Application of corn Lc gene as selection marker in cotton transgenosis breeding
A screening marker, transgenic technology, applied in the application, genetic engineering, plant genetic improvement and other directions, to achieve the effect of improving work efficiency, ensuring expression, and saving detection costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
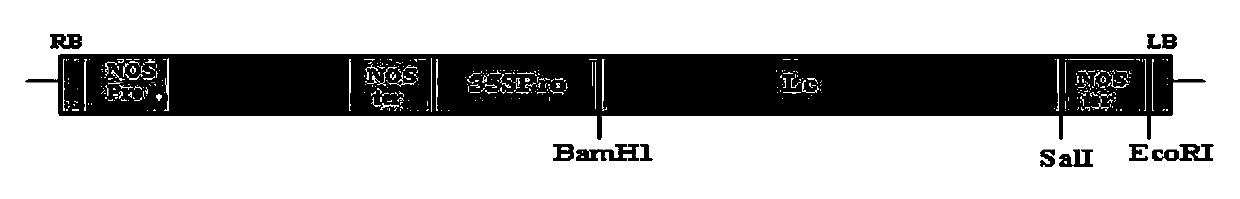
[0026] Example 1 Construction of vector
[0028] The total RNA of purple leaf sheath maize was extracted, and the full length of maize cDNA was obtained by reverse transcription. Using it as a template, primers were designed according to Genebank M26227
[0029] Lc-L(BamHI): GGGGGATCCATGGCGCTTTCAGCTTCCCG
[0030] Lc-R(SalI): GCGTCGACTCACCGCTTCCCTATAGCTTTGC
[0031] The 1.8kb PCR product was recovered, BamHI and SalI were double digested and then ligated to p EASY-T vector and sent for sequencing. The result was completely consistent with the Genbank M26227 sequence alignment. Get p EASY-T- Lc .
[0032] 2.1 Vector pBI121- Lc Build
[0033] Add SalI restriction site between NOS of GUS gene and SacI restriction site in pBI121 plasmid:
[0034] Design primers
[0035] Nos (SalI)L1: 5'-GTCGAC(SalI)GAATTTCCCCGATCGTTCAAACAT-3';
[0036] Nos R1: 5'-ATAGATGACACCGCGCGCGATAATTTATCCT-3';
[0037] Nos (SacI-SalI) L2: 5'-GCGAGCTC(SacI)GTCGAC(SalI)GAATTTCCCCGATCGTTC-3...
Embodiment 2
[0042] Example 2 Turn Lc Validation test of genetic cotton
[0043] Transform cotton with conventional Agrobacterium-mediated method. For verification Lc Genes can be used as selection marker genes. A set of experiments was designed and carried out. The hypocotyls of cotton after soaking and co-cultivation were divided into two mediums, one containing antibiotic selection agent; the other was not Callus induction medium containing antibiotic selection agent. At the same time, cultivate a group of uninfected materials as a control. repeat three times. During the cultivation process, it was found that the callus induced by the infiltrated material appeared red, see figure 2 (Reference materials for substantive examination figure 2 ), and the uninfected callus as a control did not see red, see image 3 (Reference materials for substantive examination image 3 ), so when picking callus on a medium that does not contain antibiotics, pick the red callus as soon as possible, an...
Embodiment 3
[0044] Example 3 Turn Lc Phenotype observation and molecular detection of genetic cotton
[0045] 3.1 Observation of in vitro culture
[0046] Differentiate the cell mass into embryos and transfer Lc Somatic embryos of genetic cotton and somatic embryos of untransformed cotton Figure 4 To Figure 5 (Reference materials for substantive examination Figure 4 , 5 ), until young seedlings have red and purple, you can still pick materials based on color, and eliminate yellow-green materials that do not see red and purple.
[0047] The results of a comparative test with or without antibiotic screening found that the materials that have been screened by color change without antibiotics are finally positive after PCR verification; while 10% of the materials screened by NPTII only contain NPTII Gene without detection Lc Genes, these materials also have no color change as the control.
[0048] Take a leaflet of the seedling, extract DNA for PCR detection (such as Image 6 ), it was found that...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com