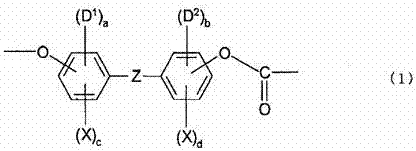
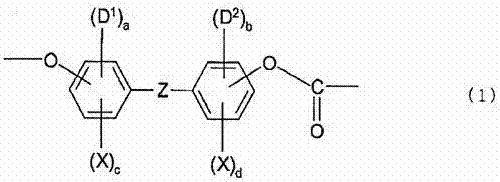
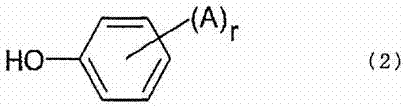Optical films made of halogenated polycarbonate
A polycarbonate and optical film technology, applied in the field of optical films, can solve the problems of large coloring and neglect, and achieve the effects of less coloring, fire suppression, and high flame retardancy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0057]
[0058] In the reaction by the interfacial polymerization method, halogenated dihydric phenols are generally reacted with phosgene, and the reaction is carried out in the presence of an acid binder and an organic solvent.
[0059] As the acid binder, alkali metal hydroxides such as sodium hydroxide and potassium hydroxide, or amine compounds such as pyridine are used. As the organic solvent, halogenated hydrocarbons such as dichloromethane and chlorobenzene are used.
[0060] In addition, in the reaction by the interfacial polymerization method, for example, an amine-based catalyst or a phosphonium-based catalyst may be used in order to promote the reaction. Examples of amine catalysts include trimethylamine, triethylamine, tripropylamine, tributylamine, trihexylamine, trioctylamine, tridecylamine, dimethyl-n-propylamine , Diethyl-n-propylamine, N,N-dimethylcyclohexylamine, pyridine, N,N-dimethylaniline, N,N-dimethyl-4-aminopyridine, N,N-di Tertiary amines such as ...
preparation example
[0062] As halogen-substituted dihydric phenols, halogen-substituted dihydric phenols with a structure in which a large halogen element is bonded to the 1 and 5 positions of the hydroxyl group such as tetrabromobisphenol A, due to the steric hindrance of the halogen element, the Since the reactivity of the bulk substance tends to decrease, in order to obtain a carbonate having a high molecular weight and very few oligomers, the production method by the following interfacial polymerization method is preferable.
[0063] That is, when producing a halogenated carbonate by reacting an aqueous alkali solution of a halogen-substituted dihydric phenol with phosgene in the presence of an organic solvent, the following conditions (a) to (c) are preferably satisfied.
[0064] (a) Until the end of the phosgenation reaction, the total amount of base used is suppressed to 2.0 times moles or less relative to the halogenated dihydric phenols, and transferred to the subsequent polymerization re...
Embodiment 1
[0197]
[0198] Add tetrabromobisphenol A 130g (0.239 mol), 7.0% sodium hydroxide aqueous solution 161ml (sodium hydroxide 0.299 mol), dichloromethane 393ml, and triethylamine 0.2 ml (0.002 mol) and dissolved, kept at 20-25°C under stirring, and 28.5 g (0.289 mol) of phosgene was blown in for 60 minutes. In the final stage of blowing in phosgene, 5 ml of 25% aqueous sodium hydroxide solution (0.041 mol of sodium hydroxide) was added, while maintaining the pH of the reaction mixture at 10.5 to 11.0 to carry out the phosgenation reaction.
[0199] After the phosgenation reaction finishes, add p-tert-butylphenol 0.20g (0.0013 mole), then use about 60 minutes to mix triethylamine 0.8ml (0.008 mole) and 25% sodium hydroxide aqueous solution 44ml (sodium hydroxide 0.363 mole) Add it into the reaction mixture, and react at a temperature of 35-40° C. for 90 minutes.
[0200] The separated dichloromethane phase was washed with acid and water until the inorganic salts and amines disa...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| glass transition temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| glass transition temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com