Method of preventing interphase impurity in vanadium-chromium extraction separation process
A technology for separation process and interface contamination, applied in the direction of improving process efficiency, etc., can solve the problems such as inability to circulate extraction-stripping, incomplete separation of vanadium and chromium, prolonging phase separation time, etc., and achieve good vanadium and chromium separation effect and extraction. Good separation effect and the effect of eliminating interface dirt
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
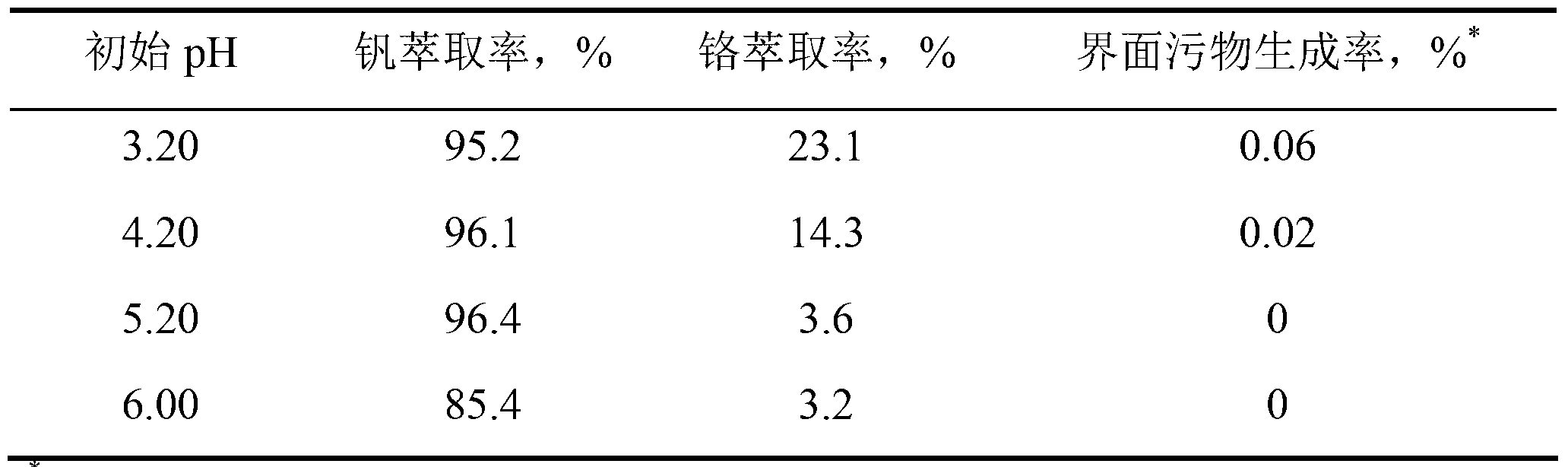
[0020] Taking the material liquid after deep removal of impurities in the chromium-containing vanadium slag leachate as the extraction liquid, the organic phase was prepared with the primary amine N1923, the tertiary amine TOA, the demulsifier with the commodity number PAG, and the diluent cyclohexane, and the extraction and separation test was carried out. The pH values of the feed liquid were adjusted to 3.20, 4.20, 5.20, and 6.00, the volume percentage concentration of the extraction agent primary amine was selected as 15%, the volume percentage concentration of the tertiary amine was 5%, the volume percentage concentration of the demulsifier was 1%, and the extraction temperature was room temperature 25 °C, mix the aqueous phase and the organic phase in a separatory funnel, then fix the separatory funnel on a Conrad shaker and shake for 15 minutes, remove the shaker and let the layers stand for 30 minutes, then take out the gap between the aqueous phase and the organic pha...
Embodiment 2
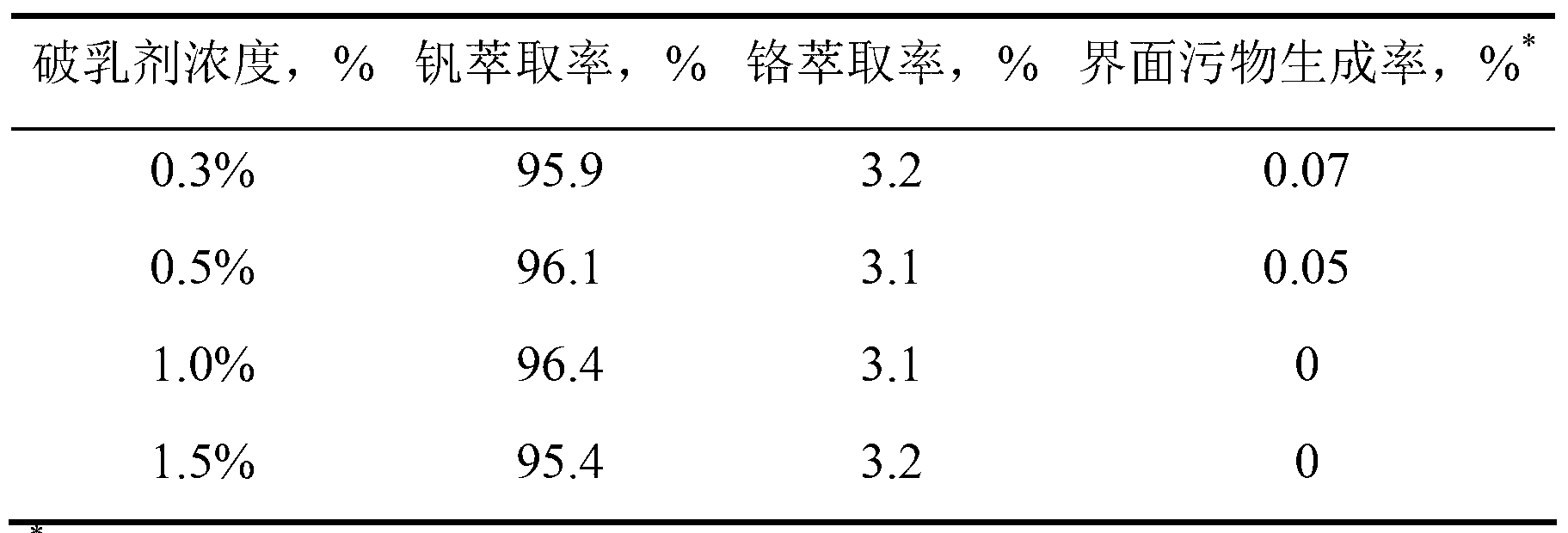
[0025]The material liquid after deep removal of impurities in the chromium-containing vanadium slag leaching liquid is used as the extraction liquid, and the organic phase is prepared with the primary amine N1923, the tertiary amine TOA, the demulsifier and the diluent cyclohexane, and the extraction and separation test is carried out. The volume percentage concentration of the demulsifier PAG 0.3%, 0.5%, 1%, and 1.5%, respectively, wherein the pH value of the feed liquid is adjusted to 5.20, the volume percentage concentration of the extraction agent primary amine is 15%, the volume percentage concentration of the tertiary amine is 5%, and the extraction temperature is room temperature 25°C. Mix the aqueous phase and the organic phase in a separatory funnel, then fix the separatory funnel on a Conrad shaker for 15 minutes, remove the shaker and let the layers stand for 30 minutes, then take out the interface between the aqueous phase and the organic phase Dirt, use a graduated...
Embodiment 3
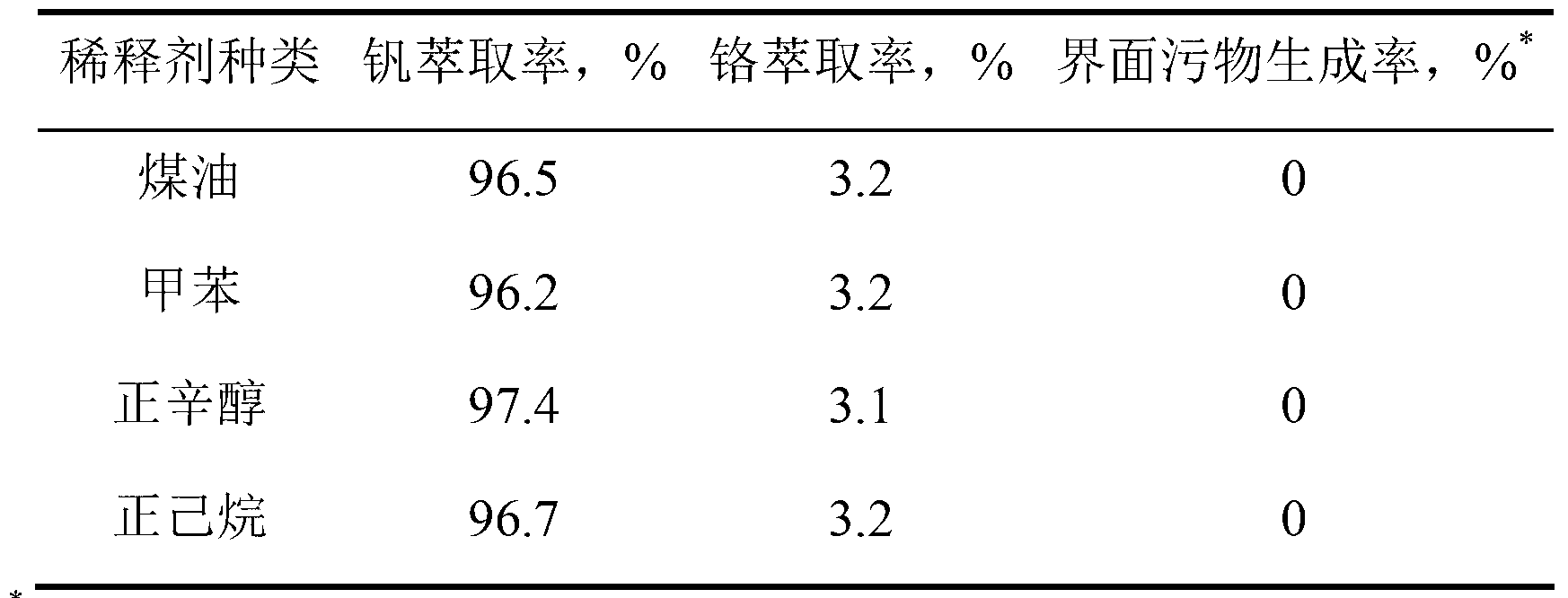
[0030] Taking the material liquid after deep removal of impurities in the chromium-containing vanadium slag leachate as the extraction liquid, the organic phase was prepared with the primary amine N1923, the tertiary amine TOA, the demulsifier with the commodity number PAG, and the diluent cyclohexane, and the extraction and separation test was carried out. The diluents are kerosene, toluene, n-octanol, and cyclohexane respectively, the pH value of the feed liquid is adjusted to 5.20, the volume percentage concentration of the extractant is 15%, the volume percentage concentration of the tertiary amine is 5%, and the extraction temperature is room temperature 25°C. Mix the aqueous phase and the organic phase in a separatory funnel, then fix the separatory funnel on a Conrad shaker for 15 minutes, remove the shaker and let the layers stand for 30 minutes, then take out the interface between the aqueous phase and the organic phase Dirt, use a graduated cylinder of appropriate spe...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com