Beneficial microorganism antibiont-free feed and preparation method thereof
An anti-biological and microbial technology, applied in animal feed, animal feed, application, etc., can solve problems such as scientific selection and compounding of strains, and achieve the effect of promoting healthy development, easy assembly line operation, and improving animal health.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
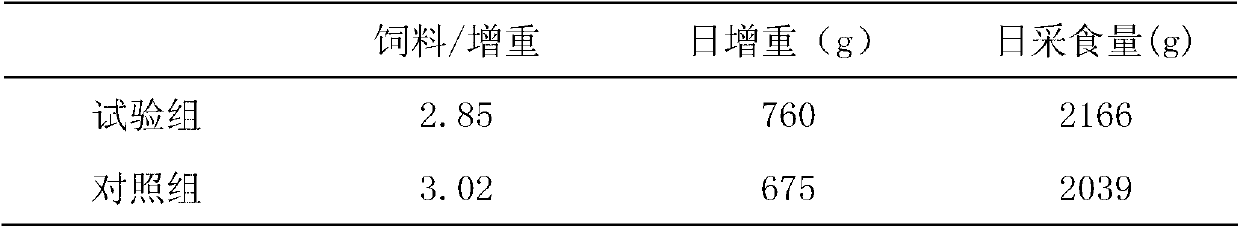
[0026] Secondary fermentation preparation of beneficial microorganism liquid
[0027] Preparation of Lactobacillus acidophilus bacterial liquid: primary bacterial liquid - inoculate the activated strains in 500ml sterile MRS medium, the inoculum amount is 2% by volume, and culture in an anaerobic incubator at 37°C for 24 hours , the number of viable bacteria ≥ 1 × 10 9 CFU / ml; secondary bacterial liquid——put the primary bacterial liquid into 100L sterile MRS medium (in a fermentation tank) according to aseptic procedures, with an inoculation amount of 2%, anaerobic culture at a constant temperature of 37°C for 24 hours, every Stir the medium for 2 hours for 1 minute, the number of viable bacteria ≥ 1×10 9 CFU / ml;
[0028] Preparation of Lactobacillus plantarum liquid: primary bacterial liquid—inoculate the activated strain into 500ml of sterile MRS medium, the inoculum amount is 3% by volume, and culture it in an anaerobic incubator at 37°C for 36 hours. The number of viabl...
Embodiment 2
[0043] In step , 2 kg of Bacillus licheniformis bacterial liquid, fermented cottonseed meal small peptide content is 8%; According to the weight ratio of 3:3:1) 7kg, no antibiotic feed, small peptide content of 2.1% (calculated on a dry basis), pH value of 4.7. In addition, others are basically the same as in Embodiment 1.
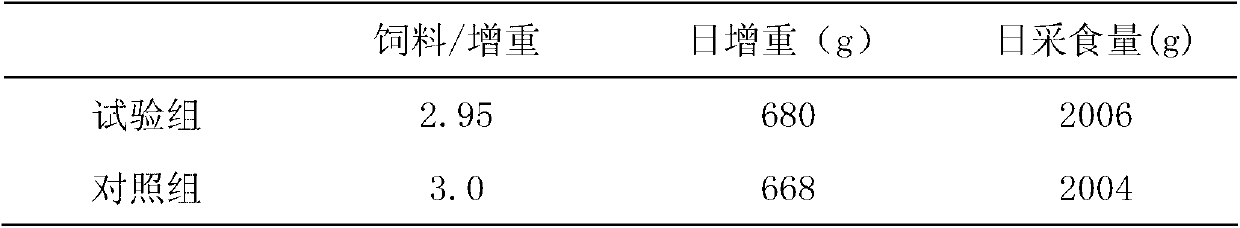
[0044] Feeding test: select 80 lean-meat pigs with an initial body weight of 45 ± 0.68kg, divide them into test groups and control groups, and the test groups are fed with the antibiotic-free feed made in Example 2 (the amount of feed is converted to 88% by dry matter content) ), the control group was fed conventional diets containing antibiotics (without fermentation treatment), the pre-feeding period was 5 days, and the formal test period was 25 days. The results are shown in Table 2.
[0045] Table 2 embodiment 2 no antibiotic feed feeding test result
[0046]
Embodiment 3
[0048] In step , 3.5kg of Bacillus licheniformis bacterial liquid, the small peptide content of fermented cottonseed meal is 9.5%; Liquid (2:1:3 by weight ratio) 6kg, no antibiotic feed, small peptide content of 2.8% (calculated on a dry basis), pH value of 5.2. In addition, others are basically the same as in Embodiment 1.
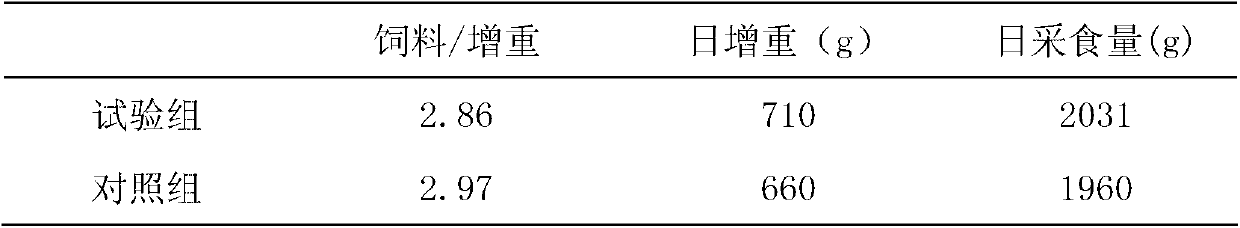
[0049] Feeding test: select 100 lean-meat pigs with an initial body weight of 46 ± 0.95kg, divide them into test groups and control groups, and the test groups are fed with the antibiotic-free feed made in Example 3 (the amount of feed is converted to 88% by dry matter content) ), the control group was fed conventional diets containing antibiotics (without fermentation treatment), the pre-feeding period was 5 days, and the formal test period was 25 days. The results are shown in Table 3.
[0050] Table 3 embodiment 3 no antibiotic feed feeding test result
[0051]
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com