Tri-strain tri-polycrystal-plane BiCMOS (Bipolar complementary metal oxide semiconductor) integrated device and preparation method thereof
An integrated device, three-strain technology, applied in semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturing, electric solid-state devices, semiconductor devices, etc., can solve problems such as incompatibility, low mobility of Si material carrier materials, and limitations
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
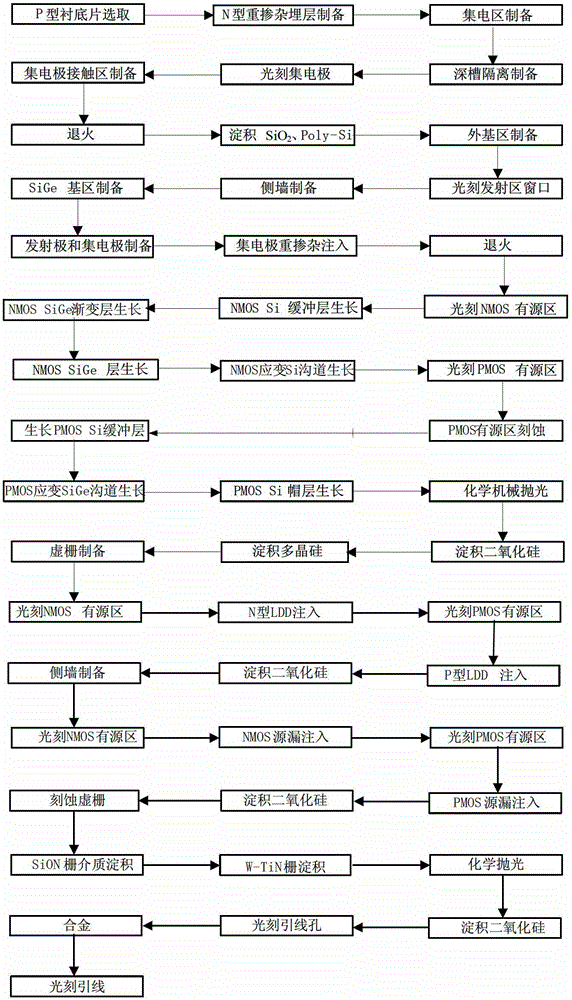
[0124] Embodiment 1: The preparation of a three-strain, three-polycrystalline planar BiCMOS integrated device and circuit with a conductive channel of 45nm, the specific steps are as follows:
[0125] Step 1, epitaxial growth.
[0126] (1a) Select the doping concentration to be 5×10 14 cm -3 A P-type Si sheet as a substrate;
[0127] (1b) Thermally oxidize a layer of SiO with a thickness of 300nm on the substrate surface 2 layer;
[0128] (1c) Photoetching the buried layer region, implanting N-type impurities into the buried layer region, and annealing at 800° C. for 90 minutes to activate the impurities to form an N-type heavily doped buried layer region.
[0129] Step 2, isolation area preparation.
[0130] (2a) Remove the excess oxide layer on the surface, and epitaxially grow a layer with a doping concentration of 1×10 16 cm -3 The Si layer, with a thickness of 2 μm, serves as the collector area;
[0131] (2b) Thermally oxidize a layer of SiO with a thickness of 30...
Embodiment 2
[0193] Embodiment 2: The preparation of a three-strain, three-polycrystalline planar BiCMOS integrated device and circuit with a conductive channel of 30 nm, the specific steps are as follows:
[0194] Step 1, epitaxial growth.
[0195] (1a) Select the doping concentration as 1×10 15 cm -3 A P-type Si sheet as a substrate;
[0196] (1b) Thermally oxidize a layer of SiO with a thickness of 400nm on the substrate surface 2 layer;
[0197] (1c) Photoetching the buried layer region, implanting N-type impurities into the buried layer region, and annealing at 900° C. for 60 minutes to activate the impurities to form an N-type heavily doped buried layer region.
[0198] Step 2, isolation area preparation.
[0199] (2a) Remove the excess oxide layer on the surface, and epitaxially grow a layer with a doping concentration of 5×10 16 cm -3 A Si layer with a thickness of 2.5 μm acts as a collector area;
[0200] (2b) Thermally oxidize a layer of SiO with a thickness of 400nm on t...
Embodiment 3
[0262] Embodiment 3: The preparation of a three-strain, three-polycrystalline planar BiCMOS integrated device and circuit with a conductive channel of 22nm, the specific steps are as follows:
[0263] Step 1, epitaxial growth.
[0264] (1a) Select the doping concentration to be 5×10 15 cm -3 A P-type Si sheet as a substrate;
[0265] (1b) Thermally oxidize a layer of SiO with a thickness of 500nm on the surface of the substrate 2 layer;
[0266] (1c) Photoetching the buried layer region, implanting N-type impurities into the buried layer region, and annealing at 950° C. for 30 minutes to activate the impurities to form an N-type heavily doped buried layer region.
[0267] Step 2, isolation area preparation.
[0268] (2a) Remove the excess oxide layer on the surface, and epitaxially grow a layer with a doping concentration of 1×10 17 cm -3 The Si layer, with a thickness of 3 μm, serves as the collector area;
[0269] (2b) Thermally oxidize a layer of SiO with a thicknes...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com