and antibiotic concentration in inhibition percentage can be optionally provided. In clinic, the method can be used for quick evaluation of antimicrobial susceptibility to instruct doctors to perform drug administration on patients more pertinently, thereby not only treatment efficiency is improved, but also drug resistance caused by incorrect use of the antibiotics is lowered. Meanwhile, the method for evaluating antimicrobial susceptibility of drugs can also have profound effects in terms of food safety, environment detecting, and the like. Formula I and formula II are as followed.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Methods and devices for the detection of pathogenic microorganisms and their antimicrobial susceptibility
ActiveUS7384778B2Improve trustPromote growthBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBacteroidesBiological body
The present invention provides devices and methods for determining the presence or absence of pathogens in a biological sample and for the concurrent determination of the antimicrobial susceptibility of pathogens present. The devices and methods of the present invention are able to make the determinations without pre-selection of target bacteria. Instead, all organisms from the sample are applied to the device. In wells where one or more antimicrobial agents are present only pathogens resistant to the antimicrobial agent grow. This allows the user to determine the presence of target pathogens and concurrently determine the resistance patterns of the organisms without the need to subculture the organisms. The present invention also provides methods of performing a business service of performing the determinations described above, and kits containing the devices and descriptions of the methods.
Owner:IDEXX LABORATORIES
Probiotic strains from Lactobacillus salivarius and antimicrobial agents obtained therefrom
A strain of Lactobacillus salivarius isolated from resected and washed human gastrointestinal tract inhibits a broad range of Gram positive and Gram negative microorganisms and secretes a product having antimicrobial activity into a cell-free supernatant. The activity is produced only by growing cells and is destroyed by proteinase K and pronase E, the inhibitory properties of the strain and its secretory products being maintained in the presence of physiological concentrations of human bile and human gastric juice. The strain exhibits a broad-spectrum of activity against bacteria including Listeria, Staphylococcus, including methocillin resistant St. aureus (MRSA), and Bacillus, but does not inhibit many closely related lactobacilli. An antimicrobial agent is obtained from the strain which has bacteriocin-like properties.
Owner:ENTERPRISE IRELAND & UNIV COLLEGE CORK +1
Probiotic strains from lactobacillus salivarius and antimicrobial agents obtained therefrom
Owner:ENTERPRISE IRELAND +1
Instrument and system for rapid microorganism identification and antimicrobial agent susceptibility testing
ActiveUS10253355B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsTelevision system detailsMicroorganismMicrobial Susceptibility
A system for automated microorganism identification and antibiotic susceptibility testing comprising a reagent cartridge, a reagent stage, a cassette, a cassette, stage, a pipettor assembly, an optical detection system, and a controller is disclosed. The system is designed to dynamically adjust motor idle torque to control heat load and employs a fast focus process for determining the true focus position of an individual microorganism. The system also may quantify the relative abundance of viable microorganisms in a sample using dynamic dilution, and facilitate growth of microorganisms in customized media for rapid, accurate antimicrobial susceptibility testing. Automated quality control test components and methods of their use are also disclosed.
Owner:ACCELERATED MEDICAL DIAGNOSTICS INC
Mechanisms of Antimicrobial Susceptibility
ActiveUS20160348187A1Growth inhibitionCompromise its viabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementBacteriophagesMicrobiologyAntibacterial susceptibility
Disclosed herein are methods and compositions for determining the presence or absence of a mechanism of antimicrobial resistance in a sample.
Owner:ROCHE MOLECULAR SYST INC
Reagents, methods and kits for classification of fungi and direction of anti-fungal therapy
InactiveUS20070082351A1Quickly availableEasy to analyzeSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementFungal microorganismsBiology
Provided herein are methods, kits and compositions to classify fungi. Methods are provided for classification of fungi according to established phenotypes, for example, antimicrobial susceptibility profiles. More specifically, the invention provides methods for the use of PNA probes in diagnostic applications, which will aid in the direction of appropriate therapy against fungi.
Owner:ADVANDX
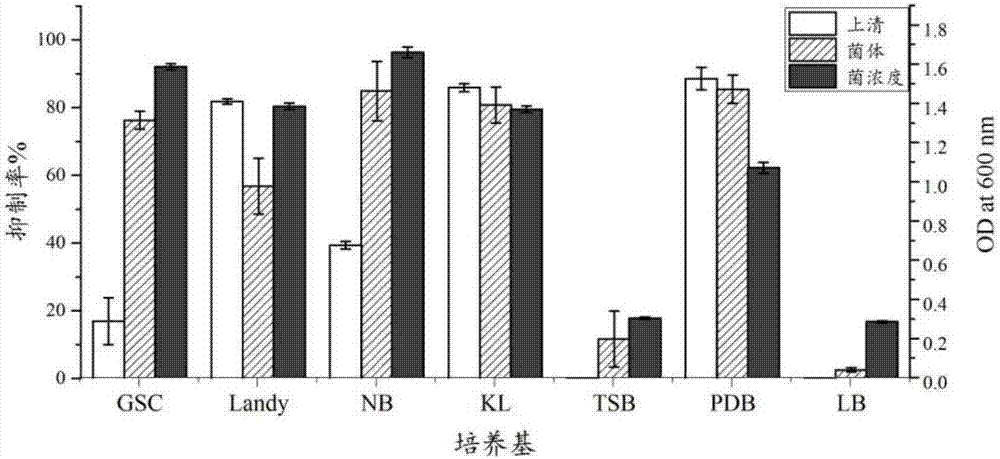
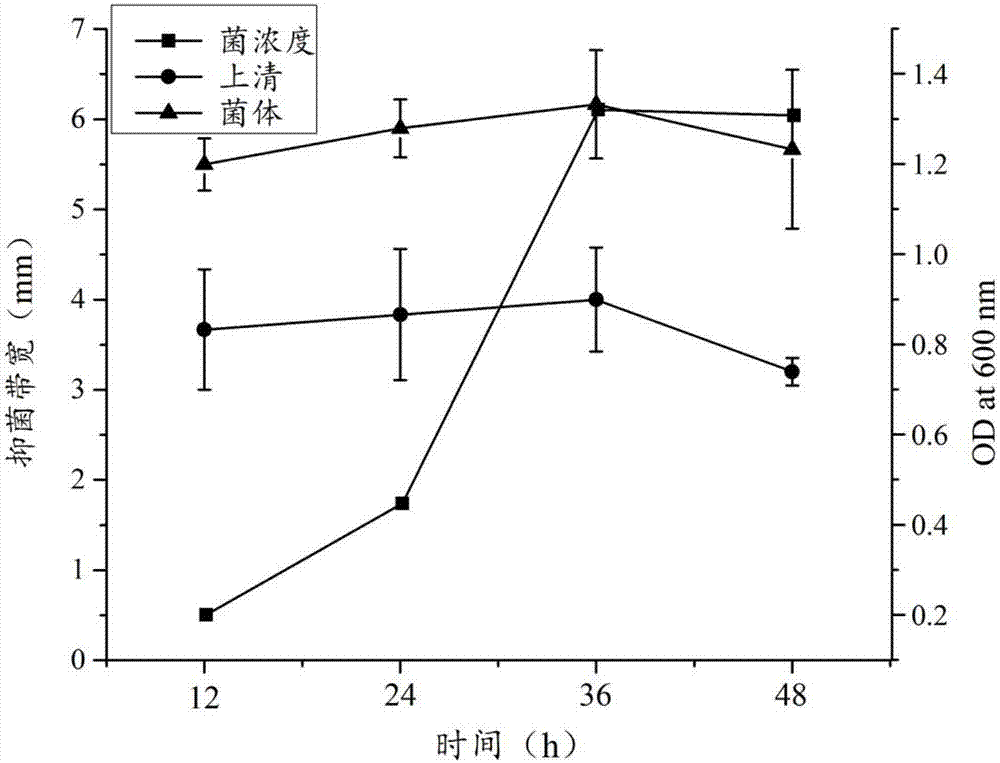
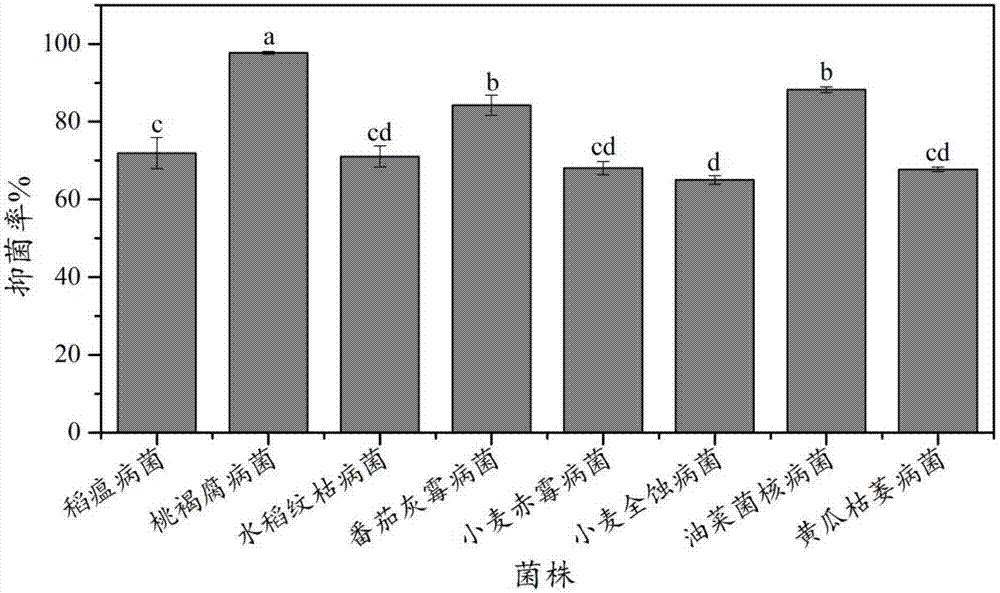
Paenibacillus polymyxa antimicrobial agent and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a Paenibacillus polymyxa antimicrobial agent and a preparation method thereof. The antimicrobial agent is prepared by the following steps: Paenibacillus polymyxa CGMCC No.12410 is fermented on a KL medium for 36 hours, and fermented supernatant or a methanol extract product of bacteria is used as the antimicrobial agent. CGMCC No.12410 is cultivated in LB, PDB, Landy, GSC, NB, KL, and TSC under the same conditions, and antimicrobial capability of the fermented supernatant has large difference. In the same medium, the antimicrobial capability of the fermented supernatant is obviously lower than the antimicrobial capability of the methanol extract product of bacteria. An experiment proves that the bacterial strain CGMCC No.12410 is fermented in the KL medium for 36 hours, the methanol extract product of bacteria has wide antimicrobial spectrum, and the methanol extract product of bacteria can inhibit a plurality of pathogenic fungi. At the same time, diseases prevention and inoculation experiments of Botrytis cinerea which are carried out on tomato fruits show that lowest antimicrobial rate of the methanol extract product of bacteria is 88.6%, and antimicrobial effects are good.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
Drug-sensitive kit and preparation method thereof and bacterial drug sensitivity testing method
ActiveCN110846377AThe test result is accurateShort timeMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisBacterial diseaseVeterinary Drugs
The invention belongs to the technical field of drug testing and discloses a drug-sensitive kit and a preparation method thereof and a bacterial drug sensitivity testing method. The kit comprises a drug-sensitive plate, liquid culture media and solid culture medium panels. Conventional and latest veterinary drugs are selected for making the drug-sensitive plate, and the different culture medium panels are prepared according to different infection bacteria. The prepared drug-sensitive kit has advantages of accurate testing results, low time consumption, simplicity and convenience in operation and low cost and is suitable for drug sensitivity testing for bacterial diseases in large-scale farms and basic veterinary institutions, and accordingly accuracy in animal medication can be realized.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
Method for testing antimicrobial susceptibility
PendingUS20210292807A1Rapid determinationCompound screeningApoptosis detectionBiotechnologyMicrobial agent
The present invention relates to methods for the qualitative and quantitative determination of the susceptibility of microbial organisms such as bacteria to antimicrobial agents such as antibiotics. For example, the present invention provides a method of determining the susceptibility of a unicellular or multicellular microorganism to an antimicrobial agent by acoustic flow cytometry. The method comprising exposing cells of the microorganism to at least one antimicrobial agent, wherein said cells of the microorganism are in and / or derived from a sample obtained from a subject having or suspected of having an infection with said microorganism; measuring effect of said at least one antimicrobial agent on cellular morphology of said cells of the microorganism by acoustic flow cytometry; and determining susceptibility of the microorganism to the at least one antimicrobial agent from the acoustic flow cytometry data output.
Owner:UNIV OF WESTERN AUSTRALIA
Mycobacterium tuberculosis drug sensitivity test method as well as application and solid culture medium of indicator
ActiveCN102010886AShort initial bacterial countTake advantage ofBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBiotechnologyTuberculosis mycobacterium
The invention discloses a mycobacterium tuberculosis drug sensitivity test method, application and a solid culture medium of an indicator for the mycobacterium tuberculosis drug sensitivity test method as well as a heating thermostat unit and a culture box used for the mycobacterium tuberculosis drug sensitivity test method. The drug sensitivity test method thereof comprises the following steps of adding a liquid enriched medium to carry out enriched culture after subjected to pre-treatment on a supplied sample, warming and melting the solid culture medium to prepare a liquid solid culture medium, mixing the sample subjected to enriched culture and the liquid solid culture medium, then cooling and solidifying to prepare a solid drug sensitivity test sample with a drug sensitivity paper scraps, culturing the solid drug sensitivity test sample for 5-15 days, observing a drug inhibition zone through indication of the indicator, and determining the drug sensitivity. The invention has the advantages of short testing process time, little investment, low use cost and safe and convenient use with an average testing time of about 10 days.
Owner:HUNAN TECH NEW MEDICAL SYST
Compound bactericide with broad-spectrum bactericidal effect
PendingCN110946848AGood antibacterial and bactericidal effectAntibacterial agentsAntimycoticsBiotechnologyEscherichia coli
The invention provides a compound bactericide with bacteriostatic or bactericidal activity. The composition comprises, by weight, 40% to 50% of linalool, 18% to 25% of terpilenol, 8% to 15% of geraniol, 2% to 4% of beta-cyclocitral, 2.5% to 5% of nerol, 1% to 3% of myrcene, 1% to 3% of ocimene, 3% to 6% of ionone and 5% to 8% of 2H-beta-ionone. Antibacterial and bacteriostatic drug sensitivity tests show that the bactericide artificially prepared on the basis of natural essential oil components has a broad-spectrum inhibition effect on bacteria and fungi. The bactericide has bacteriostatic andbactericidal effects on bacteria (escherichia coli, bacillus subtilis, staphylococcus aureus, staphylococcus epidermidis and the like) and fungi (candida albicans, Schlechospora crassa, trichophytonrubrum, saccharomyces cerevisiae and the like), and particularly has an obvious effect on zoonosis. The bactericide can be applied to development of zoonosis infection and other sterilization products.
Owner:NORTHEAST NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com