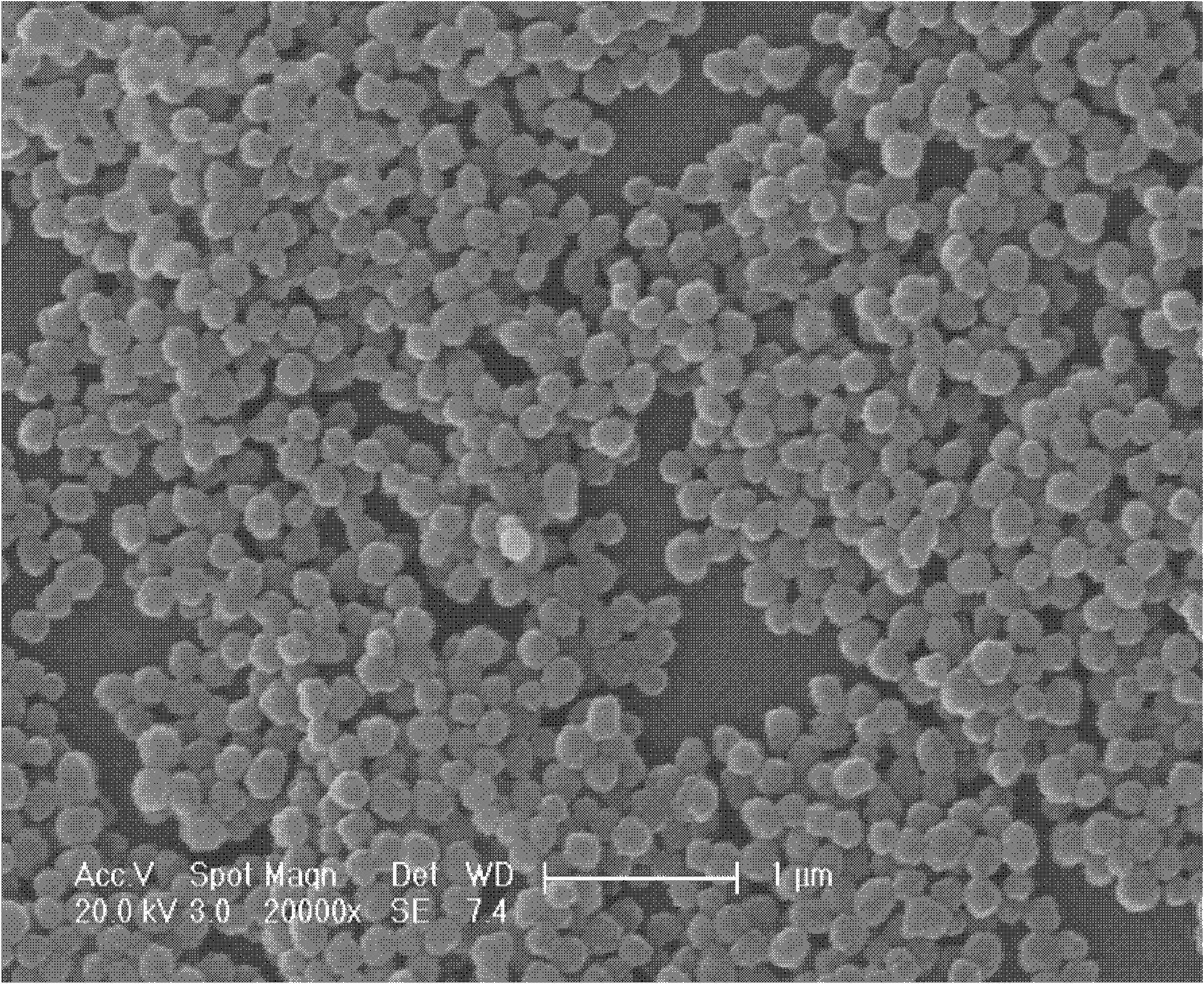Affinity adsorption biodegradation membrane and preparation method thereof
A biodegradable membrane and affinity technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, biological water/sewage treatment, and other chemical processes, can solve problems such as high treatment costs, residual nano-microspheres, and highly toxic secondary pollutants. Achieve the effects of high adsorption and degradation efficiency, high adsorption specificity, and resistance to interference from impurities
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
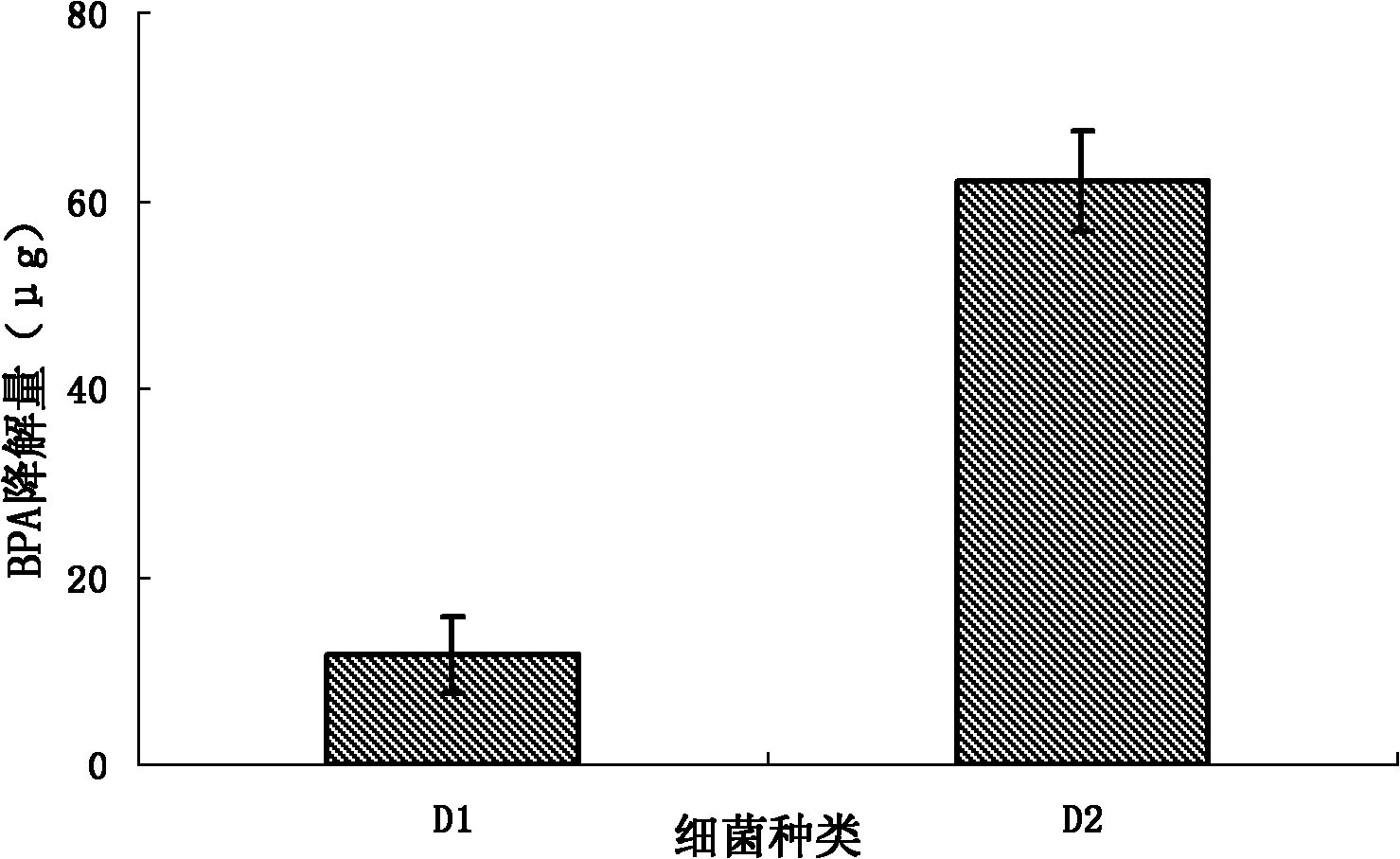
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0043] Example 1: Degradation of BPA in pure water by affinity adsorption biodegradable membrane
[0044] Accurately weigh several 10mg membranes (group A: bacteria+MIM; group B: bacteria+nMIM; group C: dominant bacteria) and add them into 20mL spiked pure water (BPA=500μg / L) to start the degradation reaction. At each reaction termination time point (0, 3, 6, 12, 24h), take parallel samples, centrifuge the reactant at a speed of 6000rpm / min for 3min, and detect BPA in the solid phase (membrane + bacteria) and water phase respectively . Add 3mL methanol into the solid phase and soak for 10min; add 15mL dichloromethane into the water phase three times, shake and extract for 3min each time, collect and combine the organic phases, evaporate to dryness on a nitrogen blower (50°C), and redissolve the residue in 1mL of acetonitrile, and then detected by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. It was found that the 24h degradation rate of bacteria+MIM BPA was 47.25%, which was sign...
Embodiment 2
[0045] Example 2: BPA in pure water with heavy metal lead ions degraded by affinity adsorption biodegradable membrane
[0046] Accurately weigh several 10mg films (group A: bacteria+MIM; group B: bacteria+nMIM; group C: dominant bacteria) and add them into 20mL spiked pure water containing lead (BPA=500μg / L, Pb(CH 3 COO) 2 =1mg / L) to start the degradation reaction. At each reaction termination time point (0, 3, 6, 12, 24h), take parallel samples, centrifuge the reactant at a speed of 6000rpm / min for 3min, and detect BPA in the solid phase (membrane + bacteria) and water phase respectively . Add 3mL methanol into the solid phase and soak for 10min; add 15mL dichloromethane into the water phase three times, shake and extract for 3min each time, collect and combine the organic phases, evaporate to dryness on a nitrogen blower (50°C), and redissolve the residue in 1mL of acetonitrile, and then detected by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. Find to utilize bacterium+MIM o...
Embodiment 3
[0047] Example 3: BPA in pure water with heavy metal cadmium ions degraded by affinity adsorption biodegradable membrane
[0048] Accurately weigh several 10mg films (group A: bacteria+MIM; group B: bacteria+nMIM; group C: dominant bacteria) and add 20mL of cadmium-containing pure water (BPA=500μg / L, CdCl 2 =1mg / L) to start the degradation reaction. At each reaction termination time point (0, 3, 6, 12, 24h), take parallel samples, centrifuge the reactant at a speed of 6000rpm / min for 3min, and detect BPA in the solid phase (membrane + bacteria) and water phase respectively . Add 3mL methanol into the solid phase and soak for 10min; add 15mL dichloromethane into the water phase three times, shake and extract for 3min each time, collect and combine the organic phases, evaporate to dryness on a nitrogen blower (50°C), and redissolve the residue in 1mL of acetonitrile, and then detected by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. Find to utilize bacterium+MIM of the present inv...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com