Method for producing monoammonium phosphate and coproducing N-P binary compound fertilizer by using wet-process phosphoric acid
A technology of monoammonium phosphate and wet-process phosphoric acid, which is applied in the application, fertilization device, fertilizer mixture and other directions, can solve the problems of limited slurry source, long process flow and low level, and achieve reliable control of process indicators, improve economic benefits, The effect of simple process flow
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
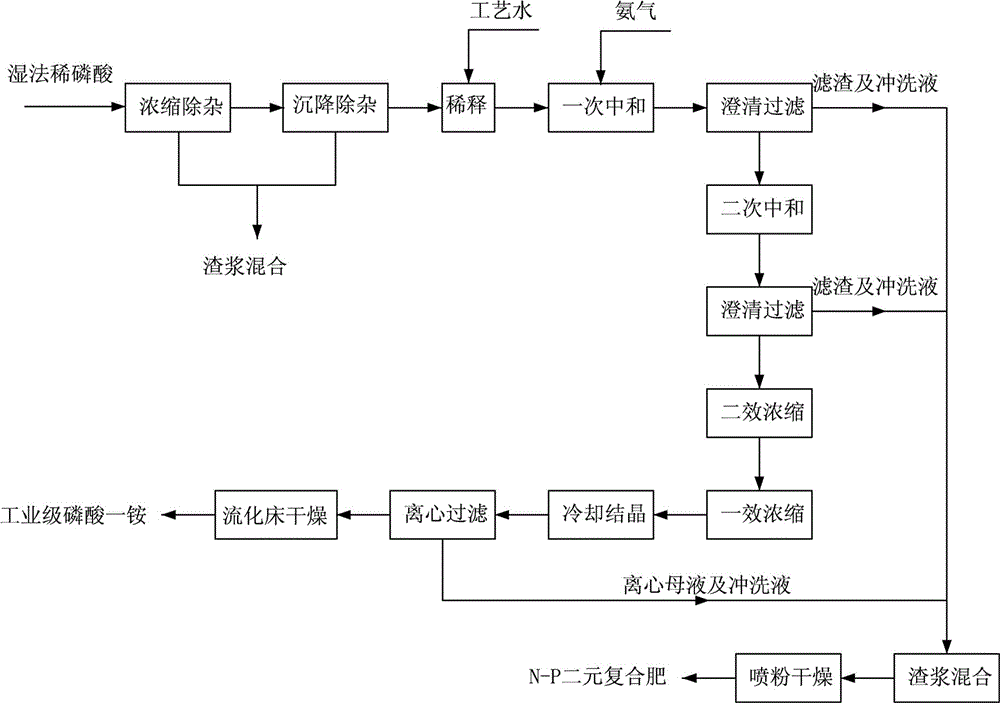
[0025] A method for producing monoammonium phosphate and co-producing N-P binary compound fertilizer with wet-process phosphoric acid,
[0026] (1) Set the weight concentration to 20-25%P 2 o 5 Concentrate the dilute phosphoric acid to remove impurities, concentrate to 46-48%, then add a sedimentation agent to settle and remove impurities, and then dilute the phosphoric acid after removal to 20-25% with process water; or directly use phosphoric acid above 46-48% After adding a settling agent to settle and remove impurities, dilute the process water to 20-25%, and send the slag acid to the slag-slurry mixing tank;
[0027] (2) Pump the diluted phosphoric acid obtained in step (1) to the ammoniation reactor, control the degree of neutralization to 1.01-1.04, and conduct a neutralization reaction with ammonia gas at a temperature of 105-115°C, and the slurry after neutralization Naturally clarified in the slurry clarification tank, the supernatant overflows to the secondary neu...
Embodiment 2
[0037] Concentrate 20-25% of dilute phosphoric acid by using waste heat steam produced by the sulfonic acid plant and self-generated electricity through the concentration device, remove part of the fluorine-containing compounds and most impurities during concentration, and pump it in after the acid concentration reaches 46-48% by weight In the clarification tank, after adding a settling agent to settle and remove impurities, the settling agent is polyacrylamide or similar additives with the same function, and the amount added is 1 / 1000 to 5 / 1000 in terms of volume ratio; after the settlement is completed, use The process water is diluted to 20-25%. The process water refers to the secondary steam condensed water of the concentration system. The slag acid is sent to the slurry mixing tank, and the adjusted dilute acid is pumped into the ammoniation reactor to complete the primary neutralization with ammonia gas. Control the degree of neutralization of the slurry to be 1.01 to 1.0...
Embodiment 3
[0039]Use more than 48% phosphoric acid to settle and remove impurities with a sedimentation agent, then dilute to 20-25% with process water, send the slag acid to the slurry mixing tank, and pump the adjusted dilute acid into the ammoniation reactor to complete one-time neutralization with ammonia gas And, the degree of neutralization of the slurry is controlled to be 1.01-1.04, and the temperature is 105-115°C. After the primary neutralization slurry is filtered by the plate and frame filter, the filtrate enters the secondary neutralization tank, and dilute acid is added to the tank to control its pH value from 4.4 to 4.6, and the secondary neutralization slurry is clarified and filtered, and the filtrate is concentrated After the system is concentrated, it is cooled and crystallized, and the crystallization slurry is centrifuged, and the crystals obtained by the centrifugation are dried in a vibrating fluidized bed, which is the finished product of industrial grade monoammon...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com