Method for recovering sludge from smelting ironmaking
A technology of ironmaking sludge and recycling method, which is applied in the direction of improving process efficiency, etc., can solve the problems of not too high usage ratio, high cost, complicated process, etc., and achieve the goals of reducing fuel consumption, reducing recycling, and avoiding a large amount of accumulation Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
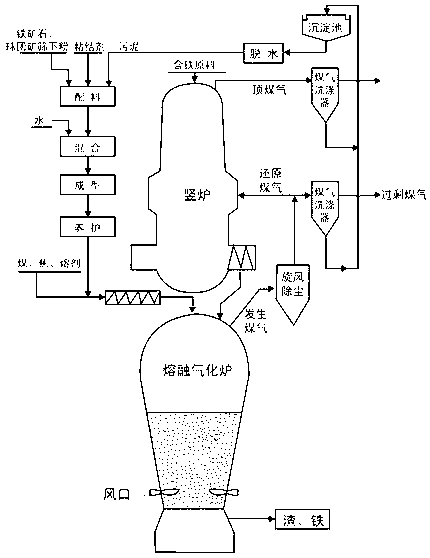
[0038] Recycling and utilization of sludge with a moisture content of 10% after dehydration, the ratio of sludge, binder, iron ore or pellet under-screen powder or the mixture of the two is: sludge 55%, binder 15% , 30% of iron ore or pellet under sieve powder or a mixture of the two. The binder is 50% Portland cement + 50% diatomaceous earth, the particle size of iron ore or pellet under-sieve powder is less than 3.15mm, the amount is more than 90%, the moisture content of the mixture is 10%, and the molding pressure is 10MPa , and cured for 2 hours in a steam atmosphere. After the curing is completed, it will be fed into the melting gasifier through the screw feeder together with coal, coke and flux.
[0039] This embodiment can make the briquette strength reach 1716N, fully meeting the strength requirements for directly feeding into the gasifier. If calculated by recycling 400 tons of briquettes per day, 55-110 tons of iron and 44-88 tons of carbon powder can be recovered...
Embodiment 2
[0041]Recycling sludge with moisture content of 15% after dehydration, the proportion of sludge and binder, iron ore or pellet under-screen powder or the mixture of the two is: sludge 45%, binder 13% , iron ore or pellets under sieve powder or a mixture of the two 42%. The binder is 40% Portland cement + 30% slag cement + 30% diatomaceous earth, the iron ore or pellet under-sieve powder with a particle size less than 3.15mm is more than 95%, and the moisture content of the mixture is 15% , The molding pressure is 15MPa, and it is cured in a steam atmosphere for 4 hours. After the curing is completed, it will be fed into the melting gasifier through the screw feeder together with coal, coke and flux.
[0042] This embodiment can make the strength of the briquette reach 2574N, fully meeting the strength requirement for directly feeding into the gasifier. If calculated by recycling 400 tons of briquettes per day, 45-90 tons of iron and 36-72 tons of carbon powder can be recover...
Embodiment 3
[0044] Recycling sludge with moisture content of 20% after dehydration, the proportion of sludge and binder, iron ore or pellet under-screen powder or the mixture of the two is: sludge 30%, binder 10% , 60% of iron ore or pellet sieve powder or a mixture of the two. The binder is 30% Portland cement + 40% slag cement + 30% diatomaceous earth, iron ore or pellets with a particle size less than 3.15mm is 100%, and the moisture content of the mixture is 18% , The molding pressure is 20MPa, and it is cured in a steam atmosphere for 12 hours. After the curing is completed, it will be fed into the melting gasifier through the screw feeder together with coal, coke and flux.
[0045] This embodiment can make the strength of the briquette reach 3361N, fully meeting the strength requirements for directly feeding into the gasifier. If calculated by recycling 400 tons of briquettes per day, 30-60 tons of iron and 24-48 tons of carbon powder can be recovered from sludge a day, which can ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com