High-activity chitosanase and preparation method thereof
A chitosanase, high-activity technology, applied in the field of bioengineering, can solve the problems of difficult commercialization, long enzyme production cycle, large enzyme production and other problems, achieve a wide range of temperature and pH, reduce processing costs, The effect of high biological activity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
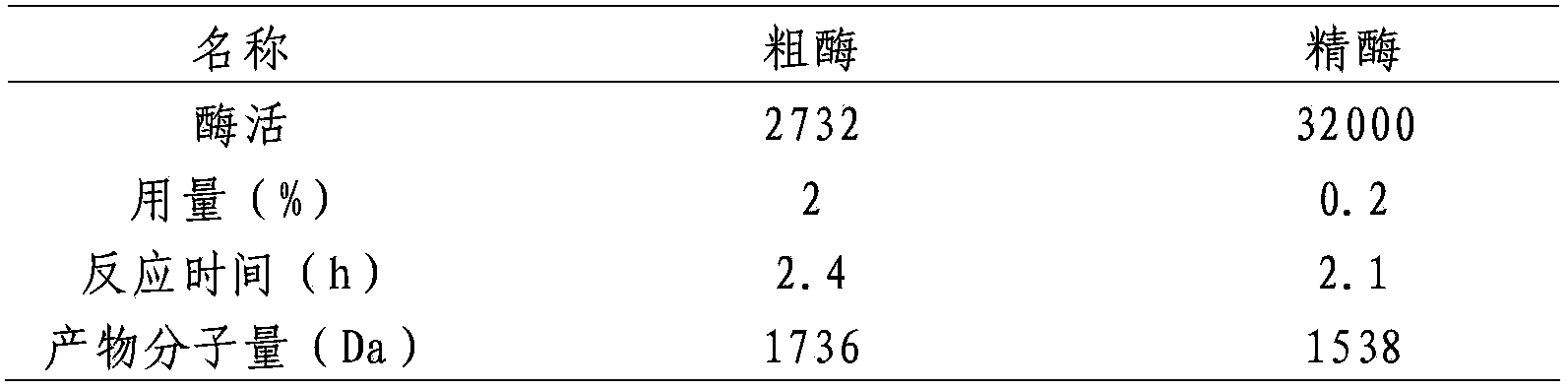
[0039] Enzyme activity detection: DNS method.
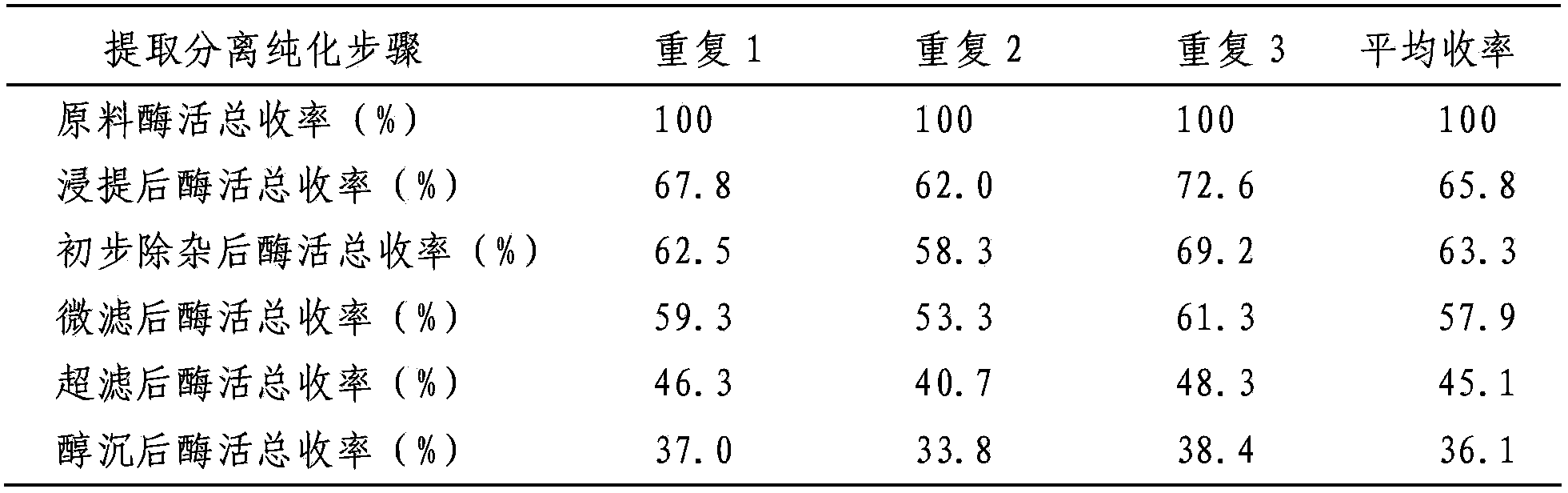
[0040] Chitosanase preparation: take 1g of the prepared chitosanase, dissolve it in 80ml of distilled water, and set the volume to 100ml to obtain the chitosanase solution.
[0041] Accurately weigh 0.1g of chitosan powder into a test tube, add 10mL of 0.2M acetic acid solution to make a 1% chitosan solution, shake for 10min, and keep warm in a water bath at 50°C for 10min. Accurately measure 1mL of the above-prepared chitosan enzyme solution, add it to the test tube of chitosan solution, keep it warm at 50°C for 30min, adjust the pH value to 8 with NaOH solution, and centrifuge to remove the precipitate. Aspirate 1mL of the supernatant, add 9mL of 2M / mL hydrochloric acid, hydrolyze at 100°C for 2h, measure the reducing sugar content by DNS method, and calculate the enzyme activity. The enzyme activity unit U is the amount of enzyme required to produce 1 μmol of reducing sugar per minute.
Embodiment 2
[0042] Embodiment 2 solid fermentation
[0043] Determination of the Composition and Culture Conditions of Medium for Enzyme Production in Solid Fermentation
[0044] Using single factor test and orthogonal test, by changing the temperature, initial pH value, inoculum size, loading amount and culture time, the optimal culture conditions of liquid seeds and the best enzyme production conditions of solid fermentation were determined; Cross experiment, by changing the carbon and nitrogen source and inorganic salt composition of the culture to determine the optimal composition of the medium for liquid seeds and the composition of the optimal enzyme-producing medium for solid fermentation of the strain.
[0045] Solid fermentation medium composition and enzyme production conditions determined by the above-mentioned test method:
[0046] The composition of the solid medium, in parts by weight, is: 65-80 parts of bran, 10-20 parts of soybean meal, 8-15 parts of corn flour, 1-3 parts...
Embodiment 3
[0053] Embodiment 3 liquid fermentation
[0054] Determination of the Composition and Culture Conditions of Medium for Enzyme Production in Liquid Fermentation
[0055] Using single factor test and orthogonal test, by changing the temperature, initial pH value, inoculum size, loading amount and culture time, the optimal culture conditions of liquid seeds and the best enzyme production conditions of solid fermentation were determined; Cross experiment, by changing the carbon and nitrogen source and inorganic salt composition of the culture to determine the optimal composition of the medium for liquid seeds and the composition of the optimal enzyme-producing medium for solid fermentation of the strain.
[0056] The composition of the seed liquid culture medium determined by the above-mentioned test method and the fermentation conditions are as follows:
[0057] Activation of strains: move the slant strains of CGMCC No.6129 test tubes stored on nutrient agar medium at 4°C to roo...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| recovery rate | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com