Method and device for removing heavy metals in industrial wastewater by nanoscale zero-valent iron-multilevel reversed filter type system
A nano-zero-valent iron, industrial wastewater technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, water/sewage multi-stage treatment, water pollutants, etc., can solve the problems of high cost and energy consumption, long operation time, complex equipment, etc. Simple structure, low cost and low energy consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
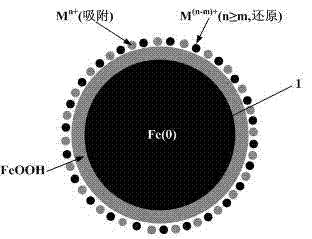
[0037] The nanometer zero valent iron that the present invention adopts is FeCl 3 solution and NaBH 4 The solution is mixed and produced by oxidation-reduction reaction, the particle size range is 1-100 nm, the average particle size is 30-70 nm, and the specific surface area is 20-40 m 2 / g, such as figure 1 Structural model diagram of nano zero-valent iron, a typical core-shell double structure, with dense zero-valent iron inside for reduction; the outer ring is covered with a thin layer of iron oxide (or FeOOH) for adsorption. Synthesize ready-to-use nano-zero-valent iron by adding ethanol, isopropanol and other organic reagents to make it fluid and enter the dense reaction zone of the closed reactor. The wet nano-zero-valent iron has a solid content between 20 and 80 g / L, and the nano-zero Valence iron must be stored in an oxygen-free environment.
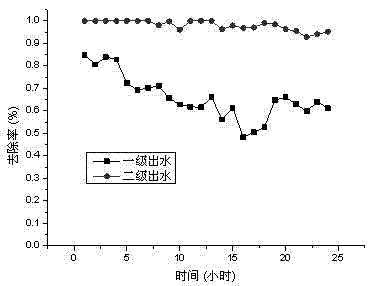
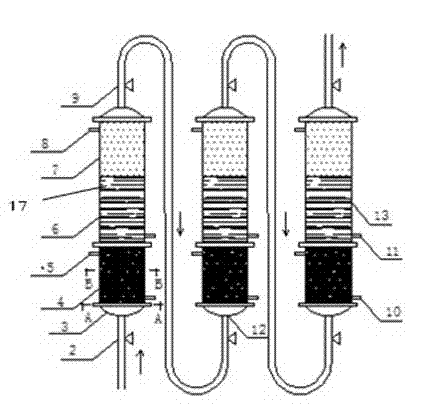
[0038] A nano-zero-valent iron-multi-stage reverse filter system for removing medium and low-concentration heavy metal-con...
Embodiment 2
[0044] Take the stock solution of wastewater effluent from a copper mine factory, firstly pretreat the stock solution of copper mine wastewater: add a certain amount of PAM flocculant, first stir rapidly for 1-2 minutes to mix the added flocculant evenly in the solution, then reduce the stirring speed, slowly Slowly stir the mining wastewater for 30-60 minutes to coagulate the suspended impurities in the copper ore wastewater stock solution into flocculation. After the flocculation is completed, stop stirring and let the electroplating wastewater stand for 1-3 hours to settle. After the precipitation is completed, filter it with filter paper to obtain Clarified electroplating wastewater. Pretreated mining wastewater containing Cu 2+ 200~800 mg / L, Ni 2+ 50~100 mg / L, Zn 2+ 10~30mg / L, pH between 7~8.5. The nanometer zero valent iron used in this embodiment consists of 0.050 mol / LFeCl 3 solution and 0.25 mol / L NaBH 4 Prepared by equal-volume mixed reaction, the solid content...
Embodiment 3
[0048] Take the stock solution of electroplating wastewater at the exit of the electroplating workshop of an electroplating factory, firstly pretreat the stock solution of electroplating wastewater: add a certain amount of PAM flocculant, first stir rapidly for 1-2 minutes to mix the added flocculant in the solution evenly, then reduce the stirring speed, Slowly stir the electroplating wastewater for 30-60 minutes to coagulate the suspended impurities in the raw solution of the electroplating wastewater into flocculation. After the flocculation is completed, stop stirring and let the electroplating wastewater stand for 1-3 hours to settle. After the precipitation is completed, filter it with filter paper to obtain clarified Electroplating wastewater. The pretreated electroplating wastewater contains 300-800 mg / L of Pb and Ni, and the pH is between 6 and 8. Nano zero valent iron used in this embodiment is made of 0.050mol / L FeCl 3 solution and 0.25 mol / L NaBH 4 Prepared by eq...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| The average particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com