Resistance gene capable of degrading herbicide glyphosate and encoded protein of resistance gene
A technology for encoding protein and glyphosate, applied in the field of resistance gene isolation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
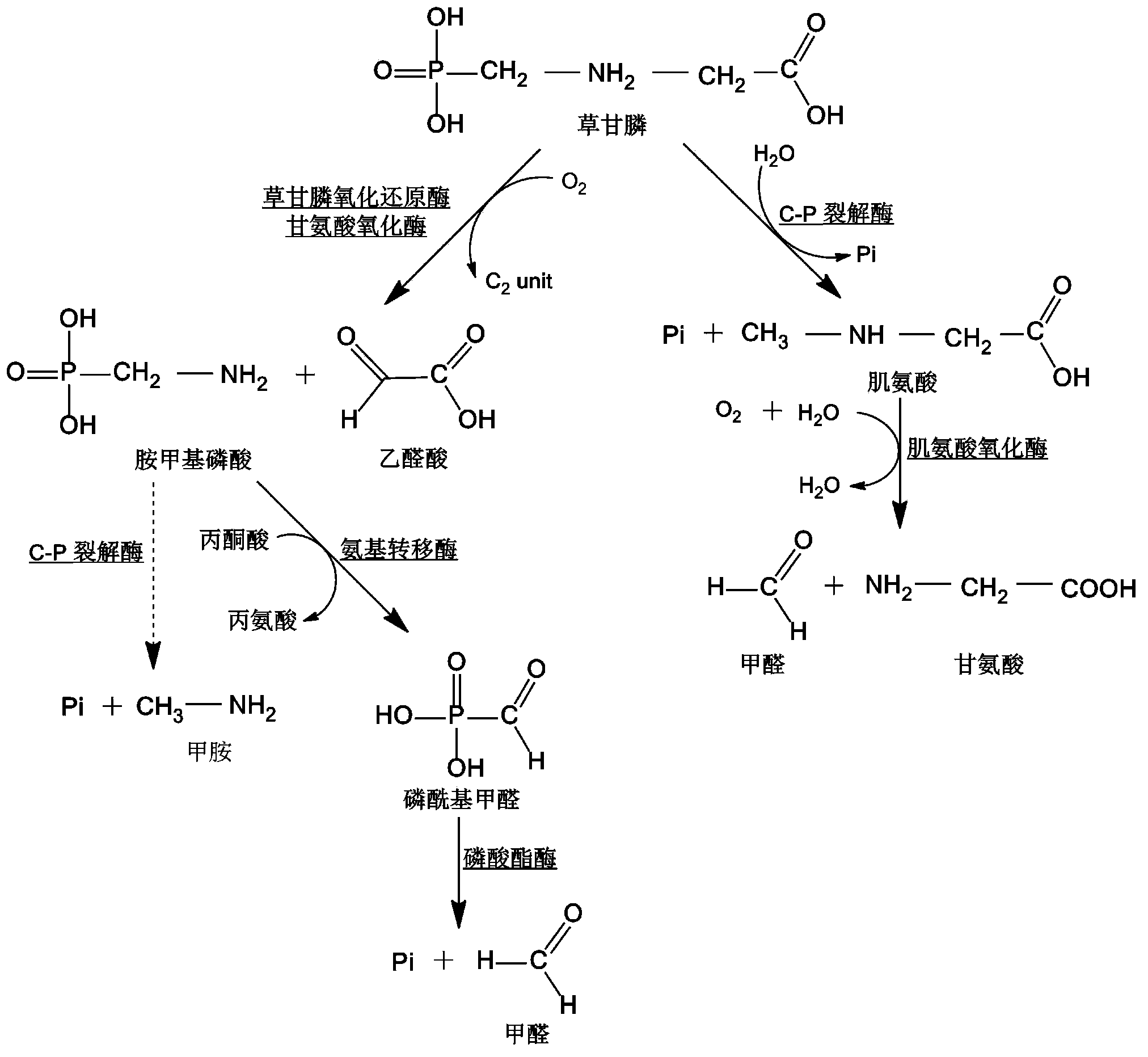
[0028] Cloning of embodiment 1 bacillus cereus glycine oxidase BceGO original gene
[0029] According to the published GenBank glycine oxidase gene thiO of Bacillus cereus (GenBank sequence number KC203486), specific primers were designed for PCR amplification of the original gene of BceGO glycine oxidase of Bacillus cereus.
[0030] The primer names and DNA sequences are as follows:
[0031] BceGO-F:5'-CGC GGATCC ATGTGTAAGAAGTATGATGTAGCGAT-3'
[0032] BceGO-R:5'-CCG CTCGAG CTAAACTCTCCTAGAAAAGCAATGAAT-3'
[0033] Restriction sites are underlined: BamHI and XhoI.
[0034] The PCR reaction system is shown in Table 1.
[0035] Table 1 PCR reaction system
[0036]
[0037] The PCR reaction procedure is:
[0038] Pre-denaturation at 94°C for 4 min; denaturation at 94°C for 30 sec, annealing at 55°C for 30 sec, extension at 72°C for 90 sec, a total of 30 cycles; extension at 72°C for 10 min; incubation at 15°C for 5 min. After the reaction, the amplified products were d...
Embodiment 2
[0040] Example 2: Construction of a random mutant library using error-prone PCR
[0041] The error-prone PCR reaction system is shown in Table 2
[0042] Table 2 Error-prone PCR reaction system
[0043]
[0044]
[0045] The error-prone PCR reaction procedure is:
[0046] Pre-denaturation at 94°C for 4 min; denaturation at 94°C for 30 sec, annealing at 55°C for 30 sec, extension at 72°C for 90 sec, a total of 30 cycles; extension at 72°C for 10 min; incubation at 15°C for 5 min. After the reaction, the amplified products were detected by 0.8% agarose gel electrophoresis.
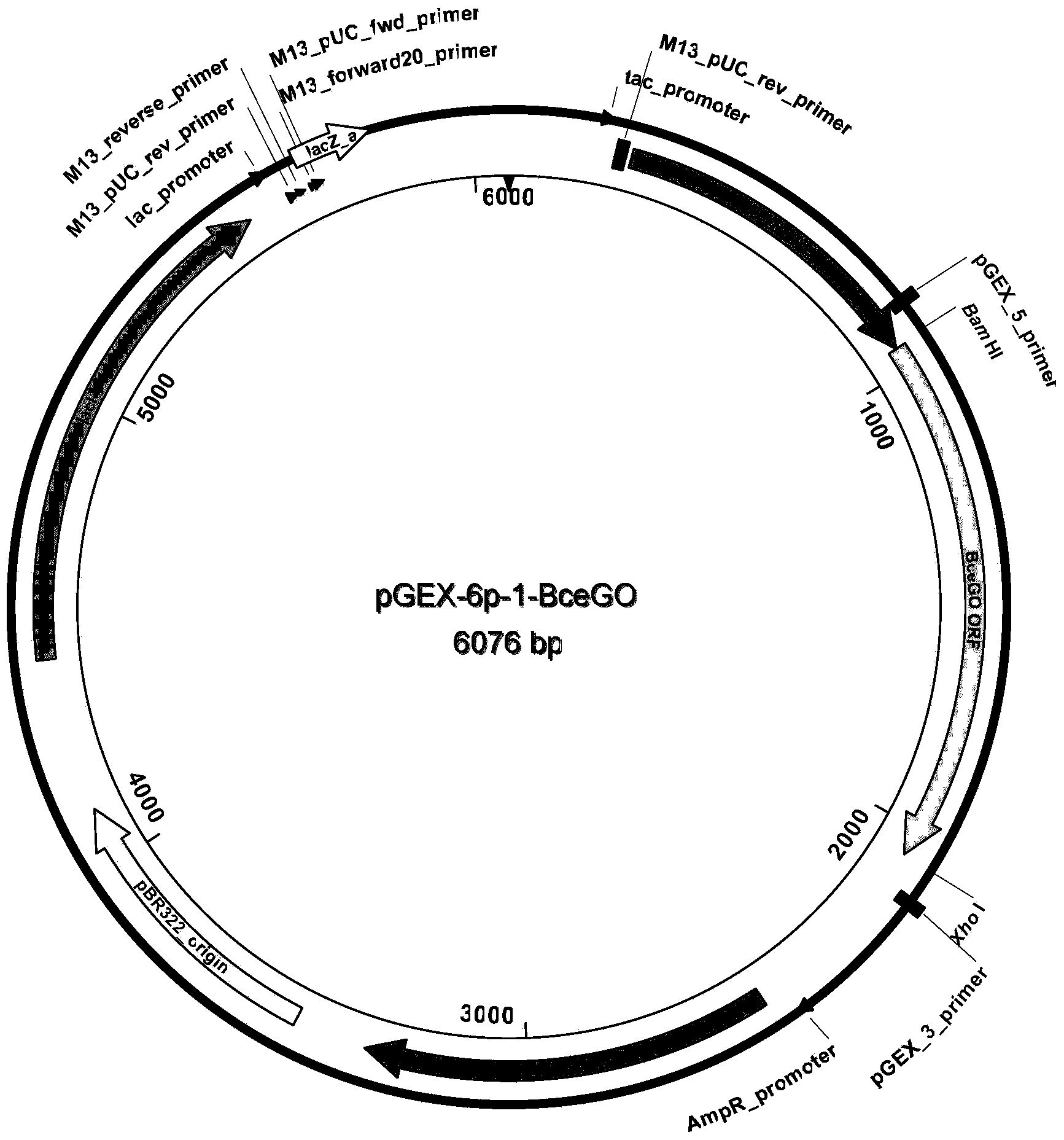
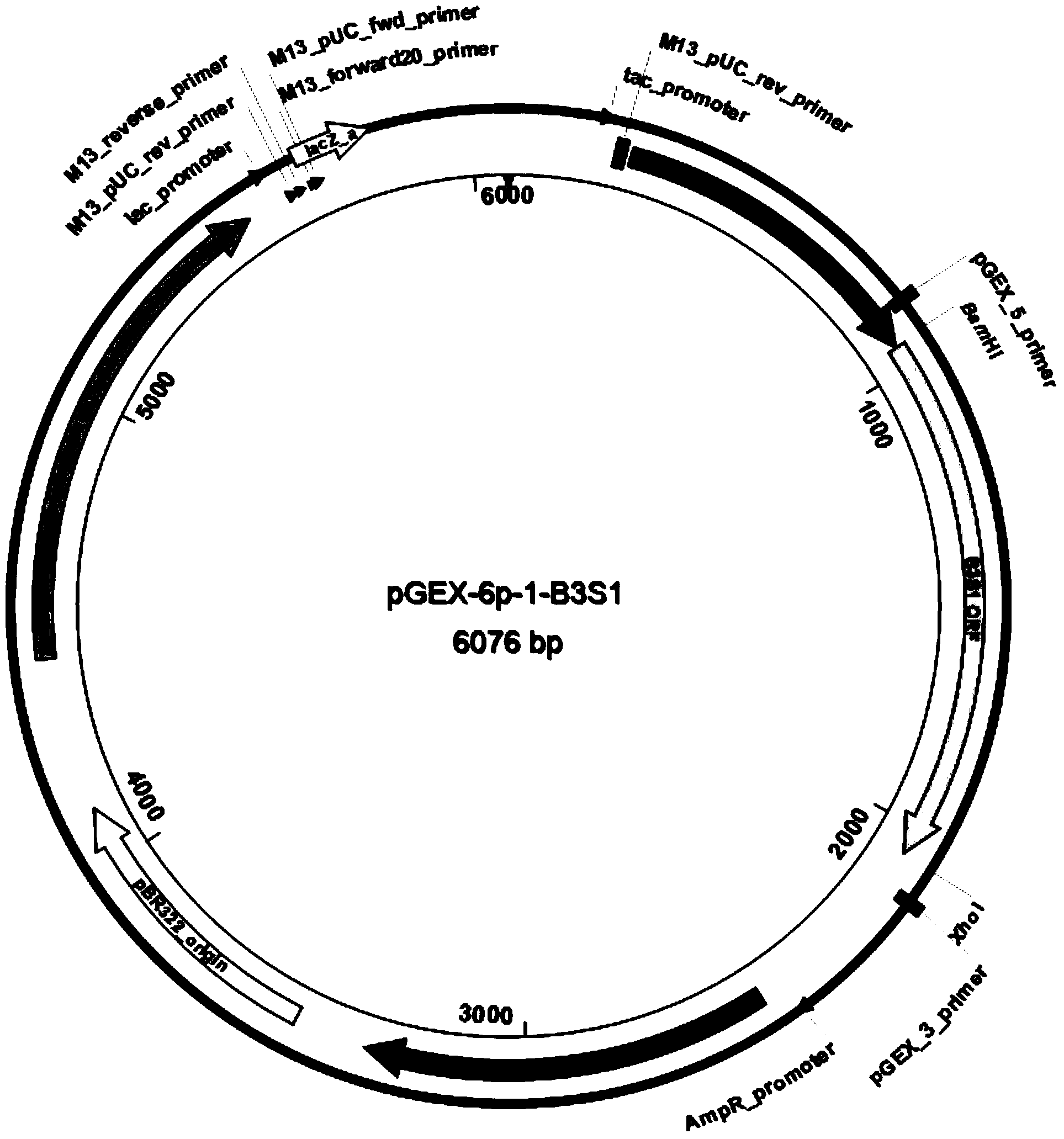
[0047] After recovering the error-prone PCR products, they were digested with BamHI-XhoI, enzyme-linked to the pGEX-6p-1-BamHI-XhoI double-cut vector, and then transformed into E. coli DH5α to construct a random mutation library. Ten clones were randomly selected for sequencing. After sequence comparison, it was found that the number of nucleotide substitutions in each gene was 1 to 3 bases, and the...
Embodiment 3
[0048] Example 3 Using site-directed mutagenesis to superimpose mutation sites
[0049] Two single-point mutants 22D11 (mutation site: G51R) and 23B1 (mutation site: D60G) were obtained from the first round of random mutation library screening, and the two points were merged into one by site-directed mutagenesis (Cadwell and Joyce1992). On the mutant, a double-point mutant B1R (G51R / D60G) was obtained. The coded nucleotides (Weiner and Costa1994) of the mutation site were designed using the codon preference frequency of Escherichia coli, and the site-directed mutagenesis primer name and sequence are:
[0050] G51R-F:5'-GCTGCTGGTTTACTT CGT GTTCAGGC-3'
[0051] G51R-R:5'- ACG AAGTAAACCAGCAGCTGCTTTTG-3'
[0052] The restriction site is underlined: G51R (GGT→CGT)
[0053] See Table 3 for site-directed mutagenesis PCR reaction system
[0054] Table 3 site-directed mutagenesis PCR reaction system
[0055]
[0056]
[0057] The PCR reaction procedure is:
[0058] Pre-...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com