Method for selectively extracting gallium and germanium from peracid lixivium containing gallium and germanium
A high acid leaching and selectivity technology, applied in the field of hydrometallurgy, can solve the problems of high environmental damage, consumption of reducing agent and high cost, and achieve the effects of reducing production cost, simplifying process and easy operation.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
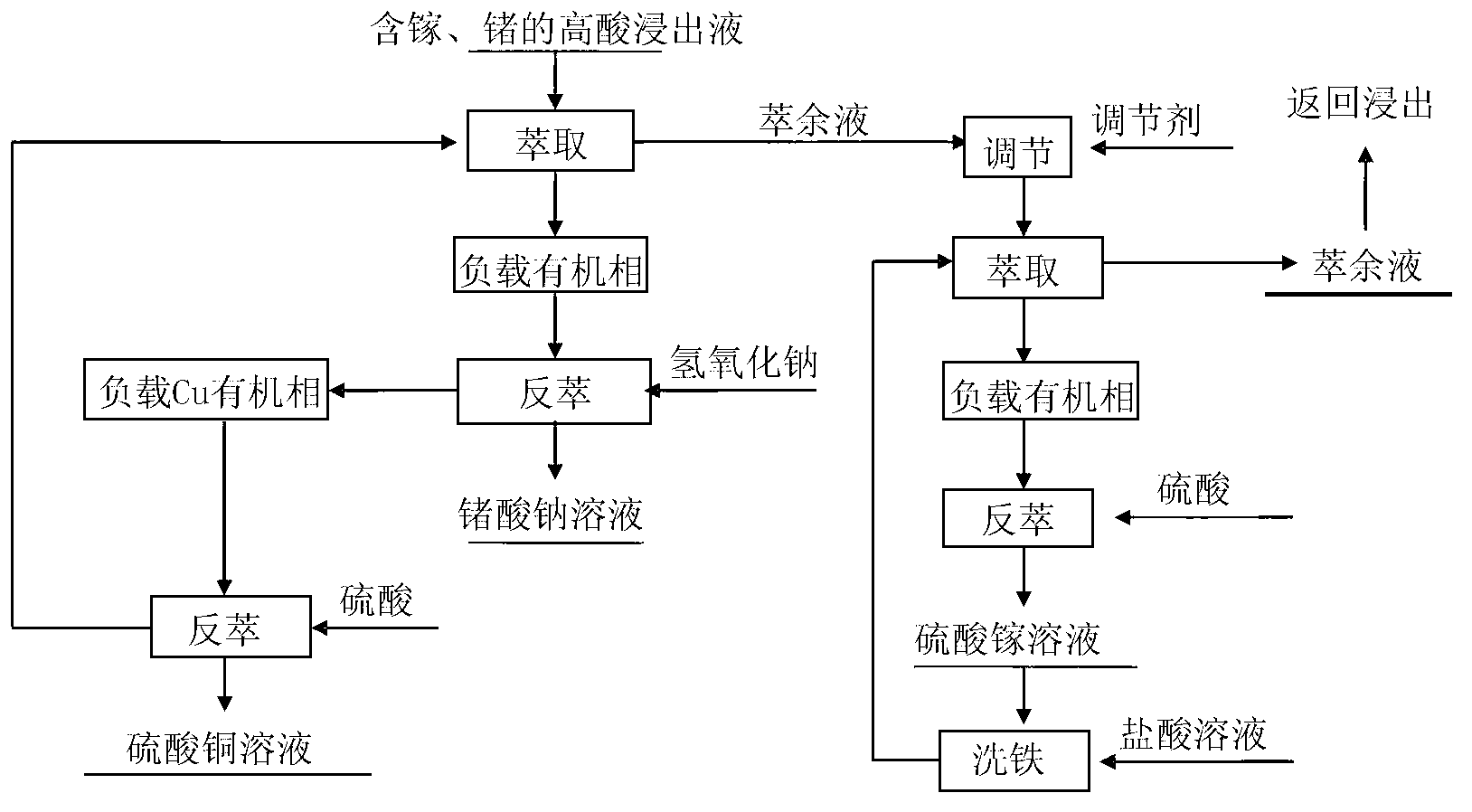
[0058] according to figure 1 The process flow is operated;
[0059] The feed liquid is a simulated industrial feed liquid, containing gallium 0.2042g / L, germanium 0.2468g / L, free acid concentration 2.3mol / L, sulfuric acid system;
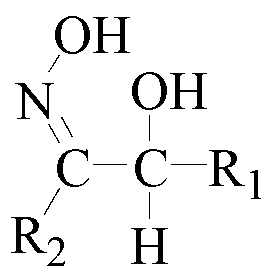
[0060] The organic phase is 20% oxime chelating extractant + 80% sulfonated kerosene;
[0061] A separatory funnel was used for single-stage extraction, the extraction ratio was O / A=1:1, the extraction time was 20 min, the temperature was 25°C, and the phase separation time was 1 min. The results are shown in Table 1.
[0062] Table 1 Extraction Process Separation Results
[0063] Element
[0064] The results in Table 1 show that the single-stage extraction rate of germanium in the extraction process can reach 79.1666%, only a small amount of Cu is extracted, and Ga, Fe, Cu, Zn, Al, As, Cd, etc. are almost not extracted.
Embodiment 2
[0066] according to figure 1 The process flow is operated;
[0067] The feed liquid is a simulated industrial feed liquid, containing gallium 0.2042g / L, germanium 0.2468g / L, free acid concentration 2.3mol / L, sulfuric acid system;
[0068] The organic phase is different proportions of oxime chelating extractant + sulfonated kerosene (volume fraction)
[0069] A separatory funnel was used for single-stage extraction, the extraction ratio was O / A=1:1, the extraction time was 20 minutes, the temperature was 25°C, and the phase separation time was 1 minute. The results are shown in Table 2.
[0070] The impact of different extractant concentrations in table 2 on the extraction
[0071] Extractant concentration (%)
[0072] The results in Table 2 show that the organic phase is 30% oxime chelating extractant+70% sulfonated kerosene, and the extraction rate of germanium above 93% can be obtained.
Embodiment 3
[0074] according to figure 1 The process flow is operated;
[0075] The feed liquid is a simulated industrial feed liquid, containing gallium 0.2042g / L, germanium 0.3247g / L, hydrochloric acid system;
[0076] The organic phase is 30% oxime chelating extractant + 70% sulfonated kerosene (volume fraction)
[0077] A separatory funnel was used for single-stage extraction, the extraction ratio was O / A=1:1, the extraction time was 15 minutes, the temperature was 25°C, and the phase separation time was 1 minute. The results are shown in Table 3.
[0078] Table 3 Effects of different feed liquid free acid concentrations on extraction
[0079] Free acid concentration (mol / L)
[0080] The results in Table 3 show that when the free acidity is 1.0-4.5mol / L, the extraction rate of Ge reaches more than 80%, and as the acidity increases, the extraction rate tends to increase; at the same time, other impurities are hardly extracted, and only a small amount of co-extraction The e...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| extraction efficiency | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| extraction efficiency | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com