Method for preparing poly (1-amino-5-chloro anthraquinone) nanofiber through interface chemical oxidative polymerization
A technology of interfacial chemistry and oxidative polymerization, applied in the field of material chemistry, can solve the problems of low stability of nano-dispersion, reduced solubility, low molecular weight, etc., and achieve the effects of low synthesis cost, pure product, and high molecular weight of the product
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0026] Embodiment 1: The method for preparing poly(1-amino-5-chloroanthraquinone) nanofibers by interfacial chemical oxidative polymerization, the specific operation is as follows:
[0027] (1) Weigh 0.9 mmol (0.2319 g) of 1-amino-5-chloroanthraquinone monomer into a 100 mL Erlenmeyer flask, add 30 mL of nitrobenzene, and pipette 150 μL (1.75 mmol) perchloric acid was dropped into the Erlenmeyer flask, the concentration of perchloric acid in the whole reaction system was 50 mmol / L, another 1.8 mmol (0.1865 g) chromium trioxide was taken as an oxidant and dissolved in 5.0 mL of distilled water ;
[0028] (2) Put the chromium trioxide aqueous solution and the 1-amino-5-chloroanthraquinone acidic nitrobenzene solution in a constant temperature water bath at 30°C for about 30 minutes, and then add the oxidant solution to the 1-amino-5 -In acidic nitrobenzene solution of chloranthraquinone, magnetic stirring was carried out at the same time, constant temperature reaction was carri...
Embodiment 2
[0030] Embodiment 2: The method for preparing poly(1-amino-5-chloroanthraquinone) nanofibers by interfacial chemical oxidative polymerization, the specific operation is as follows:
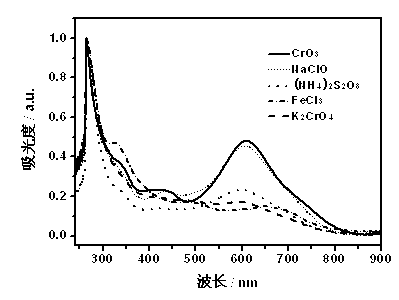
[0031] The method is the same as in Example 1, except that the organic solvent for dissolving the 1-amino-5-chloroanthraquinone monomer is changed to o-dichlorobenzene, nitromethane or chloroform respectively, and the resulting poly(1-amino-5-chloroanthraquinone ) nanofiber yields were 12.8%, 34.7% and 10.3%, respectively. The electrical conductivity of poly(1-amino-5-chloroanthraquinone) nanofiber pellets measured by two-electrode method was 6.9×10 -6 S / cm, 4.3×10 -6 S / cm and 5.5×10 -7 S / cm.
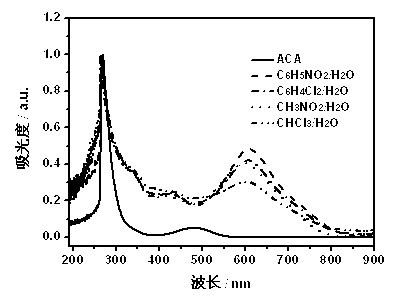
[0032] The UV-Vis spectra of PACA and ACA monomers synthesized in different media are shown in figure 1 , the figure shows: the monomer has a strong absorption at 267 nm and a weak absorption at 481 nm, while the polymer produces a new strong and broad absorption peak at around 612 nm, and the absorp...
Embodiment 3
[0034] Embodiment 3: The method for preparing poly(1-amino-5-chloroanthraquinone) nanofibers by interfacial chemical oxidative polymerization, the specific operation is as follows:
[0035] (1) Weigh 0.9 mmol (0.2328 g) of 1-amino-5-chloroanthraquinone monomer into a 100 mL Erlenmeyer flask, add 30 mL of nitrobenzene, and pipette 150 μL (1.75 mmol) perchloric acid was dropped into the Erlenmeyer flask, the concentration of perchloric acid in the whole reaction system was 50 mmol / L, another 1.8 mmol NaClO (1.04 mL NaClO solution, the NaClO solution contained no less than 5.2 %, OH – content of 7.0–8.0%) as an oxidizing agent, with HClO 4 Adjust the pH value to close to 7.0, then dilute to 5.0 mL with distilled water;
[0036] (2) Put NaClO aqueous solution and 1-amino-5-chloroanthraquinone acidic nitrobenzene solution in a constant temperature water bath at 30°C for about 30 minutes, then add the oxidant solution to the monomer solution at one time, and perform magnetic Stir...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thermal decomposition temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com