Method for treating dye wastewater by catalyzing biological electro-fenton through iron ore
A technology for dye wastewater and iron ore, applied in biological water/sewage treatment, chemical instruments and methods, textile industry wastewater treatment, etc. Responsive and easy to make
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment example 1
[0031] (1) System construction.
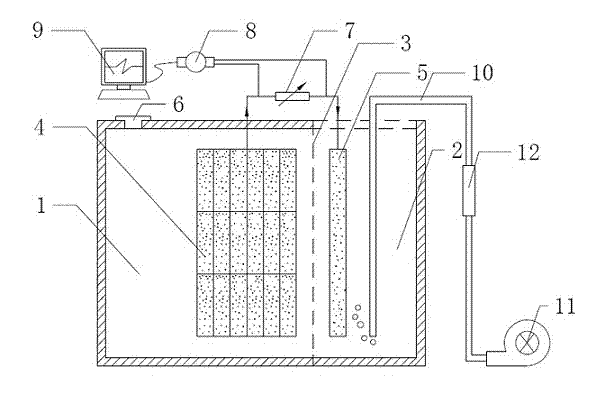
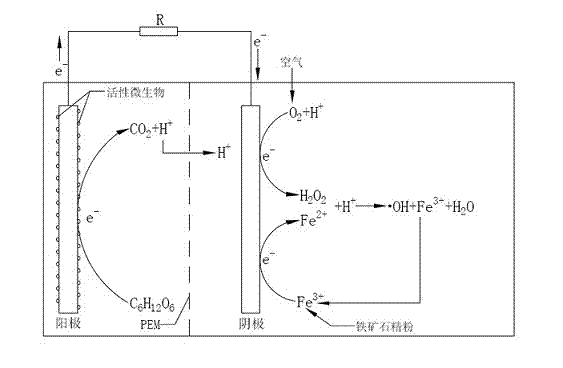
[0032] In this experiment, a double-chamber plexiglass reactor was used, such as figure 1 shown. Anode chamber 1 (5.5cm×5.5cm×5cm) and cathode chamber 2 (2.5cm×5.5cm×5cm) are separated by proton exchange membrane 3 . The anode chamber is provided with a water inlet and outlet 6 which can be opened and closed for adding and removing sewage; the upper end of the cathode chamber is open. The anode 4 is made of carbon felt (6 pieces, each 5.5cm×5cm×0.3cm, fastened with titanium wire and graphite rod to form a whole with good conductivity), and the cathode 5 is also made of carbon felt (5.5cm×5cm×0.4 cm, without any modification, made by boiling with 1M sulfuric acid for one hour to remove surface impurities), using titanium wire (diameter 0.5mm) to tightly bond and fix the two electrodes and lead out the two electrode chambers respectively, and connect them through the variable resistor 7. Both ends of the variable resistor 7 are connected with...
Embodiment example 2
[0042] (1) and (2) are the same as implementation case 1.
[0043] (3) Using magnetite fine powder as the cathodic electro-Fenton catalyst, a bioelectric-Fenton system was constructed to treat simulated dye wastewater.
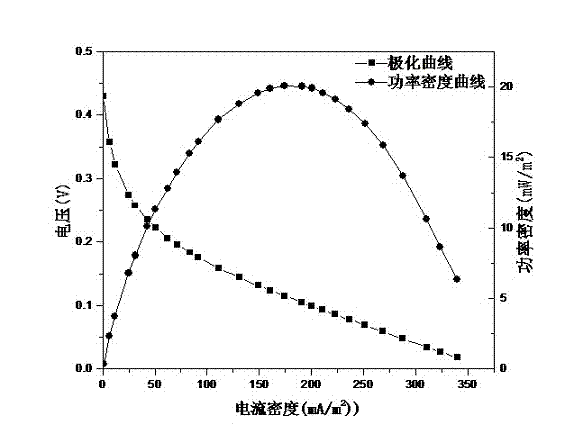
[0044] Add magnetite concentrate powder (purchased from China Tiger Trading Group Co., Ltd., particle size is 100 mesh) to the catholyte of a bioelectrochemical reactor with stable operation, so that the total amount of iron added is 1g / L . Connect the circuit with an external load of 1000Ω, introduce the cathode simulated dye wastewater and adjust the pH to 2.0±0.1, sample the catholyte every 30 minutes, and detect the absorbance at 484nm. The reaction results are as follows Figure 5 . Depend on Figure 5 It can be seen that it takes 3.5 hours for the bioelectric Fenton constructed with magnetite fine powder to achieve more than 98% of Orange II decolorization.
Embodiment example 3
[0046] (1) and (2) are the same as implementation case 1.
[0047] (3) Using hematite fine powder as the cathodic electro-Fenton catalyst, a bioelectric-Fenton system was constructed to treat simulated dye wastewater.
[0048] Add hematite concentrate powder (purchased from China Tiger Trading Group Co., Ltd., particle size is 100 mesh) in the catholyte of a bioelectrochemical reactor with stable operation, so that the total iron amount added is 1g / L . Connect the circuit with an external load of 1000Ω, introduce the cathode simulated dye wastewater and adjust the pH to 2.0±0.1, sample the catholyte every 30 minutes, and detect the absorbance at 484nm. The reaction results are as follows Figure 6 . Depend on Figure 6 It can be seen that it takes 5 hours for the bioelectric Fenton constructed with magnetite fine powder to achieve more than 98% of Orange II decolorization.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com