Method for producing ethylene glycol and 1,2-propylene glycol by continuously hydrocracking cellulose
A hydrocracking and cellulose technology, applied in 1, can solve the problems of time-consuming, waste of energy and materials, inconvenient operation, etc., and achieve the effect of reducing production cost, saving use cost and reducing consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
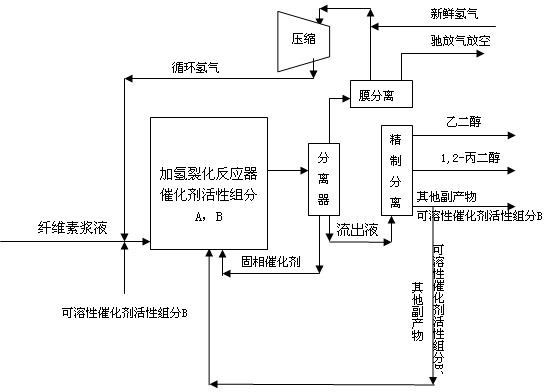
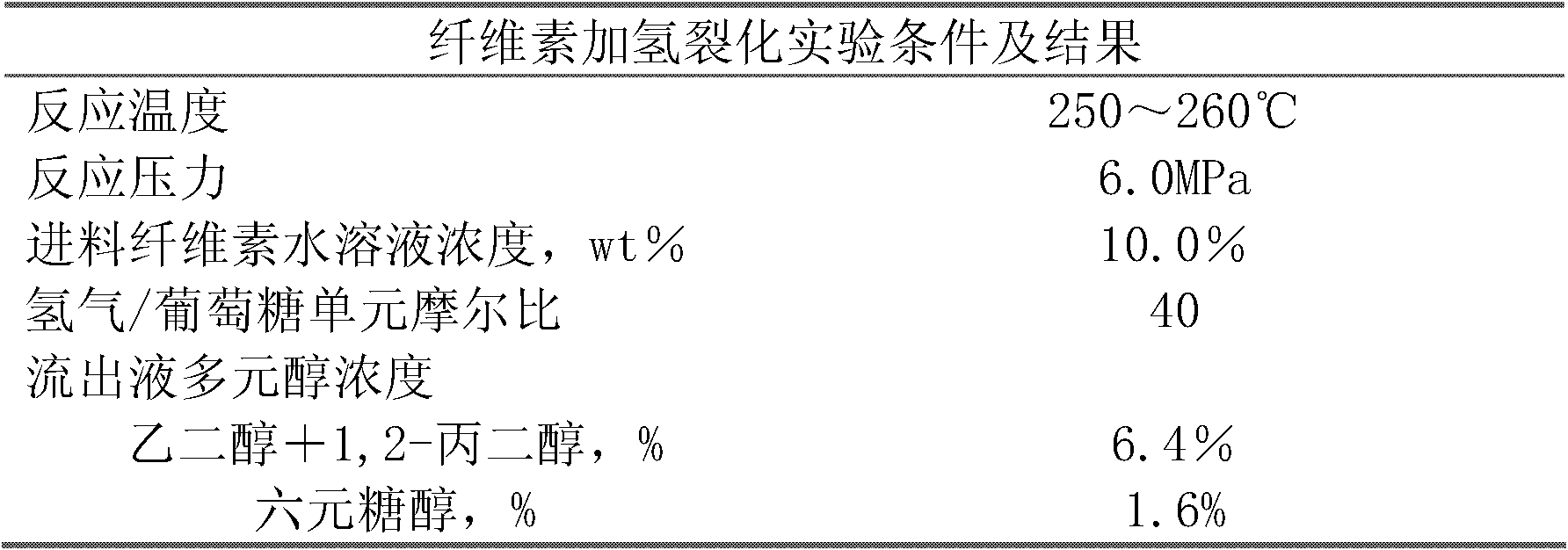
[0035] The 20wt% cellulose water mixture and the dissolved ammonium metatungstate 0.1wt% (by weight of metal tungsten) aqueous solution enter the hydrogenation reactor through the high-pressure pump, and the reactor is filled with slurry Raney nickel and tungstic acid Catalyst (the weight ratio of nickel to tungsten is 10:1, and the catalyst is submerged in water as a solvent at the beginning of the reaction), and the weight ratio of cellulose raw material to catalyst (the sum of the weight of nickel and tungsten elements) is between 20:1 and 18:1 , with a volumetric space velocity of 0.1 to 0.2. The temperature of the reactor is 240-250° C., and the hydrogen pressure is 8 MPa. Hydrogen enters from the bottom of the reactor and stirs the catalyst slurry. The reactant enters the reactor and after reaction, the liquid product is discharged from the upper outlet of the reactor, accompanied by 1-2% solid catalyst hydrogen and gas product. The reactor effluent then enters a separ...
Embodiment 2
[0043] The cellulose aqueous solution slurry of 10wt% is entered hydrogenation reactor by high-pressure pump, is filled with the Ru / AC of slurry state and tungstic acid catalyst (the weight ratio of ruthenium and tungsten is 5: 1 in the reactor, reacts initial stage with water as solvent immersion catalyst), the weight ratio of the cellulose raw material to the catalyst (the sum of the weights of ruthenium and tungsten elements) is between 50:1 and 45:1, and the volume space velocity is 0.5 to 1. The temperature of the reactor is 250-260° C., and the hydrogen pressure is 6 MPa. Hydrogen enters from the bottom of the reactor and stirs the catalyst slurry. The liquid product is discharged from the upper outlet of the reactor, accompanied by part of the hydrogen and the gas product. Then the reactor effluent enters the separator to separate the gas and liquid parts.
[0044] The gas part separated by the separator is further separated into pure hydrogen by the membrane separati...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com